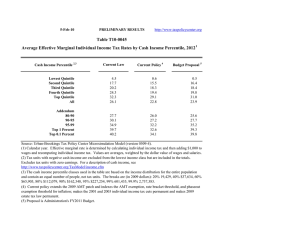
10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Click on PDF or Excel link above for additional tables containing more detail and breakdowns by filing status and demographic groups.
advertisement

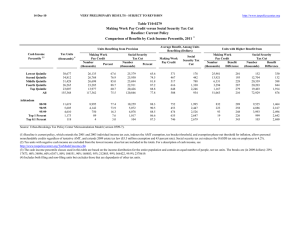
10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Click on PDF or Excel link above for additional tables containing more detail and breakdowns by filing status and demographic groups. Table T11‐0025 Administration's FY2012 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2013 1 Summary Table Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change ($) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 8.9 20.0 23.7 23.1 20.0 18.4 13.2 22.9 32.5 46.9 65.5 32.8 0.1 0.2 0.1 ‐0.1 ‐2.4 ‐1.3 ‐0.3 ‐1.3 ‐1.1 1.4 101.1 100.0 ‐10 ‐44 ‐42 65 5,325 782 ‐0.1 ‐0.2 ‐0.1 0.1 1.8 1.0 2.8 9.6 16.3 19.5 27.8 22.3 17.1 25.2 25.2 2.7 0.1 60.8 63.0 72.5 97.0 99.9 ‐0.2 ‐0.2 ‐1.3 ‐6.3 ‐7.9 2.2 1.6 13.6 83.7 46.1 231 346 3,602 87,285 472,806 0.2 0.2 1.0 4.4 5.2 22.2 23.5 26.5 34.9 38.8 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509‐7). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.2 Proposal: 3.7 (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current policy, which assumes that all the temporary provisions in place for calendar year 2011 are extended, with the exception of the payroll tax cut, and indexes the AMT exemption level after 2011. Proposal would a) index the parameters of the AMT to inflation after 2011 and allow non‐refundable credits against tentative AMT; b) extend parts of the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts, including marriage penalty relief, the 10, 15, 25, 28 and a portion of the 33 percent brackets, and the 0%/15% rate structure on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets; c) set the threshold for the 36 percent bracket at $200,000 (single), $250,000 (married), or $225,000 (head of household), indexed for inflation after 2009, less the standard deduction and one personal exemption (two if married); d) set the thresholds for PEP and Pease at $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; e) tax capital gains and qualified dividends at 20% for taxpayers in the top two brackets and repeal the 8%/18% rates for assets held more than 5 years; f) extend the $1,000 child tax credit, $3,000 (not indexed) refundability threshold, and allow against the AMT; g) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; h) extend the EITC's 45% phase‐in rate for families with 3 or more children and higher phase‐out thresholds for married couples; i) extend the maximum credit amount for the child and dependent care tax credit and increase the phase‐out threshold to $75,000 (not indexed); j) provide automatic enrollment in IRAs; k) limit itemized deductions to 28% for taxpayers in the top two brackets; and l) set the estate tax at its 2009 level ($3.5M exemption, 45% rate) and modify certain valuation discount rules. Business provisions include a) expand and make the R&E credit permanent; b) tax carried interest as ordinary income; c) repeal LIFO; d) expand section 179 expensing; e) reform international tax system; f) reform treatment of financial institutions; g) eliminate fossil fuel preferences; h) reinstate Superfund environmental income tax; and g) reform the treatment of insurance industry. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% 19,829, 40% 38,180, 60% 66,963, 80% 114,669, 90% 167,030, 95% 236,580, 99% 643,739, 99.9% 2,961,299. (4) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0025 Administration's FY2012 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2013 1 Detail Table Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Increase With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent Change in After‐Tax 5 Income Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 8.9 20.0 23.7 23.1 20.0 18.4 13.2 22.9 32.5 46.9 65.5 32.8 0.1 0.2 0.1 ‐0.1 ‐2.4 ‐1.3 ‐0.3 ‐1.3 ‐1.1 1.4 101.1 100.0 ‐10 ‐44 ‐42 65 5,325 782 ‐2.9 ‐1.5 ‐0.5 0.4 6.9 4.6 0.0 ‐0.2 ‐0.5 ‐0.7 1.5 0.0 0.5 3.6 9.9 17.0 68.9 100.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.2 ‐0.1 0.1 1.8 1.0 2.8 9.6 16.3 19.5 27.8 22.3 17.1 25.2 25.2 2.7 0.1 60.8 63.0 72.5 97.0 99.9 ‐0.2 ‐0.2 ‐1.3 ‐6.3 ‐7.9 2.2 1.6 13.6 83.7 46.1 231 346 3,602 87,285 472,806 0.7 0.7 3.9 14.4 15.6 ‐0.5 ‐0.4 ‐0.1 2.5 1.4 13.4 10.0 16.2 29.4 15.1 0.2 0.2 1.0 4.4 5.2 22.2 23.5 26.5 34.9 38.8 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile, 2013 1 4 Tax Units Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average After‐ 5 Tax Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of Pre‐ Tax Income Share of Post‐ Tax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Number (thousands) Percent of Total 40,401 35,545 32,339 27,031 23,705 159,683 25.3 22.3 20.3 16.9 14.9 100.0 11,561 29,518 53,265 91,335 295,351 79,379 332 2,882 8,701 17,715 76,702 16,896 11,229 26,636 44,564 73,620 218,649 62,484 2.9 9.8 16.3 19.4 26.0 21.3 3.7 8.3 13.6 19.5 55.2 100.0 4.6 9.5 14.4 20.0 52.0 100.0 0.5 3.8 10.4 17.8 67.4 100.0 11,940 5,860 4,707 1,197 122 7.5 3.7 3.0 0.8 0.1 142,598 204,431 366,652 1,983,475 9,019,082 31,381 47,703 93,397 604,997 3,028,194 111,217 156,728 273,255 1,378,477 5,990,888 22.0 23.3 25.5 30.5 33.6 13.4 9.5 13.6 18.7 8.7 13.3 9.2 12.9 16.5 7.3 13.9 10.4 16.3 26.9 13.7 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509‐7). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.2 Proposal: 3.7 (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current policy, which assumes that all the temporary provisions in place for calendar year 2011 are extended, with the exception of the payroll tax cut, and indexes the AMT exemption level after 2011. Proposal would a) index the parameters of the AMT to inflation after 2011 and allow non‐refundable credits against tentative AMT; b) extend parts of the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts, including marriage penalty relief, the 10, 15, 25, 28 and a portion of the 33 percent brackets, and the 0%/15% rate structure on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets; c) set the threshold for the 36 percent bracket at $200,000 (single), $250,000 (married), or $225,000 (head of household), indexed for inflation after 2009, less the standard deduction and one personal exemption (two if married); d) set the thresholds for PEP and Pease at $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; e) tax capital gains and qualified dividends at 20% for taxpayers in the top two brackets and repeal the 8%/18% rates for assets held more than 5 years; f) extend the $1,000 child tax credit, $3,000 (not indexed) refundability threshold, and allow against the AMT; g) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; h) extend the EITC's 45% phase‐in rate for families with 3 or more children and higher phase‐out thresholds for married couples; i) extend the maximum credit amount for the child and dependent care tax credit and increase the phase‐out threshold to $75,000 (not indexed); j) provide automatic enrollment in IRAs; k) limit itemized deductions to 28% for taxpayers in the top two brackets; and l) set the estate tax at its 2009 level ($3.5M exemption, 45% rate) and modify certain valuation discount rules. Business provisions include a) expand and make the R&E credit permanent; b) tax carried interest as ordinary income; c) repeal LIFO; d) expand section 179 expensing; e) reform international tax system; f) reform treatment of financial institutions; g) eliminate fossil fuel preferences; h) reinstate Superfund environmental income tax; and g) reform the treatment of insurance industry. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% 19,829, 40% 38,180, 60% 66,963, 80% 114,669, 90% 167,030, 95% 236,580, 99% 643,739, 99.9% 2,961,299. (4) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0025 Administration's FY2012 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 Detail Table Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Increase With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent Change in After‐Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 7.7 21.0 24.4 21.5 18.3 18.4 11.2 19.5 29.9 43.9 63.0 32.8 0.1 0.2 0.1 ‐0.1 ‐2.3 ‐1.3 ‐0.1 ‐1.5 ‐1.4 1.0 102.0 100.0 ‐5 ‐56 ‐56 39 4,200 782 3.0 ‐2.6 ‐0.8 0.3 6.5 4.6 0.0 ‐0.2 ‐0.4 ‐0.7 1.3 0.0 ‐0.2 2.4 7.9 16.3 73.5 100.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.2 ‐0.1 0.1 1.7 1.0 ‐1.6 7.7 14.8 18.9 27.5 22.3 18.2 21.5 18.2 2.5 0.9 55.4 61.9 75.7 97.0 99.1 ‐0.2 ‐0.2 ‐1.2 ‐6.1 ‐7.8 1.9 1.6 13.1 85.5 47.5 152 258 2,732 73,837 411,232 0.6 0.6 3.5 14.2 15.6 ‐0.6 ‐0.4 ‐0.2 2.6 1.5 14.7 11.1 17.3 30.4 15.6 0.1 0.2 0.9 4.3 5.2 22.3 23.7 26.1 34.5 38.4 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units4 Average Income (Dollars) Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average After‐ Tax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of Pre‐ Tax Income Share of Post‐ Tax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Number (thousands) Percent of Total 33,459 32,885 31,869 30,496 30,312 159,683 21.0 20.6 20.0 19.1 19.0 100.0 10,833 26,816 47,152 79,522 248,646 79,379 ‐166 2,127 7,039 15,026 64,246 16,896 11,000 24,689 40,113 64,497 184,400 62,484 ‐1.5 7.9 14.9 18.9 25.8 21.3 2.9 7.0 11.9 19.1 59.5 100.0 3.7 8.1 12.8 19.7 56.0 100.0 ‐0.2 2.6 8.3 17.0 72.2 100.0 15,281 7,600 5,988 1,444 144 9.6 4.8 3.8 0.9 0.1 121,325 174,872 311,732 1,722,207 7,944,556 26,925 41,114 78,767 520,558 2,639,811 94,399 133,758 232,964 1,201,649 5,304,746 22.2 23.5 25.3 30.2 33.2 14.6 10.5 14.7 19.6 9.0 14.5 10.2 14.0 17.4 7.7 15.3 11.6 17.5 27.9 14.1 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509‐7). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.2 Proposal: 3.7 (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current policy, which assumes that all the temporary provisions in place for calendar year 2011 are extended, with the exception of the payroll tax cut, and indexes the AMT exemption level after 2011. Proposal would a) index the parameters of the AMT to inflation after 2011 and allow non‐refundable credits against tentative AMT; b) extend parts of the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts, including marriage penalty relief, the 10, 15, 25, 28 and a portion of the 33 percent brackets, and the 0%/15% rate structure on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets; c) set the threshold for the 36 percent bracket at $200,000 (single), $250,000 (married), or $225,000 (head of household), indexed for inflation after 2009, less the standard deduction and one personal exemption (two if married); d) set the thresholds for PEP and Pease at $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; e) tax capital gains and qualified dividends at 20% for taxpayers in the top two brackets and repeal the 8%/18% rates for assets held more than 5 years; f) extend the $1,000 child tax credit, $3,000 (not indexed) refundability threshold, and allow against the AMT; g) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; h) extend the EITC's 45% phase‐in rate for families with 3 or more children and higher phase‐out thresholds for married couples; i) extend the maximum credit amount for the child and dependent care tax credit and increase the phase‐out threshold to $75,000 (not indexed); j) provide automatic enrollment in IRAs; k) limit itemized deductions to 28% for taxpayers in the top two brackets; and l) set the estate tax at its 2009 level ($3.5M exemption, 45% rate) and modify certain valuation discount rules. Business provisions include a) expand and make the R&E credit permanent; b) tax carried interest as ordinary income; c) repeal LIFO; d) expand section 179 expensing; e) reform international tax system; f) reform treatment of financial institutions; g) eliminate fossil fuel preferences; h) reinstate Superfund environmental income tax; and g) reform the treatment of insurance industry. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% 13,627, 40% 25,365, 60% 42,896, 80% 70,063, 90% 101,583, 95% 145,293, 99% 386,366, 99.9% 1,826,435. (4) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0025 Administration's FY2012 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 Detail Table ‐ Single Tax Units Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Increase With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent Change in After‐Tax 5 Income Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 8.8 15.8 19.3 17.4 12.2 14.5 10.5 21.5 29.4 39.1 60.4 28.7 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.0 ‐2.1 ‐0.9 ‐0.5 ‐2.3 ‐2.0 0.7 103.8 100.0 ‐6 ‐32 ‐31 14 2,444 323 ‐1.4 ‐1.6 ‐0.5 0.1 5.8 3.4 ‐0.1 ‐0.2 ‐0.5 ‐0.7 1.4 0.0 1.2 4.6 12.1 20.4 61.5 100.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.2 ‐0.1 0.0 1.5 0.7 5.7 9.9 16.5 20.9 27.7 21.8 13.6 10.5 12.5 1.5 0.3 51.1 63.3 75.8 97.4 99.7 ‐0.2 ‐0.3 ‐1.0 ‐6.9 ‐9.2 2.7 3.1 12.3 85.8 47.1 118 300 1,538 54,290 336,278 0.6 1.0 2.9 15.1 16.7 ‐0.4 ‐0.3 ‐0.1 2.2 1.2 15.4 10.4 14.3 21.4 10.7 0.1 0.2 0.7 4.7 5.9 23.9 24.9 25.4 35.9 41.4 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 4 Tax Units Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average After‐ 5 Tax Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of Pre‐ Tax Income Share of Post‐ Tax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Number (thousands) Percent of Total 18,053 16,001 14,578 11,876 9,681 70,516 25.6 22.7 20.7 16.8 13.7 100.0 8,179 20,442 35,077 57,277 159,815 45,439 471 2,051 5,831 11,979 41,830 9,563 7,709 18,391 29,247 45,298 117,985 35,876 5.8 10.0 16.6 20.9 26.2 21.1 4.6 10.2 16.0 21.2 48.3 100.0 5.5 11.6 16.9 21.3 45.2 100.0 1.3 4.9 12.6 21.1 60.1 100.0 5,163 2,344 1,814 360 32 7.3 3.3 2.6 0.5 0.1 87,005 124,519 215,516 1,152,428 5,673,795 20,688 30,684 53,291 359,615 2,010,792 66,317 93,835 162,225 792,813 3,663,003 23.8 24.6 24.7 31.2 35.4 14.0 9.1 12.2 13.0 5.7 13.5 8.7 11.6 11.3 4.6 15.8 10.7 14.3 19.2 9.5 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509‐7). (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current policy, which assumes that all the temporary provisions in place for calendar year 2011 are extended, with the exception of the payroll tax cut, and indexes the AMT exemption level after 2011. Proposal would a) index the parameters of the AMT to inflation after 2011 and allow non‐refundable credits against tentative AMT; b) extend parts of the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts, including marriage penalty relief, the 10, 15, 25, 28 and a portion of the 33 percent brackets, and the 0%/15% rate structure on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets; c) set the threshold for the 36 percent bracket at $200,000 (single), $250,000 (married), or $225,000 (head of household), indexed for inflation after 2009, less the standard deduction and one personal exemption (two if married); d) set the thresholds for PEP and Pease at $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; e) tax capital gains and qualified dividends at 20% for taxpayers in the top two brackets and repeal the 8%/18% rates for assets held more than 5 years; f) extend the $1,000 child tax credit, $3,000 (not indexed) refundability threshold, and allow against the AMT; g) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; h) extend the EITC's 45% phase‐in rate for families with 3 or more children and higher phase‐out thresholds for married couples; i) extend the maximum credit amount for the child and dependent care tax credit and increase the phase‐out threshold to $75,000 (not indexed); j) provide automatic enrollment in IRAs; k) limit itemized deductions to 28% for taxpayers in the top two brackets; and l) set the estate tax at its 2009 level ($3.5M exemption, 45% rate) and modify certain valuation discount rules. Business provisions include a) expand and make the R&E credit permanent; b) tax carried interest as ordinary income; c) repeal LIFO; d) expand section 179 expensing; e) reform international tax system; f) reform treatment of financial institutions; g) eliminate fossil fuel preferences; h) reinstate Superfund environmental income tax; and g) reform the treatment of insurance industry. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% 13,627, 40% 25,365, 60% 42,896, 80% 70,063, 90% 101,583, 95% 145,293, 99% 386,366, 99.9% 1,826,435. (4) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0025 Administration's FY2012 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 Detail Table ‐ Married Tax Units Filing Jointly Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Increase With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent Change in After‐Tax 5 Income Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 5.5 20.6 25.7 23.4 20.8 20.5 17.7 26.5 36.7 50.7 66.0 45.5 0.0 0.1 0.1 ‐0.1 ‐2.3 ‐1.5 0.0 ‐0.4 ‐0.5 1.2 99.6 100.0 1 ‐45 ‐44 80 5,151 1,584 ‐0.7 ‐1.8 ‐0.5 0.5 6.7 5.4 0.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.3 ‐0.7 1.0 0.0 ‐0.1 1.2 4.9 13.8 80.2 100.0 0.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.1 0.1 1.7 1.2 ‐1.4 7.2 13.4 17.9 27.4 23.5 20.5 25.9 19.7 2.8 1.1 59.6 62.6 77.0 96.9 98.8 ‐0.2 ‐0.2 ‐1.3 ‐6.0 ‐7.5 1.8 1.2 13.4 83.3 45.5 190 242 3,335 79,478 426,499 0.6 0.5 3.7 14.0 15.3 ‐0.7 ‐0.6 ‐0.3 2.6 1.5 14.5 11.9 19.3 34.5 17.4 0.1 0.1 0.9 4.2 5.0 21.7 23.3 26.4 34.1 37.8 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 4 Tax Units Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average After‐ 5 Tax Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of Pre‐ Tax Income Share of Post‐ Tax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Number (thousands) Percent of Total 7,024 8,856 11,443 15,130 18,854 61,567 11.4 14.4 18.6 24.6 30.6 100.0 14,231 34,357 60,965 97,772 297,727 132,758 ‐195 2,532 8,208 17,380 76,516 29,611 14,425 31,825 52,757 80,392 221,211 103,147 ‐1.4 7.4 13.5 17.8 25.7 22.3 1.2 3.7 8.5 18.1 68.7 100.0 1.6 4.4 9.5 19.2 65.7 100.0 ‐0.1 1.2 5.2 14.4 79.1 100.0 9,003 4,921 3,909 1,021 104 14.6 8.0 6.4 1.7 0.2 142,540 200,289 359,028 1,900,519 8,491,806 30,715 46,376 91,326 568,764 2,780,603 111,824 153,912 267,701 1,331,755 5,711,204 21.6 23.2 25.4 29.9 32.7 15.7 12.1 17.2 23.8 10.8 15.9 11.9 16.5 21.4 9.4 15.2 12.5 19.6 31.9 15.9 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509‐7). (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current policy, which assumes that all the temporary provisions in place for calendar year 2011 are extended, with the exception of the payroll tax cut, and indexes the AMT exemption level after 2011. Proposal would a) index the parameters of the AMT to inflation after 2011 and allow non‐refundable credits against tentative AMT; b) extend parts of the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts, including marriage penalty relief, the 10, 15, 25, 28 and a portion of the 33 percent brackets, and the 0%/15% rate structure on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets; c) set the threshold for the 36 percent bracket at $200,000 (single), $250,000 (married), or $225,000 (head of household), indexed for inflation after 2009, less the standard deduction and one personal exemption (two if married); d) set the thresholds for PEP and Pease at $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; e) tax capital gains and qualified dividends at 20% for taxpayers in the top two brackets and repeal the 8%/18% rates for assets held more than 5 years; f) extend the $1,000 child tax credit, $3,000 (not indexed) refundability threshold, and allow against the AMT; g) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; h) extend the EITC's 45% phase‐in rate for families with 3 or more children and higher phase‐out thresholds for married couples; i) extend the maximum credit amount for the child and dependent care tax credit and increase the phase‐out threshold to $75,000 (not indexed); j) provide automatic enrollment in IRAs; k) limit itemized deductions to 28% for taxpayers in the top two brackets; and l) set the estate tax at its 2009 level ($3.5M exemption, 45% rate) and modify certain valuation discount rules. Business provisions include a) expand and make the R&E credit permanent; b) tax carried interest as ordinary income; c) repeal LIFO; d) expand section 179 expensing; e) reform international tax system; f) reform treatment of financial institutions; g) eliminate fossil fuel preferences; h) reinstate Superfund environmental income tax; and g) reform the treatment of insurance industry. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% 13,627, 40% 25,365, 60% 42,896, 80% 70,063, 90% 101,583, 95% 145,293, 99% 386,366, 99.9% 1,826,435. (4) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0025 Administration's FY2012 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 Detail Table ‐ Head of Household Tax Units Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Increase With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent Change in After‐Tax 5 Income Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 7.0 32.9 36.3 28.9 28.1 24.5 6.9 7.5 17.8 31.7 42.4 14.0 0.1 0.4 0.4 0.1 ‐1.4 ‐0.1 ‐11.2 ‐168.9 ‐146.6 ‐36.7 462.8 100.0 ‐8 ‐120 ‐154 ‐70 1,975 22 0.5 ‐7.0 ‐2.0 ‐0.5 4.2 0.4 0.0 ‐0.7 ‐0.7 ‐0.3 1.6 0.0 ‐9.0 8.5 27.2 30.4 42.8 100.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.4 ‐0.3 ‐0.1 1.1 0.1 ‐11.6 5.1 14.8 19.6 26.1 13.4 23.7 35.7 41.5 5.4 0.9 39.6 40.4 47.7 94.2 98.9 0.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.8 ‐6.0 ‐7.8 ‐0.2 6.7 58.9 397.4 207.8 ‐1 146 1,761 62,321 396,180 0.0 0.4 2.5 13.7 15.6 ‐0.1 0.0 0.2 1.5 0.8 14.9 6.6 9.0 12.4 5.8 0.0 0.1 0.6 4.2 5.2 23.0 23.8 24.8 34.6 38.5 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 4 Tax Units Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average After‐ 5 Tax Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of Pre‐ Tax Income Share of Post‐ Tax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Number (thousands) Percent of Total 8,120 7,619 5,177 2,860 1,273 25,098 32.4 30.4 20.6 11.4 5.1 100.0 13,842 31,582 51,476 78,894 187,085 43,104 ‐1,598 1,734 7,774 15,492 46,775 5,755 15,440 29,847 43,702 63,402 140,310 37,349 ‐11.6 5.5 15.1 19.6 25.0 13.4 10.4 22.2 24.6 20.9 22.0 100.0 13.4 24.3 24.1 19.3 19.1 100.0 ‐9.0 9.2 27.9 30.7 41.2 100.0 808 249 182 35 3 3.2 1.0 0.7 0.1 0.0 115,728 161,060 289,763 1,499,445 7,613,791 26,659 38,229 69,946 455,722 2,534,198 89,069 122,831 219,818 1,043,723 5,079,593 23.0 23.7 24.1 30.4 33.3 8.7 3.7 4.9 4.8 2.0 7.7 3.3 4.3 3.9 1.5 14.9 6.6 8.8 10.9 5.0 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509‐7). (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current policy, which assumes that all the temporary provisions in place for calendar year 2011 are extended, with the exception of the payroll tax cut, and indexes the AMT exemption level after 2011. Proposal would a) index the parameters of the AMT to inflation after 2011 and allow non‐refundable credits against tentative AMT; b) extend parts of the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts, including marriage penalty relief, the 10, 15, 25, 28 and a portion of the 33 percent brackets, and the 0%/15% rate structure on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets; c) set the threshold for the 36 percent bracket at $200,000 (single), $250,000 (married), or $225,000 (head of household), indexed for inflation after 2009, less the standard deduction and one personal exemption (two if married); d) set the thresholds for PEP and Pease at $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; e) tax capital gains and qualified dividends at 20% for taxpayers in the top two brackets and repeal the 8%/18% rates for assets held more than 5 years; f) extend the $1,000 child tax credit, $3,000 (not indexed) refundability threshold, and allow against the AMT; g) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; h) extend the EITC's 45% phase‐in rate for families with 3 or more children and higher phase‐out thresholds for married couples; i) extend the maximum credit amount for the child and dependent care tax credit and increase the phase‐out threshold to $75,000 (not indexed); j) provide automatic enrollment in IRAs; k) limit itemized deductions to 28% for taxpayers in the top two brackets; and l) set the estate tax at its 2009 level ($3.5M exemption, 45% rate) and modify certain valuation discount rules. Business provisions include a) expand and make the R&E credit permanent; b) tax carried interest as ordinary income; c) repeal LIFO; d) expand section 179 expensing; e) reform international tax system; f) reform treatment of financial institutions; g) eliminate fossil fuel preferences; h) reinstate Superfund environmental income tax; and g) reform the treatment of insurance industry. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% 13,627, 40% 25,365, 60% 42,896, 80% 70,063, 90% 101,583, 95% 145,293, 99% 386,366, 99.9% 1,826,435. (4) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0025 Administration's FY2012 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 Detail Table ‐ Tax Units with Children Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Increase With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent Change in After‐Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 6.9 33.5 37.7 30.8 28.6 27.3 7.6 9.9 23.0 39.5 58.1 26.2 0.0 0.3 0.2 0.0 ‐2.5 ‐1.2 ‐0.1 ‐2.6 ‐2.7 ‐0.1 105.5 100.0 ‐6 ‐116 ‐125 ‐5 5,923 945 0.3 ‐6.1 ‐1.3 0.0 6.8 4.6 0.1 ‐0.2 ‐0.5 ‐0.9 1.5 0.0 ‐2.0 1.7 9.2 18.8 72.2 100.0 0.0 ‐0.3 ‐0.2 0.0 1.8 1.0 ‐13.6 5.0 15.1 19.4 28.6 21.8 24.9 45.3 23.9 1.7 0.1 53.8 46.2 74.8 98.2 99.9 ‐0.1 0.0 ‐1.8 ‐6.8 ‐7.9 0.7 0.3 19.0 85.5 42.8 80 76 5,510 104,409 556,230 0.2 0.1 4.9 14.8 15.5 ‐0.7 ‐0.5 0.1 2.6 1.3 15.0 10.5 17.8 28.8 13.9 0.1 0.0 1.3 4.7 5.2 22.9 24.2 28.0 36.2 39.0 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units4 Average Income (Dollars) Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average After‐ Tax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of Pre‐ Tax Income Share of Post‐ Tax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Number (thousands) Percent of Total 10,404 10,419 10,279 9,803 8,309 49,348 21.1 21.1 20.8 19.9 16.8 100.0 15,026 35,671 63,686 106,014 325,807 99,630 ‐2,032 1,902 9,717 20,556 87,211 20,790 17,059 33,770 53,969 85,458 238,595 78,840 ‐13.5 5.3 15.3 19.4 26.8 20.9 3.2 7.6 13.3 21.1 55.1 100.0 4.6 9.0 14.3 21.5 51.0 100.0 ‐2.1 1.9 9.7 19.6 70.6 100.0 4,326 1,997 1,604 382 36 8.8 4.1 3.3 0.8 0.1 162,746 233,966 425,182 2,235,730 10,656,644 37,146 56,436 113,583 704,488 3,599,393 125,600 177,530 311,600 1,531,241 7,057,252 22.8 24.1 26.7 31.5 33.8 14.3 9.5 13.9 17.4 7.8 14.0 9.1 12.9 15.0 6.5 15.7 11.0 17.8 26.2 12.6 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509‐7). Note: Tax units with children are those claiming an exemption for children at home or away from home. (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current policy, which assumes that all the temporary provisions in place for calendar year 2011 are extended, with the exception of the payroll tax cut, and indexes the AMT exemption level after 2011. Proposal would a) index the parameters of the AMT to inflation after 2011 and allow non‐refundable credits against tentative AMT; b) extend parts of the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts, including marriage penalty relief, the 10, 15, 25, 28 and a portion of the 33 percent brackets, and the 0%/15% rate structure on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets; c) set the threshold for the 36 percent bracket at $200,000 (single), $250,000 (married), or $225,000 (head of household), indexed for inflation after 2009, less the standard deduction and one personal exemption (two if married); d) set the thresholds for PEP and Pease at $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; e) tax capital gains and qualified dividends at 20% for taxpayers in the top two brackets and repeal the 8%/18% rates for assets held more than 5 years; f) extend the $1,000 child tax credit, $3,000 (not indexed) refundability threshold, and allow against the AMT; g) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; h) extend the EITC's 45% phase‐in rate for families with 3 or more children and higher phase‐out thresholds for married couples; i) extend the maximum credit amount for the child and dependent care tax credit and increase the phase‐out threshold to $75,000 (not indexed); j) provide automatic enrollment in IRAs; k) limit itemized deductions to 28% for taxpayers in the top two brackets; and l) set the estate tax at its 2009 level ($3.5M exemption, 45% rate) and modify certain valuation discount rules. Business provisions include a) expand and make the R&E credit permanent; b) tax carried interest as ordinary income; c) repeal LIFO; d) expand section 179 expensing; e) reform international tax system; f) reform treatment of financial institutions; g) eliminate fossil fuel preferences; h) reinstate Superfund environmental income tax; and g) reform the treatment of insurance industry. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% 13,627, 40% 25,365, 60% 42,896, 80% 70,063, 90% 101,583, 95% 145,293, 99% 386,366, 99.9% 1,826,435. (4) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 10‐Mar‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0025 Administration's FY2012 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 1 Detail Table ‐ Elderly Tax Units Percent of Tax Units 4 Cash Income Percentile 2,3 With Tax Increase With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent Change in After‐Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate 6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 0.8 3.2 4.6 8.0 7.1 4.6 22.9 37.9 61.7 78.4 87.4 56.3 ‐0.1 0.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.4 ‐3.0 ‐1.9 0.1 0.2 0.9 3.9 94.8 100.0 5 10 56 258 6,187 1,185 2.1 1.1 2.3 3.3 9.5 8.5 0.0 ‐0.1 ‐0.2 ‐0.5 0.8 0.0 0.3 1.6 3.3 9.7 85.1 100.0 0.1 0.0 0.1 0.4 2.3 1.5 2.3 3.9 6.0 11.3 26.4 19.4 8.2 6.9 6.7 1.7 0.3 83.2 87.9 91.8 97.7 99.6 ‐0.7 ‐0.7 ‐1.3 ‐6.3 ‐8.2 4.3 3.2 10.1 77.1 45.3 635 857 2,770 70,037 382,672 3.7 2.9 4.4 14.5 16.1 ‐0.4 ‐0.5 ‐0.7 2.5 1.7 9.5 9.1 18.9 47.7 25.5 0.6 0.5 1.0 4.4 5.4 16.3 19.2 23.5 34.9 39.1 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units4 Average Income (Dollars) Cash Income Percentile 2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average After‐ Tax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of Pre‐ Tax Income Share of Post‐ Tax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Number (thousands) Percent of Total 5,313 8,515 6,190 5,603 5,686 31,333 17.0 27.2 19.8 17.9 18.2 100.0 10,822 22,986 41,540 72,670 269,484 78,111 248 876 2,448 7,944 64,974 13,985 10,575 22,110 39,092 64,726 204,510 64,126 2.3 3.8 5.9 10.9 24.1 17.9 2.4 8.0 10.5 16.6 62.6 100.0 2.8 9.4 12.0 18.1 57.9 100.0 0.3 1.7 3.5 10.2 84.3 100.0 2,520 1,400 1,357 409 44 8.0 4.5 4.3 1.3 0.1 109,880 159,960 281,390 1,589,526 7,053,610 17,299 29,890 63,346 484,615 2,377,870 92,581 130,070 218,043 1,104,911 4,675,741 15.7 18.7 22.5 30.5 33.7 11.3 9.2 15.6 26.5 12.7 11.6 9.1 14.7 22.5 10.2 10.0 9.6 19.6 45.2 23.9 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509‐7). Note: Elderly tax units are those with either head or spouse (if filing jointly) age 65 or older. (1) Calendar year. Baseline is current policy, which assumes that all the temporary provisions in place for calendar year 2011 are extended, with the exception of the payroll tax cut, and indexes the AMT exemption level after 2011. Proposal would a) index the parameters of the AMT to inflation after 2011 and allow non‐refundable credits against tentative AMT; b) extend parts of the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts, including marriage penalty relief, the 10, 15, 25, 28 and a portion of the 33 percent brackets, and the 0%/15% rate structure on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in those brackets; c) set the threshold for the 36 percent bracket at $200,000 (single), $250,000 (married), or $225,000 (head of household), indexed for inflation after 2009, less the standard deduction and one personal exemption (two if married); d) set the thresholds for PEP and Pease at $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; e) tax capital gains and qualified dividends at 20% for taxpayers in the top two brackets and repeal the 8%/18% rates for assets held more than 5 years; f) extend the $1,000 child tax credit, $3,000 (not indexed) refundability threshold, and allow against the AMT; g) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; h) extend the EITC's 45% phase‐in rate for families with 3 or more children and higher phase‐out thresholds for married couples; i) extend the maximum credit amount for the child and dependent care tax credit and increase the phase‐out threshold to $75,000 (not indexed); j) provide automatic enrollment in IRAs; k) limit itemized deductions to 28% for taxpayers in the top two brackets; and l) set the estate tax at its 2009 level ($3.5M exemption, 45% rate) and modify certain valuation discount rules. Business provisions include a) expand and make the R&E credit permanent; b) tax carried interest as ordinary income; c) repeal LIFO; d) expand section 179 expensing; e) reform international tax system; f) reform treatment of financial institutions; g) eliminate fossil fuel preferences; h) reinstate Superfund environmental income tax; and g) reform the treatment of insurance industry. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% 13,627, 40% 25,365, 60% 42,896, 80% 70,063, 90% 101,583, 95% 145,293, 99% 386,366, 99.9% 1,826,435. (4) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income.