Computer Functions
advertisement

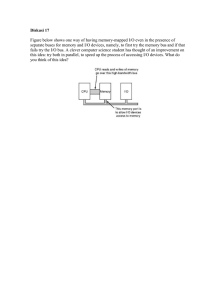
Computers Central Processor Unit Basic Computer System Processor ALU CNTL ..... BUS Interconnections I/O module CONTROLLER MAIN MEMORY Memory BUS Von Neumann Architecture CPU Fast Memory Slow Storage Binary Program: executed in sequence Computer behavior is determined by stored programs. John Von Neumann and ENIAC Computer Components Processing (CPU) Arithmetic Logic Unit Control Unit Registers Word Clock Instruction sets Interconnection Local bus Peripheral bus Primary Storage RAM/ROM Cache Input/Output Channel Controller Buffers CPU’s CPU Cycle Increment Program Counter Start FETCH FETCH EXECUTE EXECUTE Halt Instruction Format 4 Bits OP Code 12 Bits Operands Instruction: Operation Codes Operands Word: set of bits held by registers in the CPU. May contain instructions or data. Types of Instructions Chip Instructions = Built-in Machine Instructions – “microcode” = Chip Instructions + ROM Instructions Assembler Instructions = Alphabetic Abbreviations for Machine Instructions ROM Instructions INSTRUCTIONS (BIOS in PCs) ROM CNTL ALU ..... RISC and CISC CISC uses fewer processor cycles RISC has fewer instructions, requires more processor cycles How can RISC be faster? Basic Computer System Processor ALU CNTL ..... BUS Interconnections I/O module CONTROLLER MAIN MEMORY Memory BUS Local and Peripheral Bus Bus Operation Transfer Quantity (word) Address bus Control bus Data bus Speed Clock speed Memory Hierarchy COST SPEED REGISTERS CACHE MAIN MEMORY MAGNETIC DISK | DISK CACHE MAGNETIC TAPE | OPTICAL DISK Capacity Units Bit Byte Kilobyte Megabyte Gigabyte Terabyte b B=8b KB = 1,000 B MB = 1,000,000 B GB = 1,000,000,000 B TB = 1,000,000,000,000 B Memory Access Method Sequential - tape Direct - floppy or hard disk Random - internal memory Dynamic (DRAM) simple, small, must be refreshed Static (SRAM) no refresh needed Random Access Memory Chips and chip technology Flip Flop Circuit Diagram DASD Access MAIN MEMORY CPU BUFFER CACHE DASD CONTROLLER Representative Times Network speed = megabits per second Disk transfer = megabytes per second Disk access = milliseconds Memory access = nanoseconds Machine cycle = microseconds/nanoseconds DASD (direct access storage device) Read-Write Heads Cylinder/Track/Block Track Block (Sector) Cylinder Data Storage FAT (File Access Tables), Directories and Catalogs Update and Delete Fragmentation and reorganization Blocks, Headers and Interblock Gaps What makes a computer run? Word size Instruction set Bus speed Main memory Secondary storage Buffers and cache IBM 1107 with tape drives Operating Systems PROGRAM OPERATING SYSTEM HARDWARE System Structure Layers Processor Hardware functions: circuits, instruction set, procedures, interrupts Process management: multiprogramming, management of secondary storage, logical addressing External resource management: communication among process, file management, device access and addressing, user support Virtual Memory PAGE NUMBER + OFFSET PAGE TABLE FRAME NUMBER + OFFSET PAGE TABLE PAGE TABLE Pages Page Frames Comparison MVS versions (OS/390) UNIX Windows NT Linux