Water Treatment
advertisement

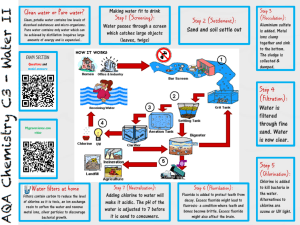
English for Architecture & Civil Engineering I Prepared by Indra Tj-2004 I.Reading Water Treatment People need water which is clear and free from disease-causing organisms. They also desire water which is soft, free from tastes and odors, and does not discolor plumbing fixtures or corrode metals. Industry requires water that will not interfere with its processes. Recently there has been an increasing concern about the presence of minute quantities of organic material, particularly chlorinated hydrocarbons, which are thought to be causative agents of a variety of diseases. Such contaminants are known to be present in many water supplies although their effect upon health is unknown. Standard disinfection practice using chlorine contributes to the production of these compounds. Chlorine In Water Disinfection of water is the killing of disease-causing microorganisms that it may contain. In the process, bacteria are reduced in number. Complete sterilization, however, is not ordinarily obtained nor necessary. Chlorine in its various forms has been widely used in disinfecting water. It is cheap, reliable and presents no' great difficulty in handling. Chlorine is a very active element and when added to water as free chlorine it will combine with organic and inorganic matter and oxidize some organic and inorganic compounds. Free available chlorine reacts with ammonia and many organic amines to form chloramines. Chlorine is used in water treatment for disinfection, prevention and destruction of odors, iron removal and color removal. While its principal use is as a disinfectant the mechanism of its bactericidal action is uncertain. It is likely that the chlorine destroys the extracellular enzymes of the bacterlal cells, and possible that it actually passes through the cell wall to attack intracellular systems. The bactericidal efficiency of chlorine is reduced by increased pH values and low temperatures. Chlorination of water is practiced for the purposes listed above, and the various needs may be satisfied simultaneously. It is extremely important as the principal, if not the only safeguard, against disease. Untreated waters are likely to be rather high in inorgartic matter and require high dosages and long contact periods for maximum safety. The chlorine may be added to the water in the pipe leading from an impounding reservoir to the city. Prechlorination is done before any other treatment. The chlorine may be added in the suction pipes of "raw-water pumps or to the water as it enters the mixing chamber. Its use in this manner has several advantages. lt may improve coagulation and will reduce tastes and odors caused by organic sludge in the English for Architecture & Civil Engineering I Prepared by Indra Tj-2004 sedimentation tank. By reducing algae and other organisms it may keep the filter sand cleaner and increase the length of filter runs. ("General Engineering", 1992) II. Vocabulary preview Disease – causing organism Soft(water) Tastes Discolor Plumbing fixtures Concern Minute [mainju:t] Contaminants Disinfection Simultaneously Impounding coagulation Jasad renik penyebab penyakit (air)lunak,tidak mengandung kapur Rasa payau Mengotori,menghitamkan Perlengkapan kran air Keprihatinan Sangat kecil Zat pencemar Pembasmian hama Sekaligus Tersendiri Waduk Penggumpalan III.Reading Comprehension 1. What properties should a good water supply have? 2. What is one kind of organic material, present in many water supplies, which is thought to cause disease? 3. What two factors can reduce the efficiency of chlorine as a bactericide? 4. What word, words, or phrases do the 12 underlined words each refer to? IV. Decide whether. the following statements are true or false according to the facts in the passage: 1. The public requires that their water supply be clean and safe to drink. 2. There has been some anxiety about organic materials which could cause disease. 3. It is certain that chlorine kills the extracellular enzymes of bacterial ceils. 4. Industry requires water that will have an effect on its processes. 5. Large quantities of organic material are found in mains water. 6. Chlorinated hydrocarbons are absent in the water supply. 7. Standard disinfection practice prevent the production of these compounds. 8. The bactericidal efficiency of chlorine is increased by increased pH values. 9. A pH smaller than 7 is acid, and larger than 7 is alkaline. 10. Chlorine is used in water treatment for disinfection, destruction of odors and English for Architecture & Civil Engineering I Prepared by Indra Tj-2004 iron addition.