Busines Intelligence - Jai Windsor
advertisement

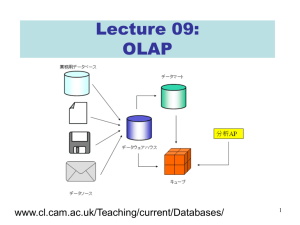
How Business Intelligence Software Works and a Brief Overview of Leading Products Jai Windsor MIS 5973 December 8, 2005 What is Business Intelligence (BI)? • Yet another IT buzzword? • “Software that enables users to obtain • • enterprise-wide information more easily” A strategy to ensure the right information is available to the right decision makers at the right time Working definition- products that are designed to extract and present data from a data warehouse (ideally) Extract and present data… • Querying capabilities • Reporting capabilities • Analysis – Using reports – Using Excel – Using OLAP • Ideally from a data warehouse, but can be from other databases, spreadsheets, flat files, etc. BI Vendors • • • • • • • • • • Business Objects Cognos Actuate Applix Information Builders Informatica MicroStrategy Microsoft Oracle SAS Querying CapabilitiesThe Business View • “Business view”, or metadata layer • Safe, user friendly environment for business users • Generates SQL queries for the user • IT users can modify or write their own queries • “Universe”, “Package”, “Project” Querying CapabilitiesPrompting the User • Helps users design their own queries • Asks users what data they want to see and how they want to filter it • Standard report templates with hundreds of variations • Do’s • Don’ts Querying CapabilitiesComplex Business Questions • Might seem innocent enough but cause a huge problem for the BI • Limited SQL functionality in some casessubqueries, multipass SQL, new functions like RANK • Proprietary methods are sometimes slow and inefficient Reporting Capability • Reporting transforms query results from raw data to meaningful information • Report design • Charting Interactive Reporting as an Analysis Tool • The least complicated method of data analysis • Investigate trends or exceptions • OLAP-lite • Formulas and functions Report Delivery – Push Strategy • Report generation scheduled by IT • “Pushed” to users • Bursting • Users can be overwhelmed and stop reading reports • Alerts Report Delivery- Pull Strategy • Users log on and request (“pull”) reports • Can create a burden on server • Schedule-and-pull recurring, heavily used, complex reports • Web portals and interactivity Analysis by Excel • Excel remains the most popular BI tool in use • Familiar • “Massage” data • Bursting • Cheap! OLAP • Online Analytical Processing • MOLAP – Multidimensional OLAP • Multidimensional data cubes • Multidimensional and cross-dimensional calculations • Response times are fast and predictable Other variations • ROLAP – relational structure • HOLAP – hybrid between MOLAP and ROLAP • DOLAP – dynamic OLAP, “personal” temporary cubes More on OLAP • Drill down, drill across • Drill to detail • Reporting integration Cognos Enterprise BI Series 7 • Query Studio and Report Studio tools • Web-based • Automatic data ranking • No problem with date dimension • Good user-defined report scheduling Actuate Actuate 8 • Analytics Cube Designer • Cross-join data from heterogeneous sources • eSpreadsheet analysis tool • No problem splitting data fields • Good user-defined report scheduling Information Builders WebFocus 7 • No OLAP architecture, no cubes • Must learn native scripting language • “Accordion reports” Applix TM1 • Newcomer to market • Seamless integration between OLAP and reporting • Displays data in Excel • Must supply own SQL to build cubes MicroStrategy 8 • Heavily dependent on proper data warehouse • • • • design. Must have star schemas to properly create cubes Must use lookup tables to create the date dimension Not tolerant of dirty data Integrates directly with Microsoft Office Better for data warehousing and data mining than reporting and OLAP analysis Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Reporting Services and Analysis Services • Analysis services supports MOLAP, ROLAP, and HOLAP • Easy to configure and define cubes • One fact table per cube • Reporting Services is an extension to Visual Studio.NET 2003 and best left to developers • Surprisingly poor integration with Excel! Business Objects Enterprise 6.1 • Unique DOLAP architecture • Flexibility and low IT maintenance Conclusion • Frees IT staff from being report writes • Business power users may know better what they want to know than IT can • Business users can explore data in new ways • Pure players vs platform vendors Any questions?