PPC notes
advertisement
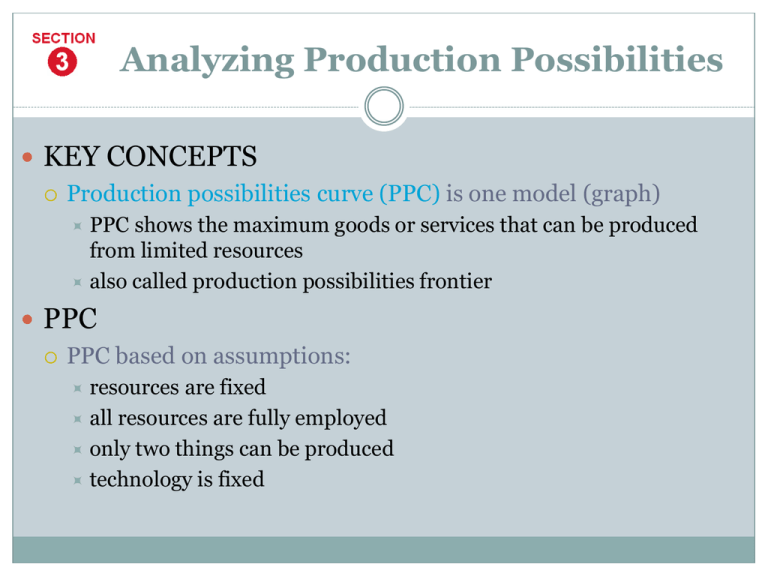
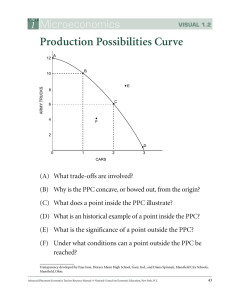
Analyzing Production Possibilities KEY CONCEPTS Production possibilities curve (PPC) is one model (graph) PPC shows the maximum goods or services that can be produced from limited resources also called production possibilities frontier PPC PPC based on assumptions: resources are fixed all resources are fully employed only two things can be produced technology is fixed Graphing the Possibilities Production Possibilities Curve PPC runs between extremes of producing only one item or the other Data is plotted on a graph; lines joining points is PPC shows maximum number of one item relative to other item PPC shows opportunity cost of each choice more of one product means less of the other What We Learn from PPCs Efficiency — producing the maximum amount of goods and services possible Underutilization — producing fewer goods and services than possible Why is the PPC a Curve? Law of increasing opportunity costs as production switches from one product to another, more resources needed to increase production of second product Reasons for increasing cost of making more of one product need new resources, machines, factories must retrain workers Costs paid by making less and less of other product Let’s Look at Some Examples PPC Practice Changing Production Possibilities A country’s supply of resources changes over time Example: U.S. in 1800s grew, gained resources, workers, new technology new resources mean new production possibilities beyond frontier Increased production shown on PPC as shift of curve outward Increase in total output called economic growth PPF—The Curve What Does Guns And Butter Curve Mean? In a theoretical economy with only two goods, a choice must be made between how much of each good to produce. As an economy produces more guns (military spending) it must reduce its production of butter (food), and vice versa. Video Clip: Individual and Society PPCs Text book-pg 20 Q#5-9 PPC Problems Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Microeconomics Microeconomics examines specific, individual elements in an economy prices, costs, profits, competition, consumer and producer behavior Some Topics of Interest: business organization, labor markets, environmental issues Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics studies sectors — combination of all individual units Includes consumer, business, public or government sectors Macroeconomics studies national or global topics: monetary system, business cycle, tax policies, international trade Examples of Macro and Micro Which is it? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. National Unemployment Figures lower. World Trade Organization Meets Shipbuilder Wins Navy Contract Cab Drivers on Strike! Gasoline Prices Jump 25 Cents