Resistors in Series • Resistors connected at a single node
advertisement
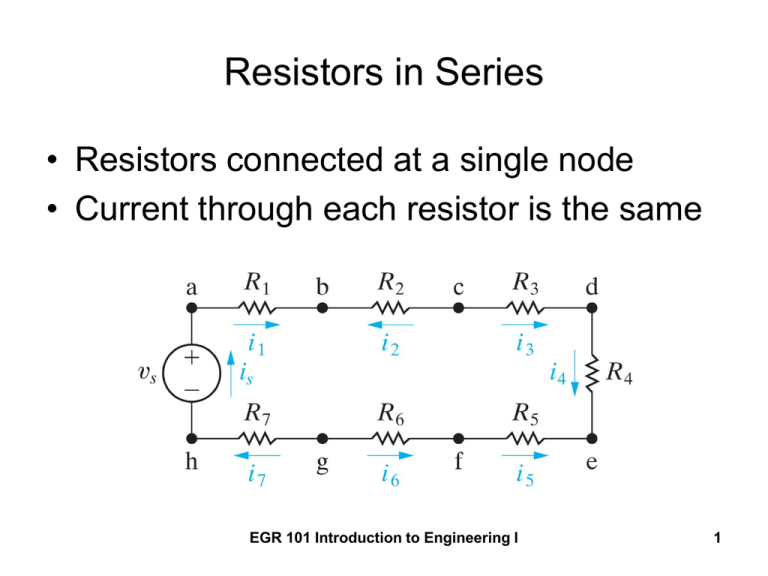
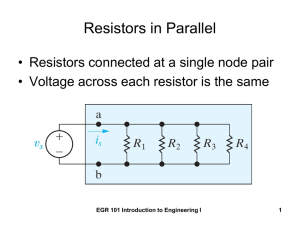
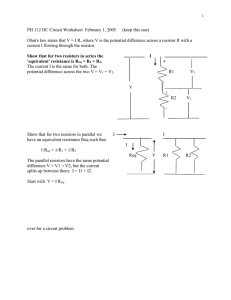
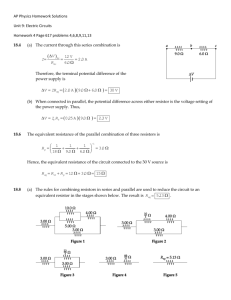
Resistors in Series • Resistors connected at a single node • Current through each resistor is the same EGR 101 Introduction to Engineering I 1 Identify the current in each Resistor Apply KCL at each node iS i1 i2 i3 i4 i5 i6 i7 a b c d e f EGR 101 Introduction to Engineering I g 2 Redraw using a single current EGR 101 Introduction to Engineering I 3 To solve for the current, write KVL vS iS R1 iS R2 iS R3 iS R4 is R5 iS R6 iS R7 0 vS iS ( R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 ) iS Req EGR 101 Introduction to Engineering I 4 Simplified version of the circuit vS iS Req 7 Req Ri R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 i 1 EGR 101 Introduction to Engineering I 5 From a “black box” point of view • These circuits are “equivalent” • Same current drawn from the source EGR 101 Introduction to Engineering I 6 Summary • Resistors in series have the same current • The resistors can be replaced by an “equivalent” resistance equal to the sum of the individual resistors • The “equivalent” resistance is larger than the largest of the individual resistors EGR 101 Introduction to Engineering I 7