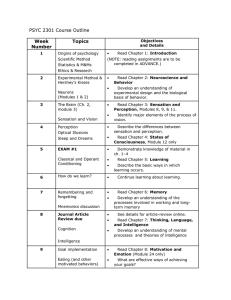
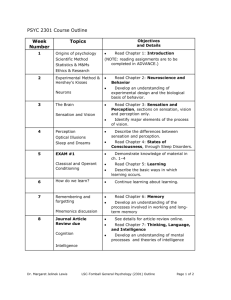
Course outline and Syllabus
advertisement

INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY FALL SEMESTER 2015 TEACHER: MR. KRAUS RM: 110 TEXT: ON-LINE TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTS OFFICE- 100 POD EMAIL- kraus@nclack.k12.or.us Objectives This course is intended to: · Introduce you to psychological science, its core topics / protocol and cutting-edge research. · Emphasize the development of critical thinking skills. · Prepare you to be a cautious and analytical consumer of information that is claimed to be scientific or based on research. · Help you gain knowledge that will enrich your personal lives and relationships through better understanding of behavior. s the district priority learning standards: R.1,R.2 and W1,2 &3 CLASS FORMAT 1. Each unit is approximately 2 weeks long (5 class days). It consists of the following assessment tools: tests and /or quiz, notebook and labs / case studies. Notebooks are checked at ANY TIME during unit.(you will need spiral notebook(100pgs.) Projects are summative in nature and have specific due dates. Labs, psychsims and case studies will be completed in class. 2. Responsibilities of student Attend class/be prepared for class(check webpage for assignments, reading & agenda) BE HONEST and AUTHENTIC ABOUT WHAT YOU KNOW.(Be honest during individual assignments, such as tests or reports. Write your own work, present your own ideas and find your own answers.) Read online materials!!! Read outside sources for information in class. Actively participate in activities/ experiments / simulations Must complete all summative assessments. Check class webpage daily for class agenda, targets, daily work and clarifications for class content. 3. Students should be on time and ready to go when class starts. Tardy policy will follow 3 strike concept. 4.quarter / semester grade scale A= 100-90% B= 89-80% C= 89-70% D= 69-60% Anything below 60% is not passing** quarter breakdown: 30% = formative assessments daily work, quizzes, research reviews & unit tests 70% = summative assessments (3) **Any FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT may be re-submitted provided they are received by teacher within the unit of study of original due date and one week before end of grading period. *This course provides an opportunity for a CRLE. UNIT SUB-TOPICS CHAPTERS ASSIGNED -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------I. INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGYUnit one text a) PSYCHOLOGY AS A SOCIAL SCIENCE b) CONDUCTING RESEARCH c) METHODS USED TO ANALYZE PSYCHOLOGY II. PHYSICAL AND MENTAL PROCESSES a) ASPECTS OF THE BRAIN b) BEHAVIOR AS A RESPONSE c) SENSATION & PERCEPTION d) STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Physical bases of Behavior SUPPLEMENTARY RDGS. III. LEARNING, MEMORY & INTELLIGENCE learning text A) OPERANT AND CLASSIC CONDITIONING MEMORY & INTELLIGENCE TEXT B) HUMAN MEMORY SUPPLEMENT LINK C) INTELLIGENCE - MEASUREMENT, VARIATIONS & INFLUENCES IV. DEVELOPMENT development text A) PHASES OF DEVELOPMENT - INFANCY, CHILDHOOD, ADOLESCENCE, ADULTHOOD B) STAGE THEORIES OF DEVELOPMENT C) FUNCTIONAL THEORIES OF DEVELOPMENT II. SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY a) SOCIAL COGNITION b) SOCIAL INTERACTION VII. REVIEW Social Psychology text & SEMESTER FINAL COURSE WEBPAGE- http://www.nclack.k12.or.us/18242019171925860/site/default.asp This will provide you with assignments, calendar and other information that will allow you the greatest success in this class. Refer to calendar for specific standards / learning targets for each class session. DOMAINS AND SPECIFIC STANDARDS FOR PSYCHOLOGY- HIGH SCHOOL I. Scientific Inquiry Domain Perspectives in Psychological Science 1.1 Define psychology as a discipline and identify its goals as a science. 1.3 Describe perspectives employed to understand behavior and mental processes. Research Methods, Measurement, and Statistics 1.1 Describe the scientific method and its role in psychology. 1.2 Describe and compare a variety of quantitative (e.g., surveys, correlations, experiments) and qualitative (e.g., interviews, narratives, focus groups) research methods. 1.3 Define systematic procedures used to improve the validity of research findings, such as external validity. 3.1 Define descriptive statistics and explain how they are used by psychological scientists. II. Biopsychology Domain Biological Bases of Behavior 1.1 Identify the major divisions and subdivisions of the human nervous system. 1.2 Identify the parts of the neuron and describe the basic process of neural transmission. 1.3 Differentiate between the structures and functions of the various parts of the central nervous system. 1.4 Describe lateralization of brain functions. Sensation and Perception 1. The processes of sensation and perception 2. The capabilities and limitations of sensory processes 3. Interaction of the person and the environment in determining perception Consciousness 1. The relationship between conscious and unconscious processes 2. Characteristics of sleep and theories that explain why we sleep and dream 3. Categories of psychoactive drugs and their effects 4. Other states of consciousness Cognition Domain Memory 1. Encoding of memory 2. Storage of memory 3. Retrieval of memory Thinking 1. Basic elements comprising thought 2. Obstacles related to thought Intelligence 1. Perspectives on intelligence 2. Assessment of intelligence 3. Issues in intelligence Sociocultural Context Domain Social Interactions 1. Social cognition 2. Social influence 3. Social relations Development and Learning Domain Learning 1. Classical conditioning 2. Operant conditioning 3. Observational and cognitive learning Life Span Development 1. Methods and issues in life span development 2. Theories of life span development 3. Prenatal development and the newborn 4. Infancy (i.e., the first two years of life) 5. Childhood 6. Adolescence 7. Adulthood and aging PYRAMID OF PROFICIENCY Social Studies-Steve Kraus-CHS The student can remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate and create information from lesson or unit. 5 EXCEEDING 4.5 4 PROFICIENT The student can remember, understand and apply information from lesson or unit. 3.5 PROGRESSING The student can remember and understand information from lesson or unit. 3 The student can remember, understand, apply and analyze information from lesson or unit. EMERGING THIS IS THE SCORING MODEL BY WHICH YOUR POINTS WILL BE EARNED / ACHIEVED. MOST DAILY WORK WILL BE SCORED USING THE 4 pt SCALE. LABS, ESSAYS, UNIT TESTS WILL BE SCORED BASED ON A MULTIPLE OF THIS SCALE.