PolypeptideMeltingVanHolde Courtesy of Dr. Van Holde (Classic Edition--Ch. 1, #4). ...
advertisement

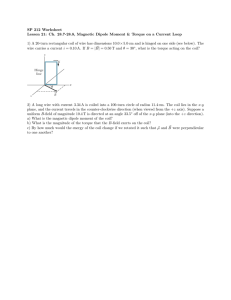
PolypeptideMeltingVanHolde Courtesy of Dr. Van Holde (Classic Edition--Ch. 1, #4). Assuming that a polypeptide chain has only one -helical conformation and that there are three possible orientations for each amino acid residue in the random coil state, calculate S for the conformational change: helix random coil for a polypeptide of 28 residues. What value of H per residue would be required to make the melting point (at which the helix converts to coil) be 37oC, which is human body temperature? Compare this to the typical hydrogen-bond energy of about 1.5 kcal/mol and comment on the ability of hydrogen bonds to stabilize the helical state.