ECG 101 Powerpoint
advertisement

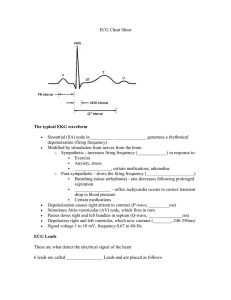
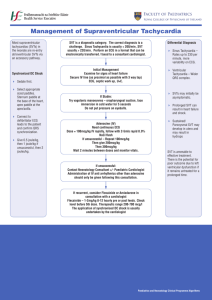
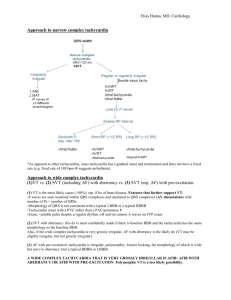
ECG 101 Yale University School of Medicine Section of Cardiovascular Medicine james.revkin@yale.edu Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Basic analysis • • • • • • • Rate (fast or slow) Rhythm (atrial, ventricular, regular, irregular) Axis Conduction disease (atrial or ventricular) Hypertrophy Ischemia, infarction Other abnormalities (QT interval, repolarization changes) EKG history Charles Einthoven electrophysiology ECG as an “imaging tool” ECG as an “imaging tool” Right side Left side Basic ECG P wave Septal Q Wave Q R wave repolarization Basic ECG Basic analysis • • • • • • • Rate (fast or slow) Rhythm (atrial, ventricular, regular, irregular) Axis Conduction disease (atrial or ventricular) Hypertrophy Ischemia, infarction Other abnormalities (QT interval, repolarization changes) Normal 12 Lead ECG 300 bpm 150 bpm 100 bpm 75 bpm 60 bpm 50 bpm ~ 45 bpm Calculating rate of an irregular rhythm Count number of beats in two 3 sec intervals ( = 6 sec total) and multiply times 10 Rate approx 60 bpm Normal Frontal Axis Lead I Lead aVF Lead V1 Normal precordial Axis Lead V6 1F Frontal Plane Axis Calculator 1G Precordial Axis 1H Frontal Plane Axis Calculation Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Session 1 ECGs 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1I 1J 1K Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities electrophysiology PR Interval PR A – V Block • At level of A-V node – 1st degree • Prolongation of PR interval > 0.2 ms – 2nd degree • Mobitz Type I - Wenckebach, progressive prolongation of PR interval, then dropped beat • Mobitz Type II – 3rd degree • Complete heart block, independent atrial and ventricular rates QRS Interval QRS Ventricular (bundle branch) blocks • LBBB – Hemiblocks • Left anterior fascicular block (left anterior hemiblock) • Left posterior fascicular block (left posterior hemiblock • RBBB LBBB RBBB Hemi-blocks • Within the Left Bundle – Hemiblocks • Left anterior fascicular block (left anterior hemiblock) • Left posterior fascicular block (left posterior hemiblock Left anterior hemi-block Left posterior hemi-block Hypertrophy • Atrial – Left atrial hypertrophy – Right atrial hypertrophy • Ventricualr – LVH – RVH Left Atrial Hypertrophy Right Atrial Hypertrophy Ventricular Hypertrophy • RVH – R > S in V1 – Right axis deviation • LVD – R wave 15 mm high in lead I – Sum deepest S wave V1 or V2 and add to tallest R wave in V5 or V6 > 35 mm Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Session 2 ECGs 2A 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F 2G 2H 2I 2J 2K Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Sinus arrhythmia Non-sinus atrial rhythm Multi-focal atrial tachycardia (MAT) Junctional rhythm Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia PSVT atrial flutter atrial fibrillation Session 3 ECGs 3A 3B 3C 3D1 3D2 3E 3F 3G 3H1 3I-1 3I-2 3I-3 3J 3K1 3K2 3L1 3L2 3M 3N 3O Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities ECG Basics • What does the QRS complex represent? • What should the axis of a normal QRS complex be: – in the frontal plane? – in the precordial plane? • What would make the QRS complex wide? Assessment of WCT • definition of wide complex tachycardia – QRS duration greater than 0.12 seconds – heart rate greater than 100 bpm • differential diagnosis of WCT – supraventricular tachycardia with: • preexisting bundle branch block • aberrant conduction (rate related) • accessory pathway – ventricular tachycardia ECG Basics • What does the QRS complex represent? • What should the axis of a normal QRS complex be: – in the frontal plane? – in the precordial plane? • What would make the QRS complex wide? Normal Frontal Axis Lead I Lead aVF Lead V1 Normal precordial Axis Lead V6 LBBB RBBB Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia • Goal: develop easier more accurate criteria for analysis. • Applied guidelines to 554 WCT patients who’d had previous EP studies (384 VT and 170 SVT). • Analyze ECGs using a four step algorithm. • Observers would stop when a positive analysis of VT was made. • SVT with aberrant conduction was the diagnosis of exclusion. Brugada P, Brugada J, et al Circulation 1991;83:1649-1659 Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? • Does any RS interval exceed 100 msec in the precordial leads? • Is A-V dissociation present? • Do the QRS complexes in V1/V2 fulfill the classic criteria? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (384 VT, 170 SVT with aberration) • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? 83 Yes 83 VT SN = 0.21 SP = 1.0 471 No Go to next step Absence of precordial RS complexes V1 V6 Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (384 VT, 170 SVT with aberration) • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? 83 Yes 83 VT SN = 0.21 SP = 1.0 471 No Go to next step Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (83 VT, 471 unknown) • RS Interval > 100 ms in one precordial lead? 175 Yes 172 VT 3 SVT SN = 0.66 SP = 0.98 296 No Go to next step Hypothesis: prolongation of the intrinsicoid deflection-RS interval > 0.1 sec-could be a marker for VT RS Interval: measured from beginning of R wave to nadir of the S wave. RS = 0.080 or 80 ms Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (83 VT, 471 unknown) • RS Interval > 100 ms in one precordial lead? 175 Yes 172 VT 3 SVT SN = 0.66 SP = 0.98 296 No Go to next step Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (255 VT, 3 SVT, 296 unknown) • Is AV Dissociation Present? 59 Yes 59 VT SN = 0.82 SP = 0.98 237 No Go to next step Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (314 VT, 3 SVT, 237 unknown) • Are classic morphology criteria for VT present in both V1- V2 and V6? 68 Yes 65 VT 3 SVT SN = 0.987 SP = 0.965 169 No 164 SVT 5 VT SN = 0.965 SP = 0.987 Classic Criteria Suggesting VT • QRS duration > 0.14 s • Superior QRS axis • Morphology in precordial leads: RBBB-like pattern V1 V6 R/S ratio < 1 LBBB-like pattern V1 V6 :qR r = 30 ms notched S wave RS > 70 ms Classic Criteria Suggesting SVT • QRS duration < 0.14 s • Normal QRS axis • Morphology in precordial leads: RBBB-like pattern LBBB-like pattern V1: V1: triphasic V6 R/S ratio > 1 absent or narrow R wave no S wave notch steep S wave descent V6 : no Q wave Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (314 VT, 3 SVT, 237 unknown) • Are classic morphology criteria for VT present in both V1- V2 and V6? 68 Yes 65 VT 3 SVT SN = 0.987 SP = 0.965 169 No 164 SVT 5 VT SN = 0.965 SP = 0.987 Treatment of Wide Complex Tachycardia of indeterminate etiology • Is patient unstable? – Immediate synchronized cardioversion – 100, 200, 300, 360 joules • Borderline or stable? – amiodarone Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? • Does any RS interval exceed 100 msec in the precordial leads? • Is A-V dissociation present? • Do the QRS complexes in V1/V2 fulfill the classic criteria? Session 4 ECGs 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 4G1 4G2 4H1 4H2 4I1 4J 4K 4L 4M1 4M2 4M3 4N1 4N2 Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities ECG Basics • What does the QRS complex represent? • What should the axis of a normal QRS complex be: – in the frontal plane? – in the precordial plane? • What would make the QRS complex wide? Assessment of WCT • definition of wide complex tachycardia – QRS duration greater than 0.12 seconds – heart rate greater than 100 bpm • differential diagnosis of WCT – supraventricular tachycardia with: • preexisting bundle branch block • aberrant conduction (rate related) • accessory pathway – ventricular tachycardia ECG Basics • What does the QRS complex represent? • What should the axis of a normal QRS complex be: – in the frontal plane? – in the precordial plane? • What would make the QRS complex wide? Normal Frontal Axis Lead I Lead aVF Lead V1 Normal precordial Axis Lead V6 LBBB RBBB Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia • Goal: develop easier more accurate criteria for analysis. • Applied guidelines to 554 WCT patients who’d had previous EP studies (384 VT and 170 SVT). • Analyze ECGs using a four step algorithm. • Observers would stop when a positive analysis of VT was made. • SVT with aberrant conduction was the diagnosis of exclusion. Brugada P, Brugada J, et al Circulation 1991;83:1649-1659 Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? • Does any RS interval exceed 100 msec in the precordial leads? • Is A-V dissociation present? • Do the QRS complexes in V1/V2 fulfill the classic criteria? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (384 VT, 170 SVT with aberration) • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? 83 Yes 83 VT SN = 0.21 SP = 1.0 471 No Go to next step Absence of precordial RS complexes V1 V6 Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (384 VT, 170 SVT with aberration) • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? 83 Yes 83 VT SN = 0.21 SP = 1.0 471 No Go to next step Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (83 VT, 471 unknown) • RS Interval > 100 ms in one precordial lead? 175 Yes 172 VT 3 SVT SN = 0.66 SP = 0.98 296 No Go to next step Hypothesis: prolongation of the intrinsicoid deflection-RS interval > 0.1 sec-could be a marker for VT RS Interval: measured from beginning of R wave to nadir of the S wave. RS = 0.080 or 80 ms Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (83 VT, 471 unknown) • RS Interval > 100 ms in one precordial lead? 175 Yes 172 VT 3 SVT SN = 0.66 SP = 0.98 296 No Go to next step Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (255 VT, 3 SVT, 296 unknown) • Is AV Dissociation Present? 59 Yes 59 VT SN = 0.82 SP = 0.98 237 No Go to next step Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (314 VT, 3 SVT, 237 unknown) • Are classic morphology criteria for VT present in both V1- V2 and V6? 68 Yes 65 VT 3 SVT SN = 0.987 SP = 0.965 169 No 164 SVT 5 VT SN = 0.965 SP = 0.987 Classic Criteria Suggesting VT • QRS duration > 0.14 s • Superior QRS axis • Morphology in precordial leads: RBBB-like pattern V1 V6 R/S ratio < 1 LBBB-like pattern V1 V6 :qR r = 30 ms notched S wave RS > 70 ms Classic Criteria Suggesting SVT • QRS duration < 0.14 s • Normal QRS axis • Morphology in precordial leads: RBBB-like pattern LBBB-like pattern V1: V1: triphasic V6 R/S ratio > 1 absent or narrow R wave no S wave notch steep S wave descent V6 : no Q wave Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia N = 554 (314 VT, 3 SVT, 237 unknown) • Are classic morphology criteria for VT present in both V1- V2 and V6? 68 Yes 65 VT 3 SVT SN = 0.987 SP = 0.965 169 No 164 SVT 5 VT SN = 0.965 SP = 0.987 Treatment of Wide Complex Tachycardia of indeterminate etiology • Is patient unstable? – Immediate synchronized cardioversion – 100, 200, 300, 360 joules • Borderline or stable? – amiodarone Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? • Does any RS interval exceed 100 msec in the precordial leads? • Is A-V dissociation present? • Do the QRS complexes in V1/V2 fulfill the classic criteria? Wide Complex Tachycardia Case 1 • 66 year old retired businessman with a history of hypertension and a subarachnoid hemorrhage who presented with dizziness and an episode of chest pain. • Patient has a lipid disorder, smokes 2 packs of cigarettes a day, and has a son with coronary disease. • Exam showed HR of 210 BPM, BP 70/50, resp 12/min Case 1 Case 1 Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 1 • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 1 • Does any RS interval exceed 100 msec in the precordial leads? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 1 • Is A-V dissociation present? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 1 • Do the QRS complexes in V1/V2 fulfill the classic criteria? Case 1 Typical RBBB Wide Complex Tachycardia Case 1 • Received adenosine 6 mg, 12 mg • Received lidocaine 100 mg, then 2 mg/min, converting briefly to NSR. • Labs showed normal electrolytes and CK. • Received bretylium 200 mg, then 500 mg. • Received procainamide 1 gm, then 2 mg/min and metoprolol • Cardiac catheterization showed total RCA occlusion and 90% LAD stenosis. Case 1: normal sinus rhythm Case 1 NSR Frontal Axis Case 1 NSR precordial Axis Wide Complex Tachycardia Case 2 • 76 yr. old woman with an extensive history of coronary artery disease presented with palpitations. • had CABG in 1992, recent history of cough felt to be bronchitis, treated with amoxicillin, history of hypothyroidism. • Exam showed HR of 180 BPM, BP 120/100, resp 32/min • labs: K+ 3.7; Mg2+; T4 10.3; TSH 0.05 Case 2 Case 2 Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 2 • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 2 • Does any RS interval exceed 100 msec in the precordial leads? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 2 • Is A-V dissociation present? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 2 • Do the QRS complexes in V1/V2 fulfill the classic criteria? Case 2 Typical LBBB Wide Complex Tachycardia Case 2 • Treated with adenosine 6 mg, repeated once, then NSR • Loaded with digoxin, 0.5 mg, then 0.25 mg, and final dose of 0.25 mg Case 2: normal sinus rhythm Case 2 NSR Frontal Axis Case 2 NSR precordial Axis Wide Complex Tachycardia Case 3 • 29 yr. old previously healthy woman, noted dizziness and fatigue at work. • She’d had similar symptoms, episodically, over the prior two weeks. • Medications included Zoloft, oral contraceptives, and occasional Sudafed. She rarely used cocaine • Exam showed HR of 280 BPM, BP 120/70, resp 18/min Case 3 Case 3 Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 3 • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 3 • Does any RS interval exceed 100 msec in the precordial leads? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 3 • Is A-V dissociation present? Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia: Case 3 • Do the QRS complexes in V1/V2 fulfill the classic criteria? Case 3 Typical LBBB Wide Complex Tachycardia Case 3 • Treated with adenosine 6 mg, 12 mg • Received Versed 1 mg, then direct current cardioversion 100 J, without success • Received Versed 1 mg, then direct current cardioversion 200 J, without success • Received Propofol, then direct current cardioversion 350 J, with success Case 3: normal sinus rhythm Case 3 NSR Frontal Axis Case 3 NSR precordial Axis Stepwise Assessment of Wide Complex Tachycardia • Are RS complexes absent in all precordial leads? • Does any RS interval exceed 100 msec in the precordial leads? • Is A-V dissociation present? • Do the QRS complexes in V1/V2 fulfill the classic criteria? Wide Complex Tachycardia summary • WCT can be VT or SVT • Knowledge of basic appearance of “normal” RBBB and LBBB can be helpful • Hemodynamic stability does NOT help make the diagnosis • If hemodynamically stable and in doubt, treat as VT • If unstable, apply direct current cardioversion Session 5 ECGs 5A 5B 5C 5D 5E 5F 5G 5H 5I 5J 5K 5L 5M 5N Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Session 6 ECGs 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E 6F 6G 6H1 6H2 6H3 Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Session 7 ECGs 7A 7B 7C 7D 7E 7F1 7F2 7F3 7F4 7F5 7G1 7G2 7G3 7H 7I 7J 7K 7L1 7L2 7L3 7M Course Outline • Basic ECG analysis and sinus rhythm • Intervals, Bundle Branch Block, Hypertrophy and Enlargement • Supraventricular arrhythmias • Ventricular arrhythmias • Bradyarrhythmias • Heart Blocks • Ischemia and Infarction • Miscellaneous Abnormalities Session 8 ECGs 8A 8B 8C 8D 8E 8F 8G 8H 8I 8J 8K 8L 8M 8N 8O1 8O2 8P1 8P2