Part 11
advertisement

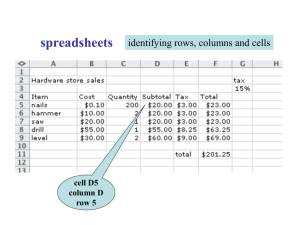
Spreadsheets • • • • Lets you store and analyze data. 2-dimensional grid Each entry location is a cell. The cells have indexes – Rows are different numbers – Columns are different letters 1 Cells • Each cell can have information in it. • The cell can have a label or a piece of text. – Set by typing the text into the cell. • The cell can have a value (number). – Set by typing the number into the cell. • The cell can have a value rule. – Set by entering a formula or function into the wide box with the = to the left of it. 2 Cells • Adjust size of cells by dragging along the borders of the cells. – L/R drag to change the size of a column. – U/D drag to change the size of a row. • You can make rows/columns “disappear” but they can be restored with dragging. 3 Insert/Delete Cells • Right click on the row/column header • Select a region • Then – – – – Insert Delete Cut Copy 4 Selecting Cells • Mouse over cells to select. • Use the name box above the A column. • Can select several disjoint areas. – Hold down Control key while selecting. 5 Marking Cells • Mouse over them holding the left button. • Enter a range into the small box on the upper left. • Click on the column/row headers to mark all cells in one row or column. • Ctrl-A for all cells. • Mark more than one range of cells by holding CTRL as they are marked. 6 Entering Labels • Just type non-numeric text and they will appear. • These don’t get used in calculations. • Can replace by typing over them again. 7 Entering values • Enter a number into a cell. • It stays constant. • It can be used in formulas. 8 Value Rules • Formulas relating cells to each other. • Generally a formula references other cells. • Copying formulas causes relative changes to the cells referenced. – If a formula in cell A6 is average(A1:A5) – If A6 is copied to B6 – The formula in B6 is average(B1:B5) 9 Copying Value Rules • If the copy is to another column, the columns change. • If the copy is to another row, the rows change. • You can fix a row or column by putting a $ in front of the row number or column letter, or both. 10 Entering Value Rules • Value rules can be formulas – A5+($B7/4+24) – E2*F5 • Value rules can be functions – AVERAGE(A3:B7) – SUM(G5:H20) • Or combinations of both. 11 Entering Value Rules • Parentheses must match. • Usually there are cell blocks being referenced. • They can be moused over while entering the formula. • Labels/blanks are ignored • Value rules can reference other value rules. 12 Sorting • Can sort by column or row. • Can sort by several factors in order – Ties in one factor get sorted in the next factor. • Will also change other information outside of the data being sorted (if it’s marked). • Can be used to organize data for plots. 13 Graphs • • • • • X-Y Correlation (scatter) plots. Height plots. Bar graphs. Pie graphs. Can pre-select data ranges by marking them, or you can clear the data ranges and mark new ranges. 14 Entering Data • Can enter thousands of data pieces at once – Enter a piece of data in a cell – Mark a row or column using the name box – CTRL-D or CTRL-R as necessary to fill in the blanks • Can use that for statisitcal analysis. 15 Importing Data • • • • Get a data source from a file or the WWW. Get it into Word Processor to neaten it up. Import it using breakpoints/delimiters. Import using copy/paste and data->text to columns. • May require some fixing to make it work. 16