Types of Memory: Sensory, Short-Term, Long-Term
advertisement

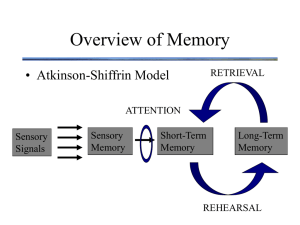
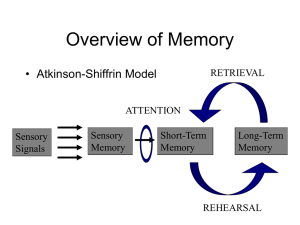
TYPES OF MEMORY • Sensory Memory – Records information from the senses for up to three seconds – Examples are Iconic (Visual) Memory and Echoic (Auditory) Memory • Short-Term Memory – Holds about seven items for up to twenty seconds before the material is forgotten or transferred to long-term memory • Long-Term Memory – Relatively permanent, can hold vast amounts of information Information-Processing Model of Memory A model of memory in which information must pass through discrete stages via the processes of attention, encoding, storage, and retrieval. l SENSORY MEMORY – Records information from the senses for up to three seconds – Iconic (Visual) Memory - form of sensory memory that holds visual information for up to one second. – Echoic (Auditory) Memory- form of sensory memory that holds auditory information for one to two seconds – Functions- 1) regulates stimulus, 2) decision time, 3) provides stability, playback, and recognition SHORT TERM MEMORY • FEATURES-A) LIMITED DURATION / MAINTENANCE REHEARSAL B) LIMITED CAPACITY / INTERFERENCE • FUNCTIONS-1) ATTENDING 2) REHEARSING TO PROCESS EX. CHUNKING 3) STORING INTO LTM COMPONENTS OF LONG TERM MEMORY • ENCODING- automatic vs. effortful-chunking, mneumonics, maintenance & elborative rehearsal • STORAGE- Procedural Memory – Stored long-term knowledge of learned habits and skills. – Examples are how to drive, ride a bike, tie one’s shoes, etc. • Declarative Memory – Stored long-term knowledge of facts about ourselves and the world. – Includes both semantic (nonpersonal) and episodic (personal) memories STEPS OF LTM cont’d • RETRIEVAL Explicit Memory – The types of memory elicited through the conscious retrieval of recollections in response to direct questions. – Conscious retention, direct tests, disrupted by amnesia, encoded in the hippocampus Implicit Memory – A nonconscious recollection of a prior experience that is revealed indirectly, by its effects on performance. – Nonconscious retention, indirect tests, intact with amnesia, encoded elsewhere Types of Memory • Photographic -ability to form detailed visual images after short exposure to picture. • Eidetic-photographic memory in children • Flashbulb - vivid recollection of dramatic or emotionally charged events • Childhood amnesia -The inability of most people to recall events from before the age of three or four • Hindsight Bias - The tendency to think after an event that one knew in advance what was going to happen