Chapter Four. Chapter 1—General Provisions
advertisement

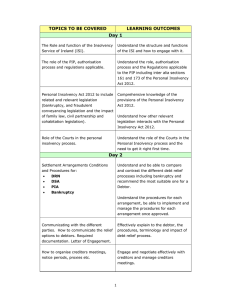
Chapter Four. Chapter 1—General Provisions After reading this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the basic motion procedures used in Bankruptcy Courts List the essential qualifications to qualify as a debtor under a particular Chapter of the Code Identify the remaining provisions of Code Chapter 1. Notice and Hearing Signifies that due process must be given to various parties involved in the proceeding before a court order authorizing the action is sought to be performed can be obtained. In the context of a bankruptcy proceeding, due process often means that the affected parties must merely be given notice and an opportunity to be heard. Get the Procedure Right the First Time! Errors can be costly. Powers of the Court Section 105 concerns the court’s powers. Section 105 specifically gives the Bankruptcy Court equitable authority to enact any orders that are necessary to carry out the provisions of the Bankruptcy Code. It is important to remember that Section 105 supplements powers already provided for under the Code. It does not create new substantive rights otherwise unavailable under the Code. Ex Parte An application made to the court without notice or with limited notice to limited parties. Ex parte applications are specifically permitted for various ministerial functions. In other circumstances, a legitimate extraordinary circumstance must exist for the court to consider ex parte relief. Evidentiary Hearing A hearing held to take sworn testimony to permit a Bankruptcy Court to make a decision in a contested matter that is not a separate adversary proceeding. An evidentiary hearing is similar to a trial in a nonbankruptcy environment. A “trial” on a contested motion for relief from the automatic stay is properly called an evidentiary hearing. Who May be a Debtor? Only persons may be debtors An individual is a person A corporation can be a person A partnership can also be a person A person has to reside or be domiciled in the United States or have a place of business or property in the United States. Practice Pointer Chapter 7 debtors can be individuals, corporations, and partnerships, but not railroads, banks or insurance companies. Chapter 9 debtors are municipalities. Chapter 11 debtors include anyone who could have filed under Chapter 7 plus railroads and certain banks. Chapter 12 debtors are family farmers or family fishermen. Chapter 13 debtors can only be individuals with regular income with less than certain specified debt. Serial Filing A serial filing exists when a debtor files a bankruptcy and has it dismissed by the court. Usually, this occurs when real estate is about to be foreclosed or when the repossession is about to occur after the automatic stay has been relieved.