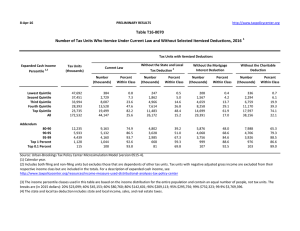
18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS Lowest Quintile Second Quintile
advertisement

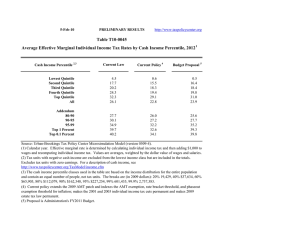
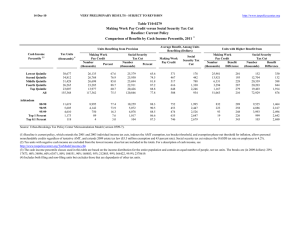
18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Click on PDF or Excel link above for additional tables containing more detail and breakdowns by filing status and demographic groups. Table T11‐0373 Herman Cain's "9‐9‐9" Tax Reform Plan without Poverty Deduction 1 Baseline: Current Law Fully Phased in Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile 2 Summary Table Tax Units with Tax Increase or Cut 5 Cash Income Percentile3,4 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Cut Pct of Tax Avg Tax Cut Units With Tax Increase Pct of Tax Avg Tax Units Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income6 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Rate7 Average Federal Tax Change ($) Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 2.8 6.1 15.9 32.6 70.9 21.0 ‐698 ‐1,271 ‐1,978 ‐4,253 ‐36,328 ‐19,275 90.4 93.7 84.1 67.4 29.1 77.0 1,857 3,490 4,203 5,082 5,856 3,499 ‐17.0 ‐13.0 ‐7.7 ‐3.0 12.2 2.3 ‐34.1 ‐56.9 ‐50.1 ‐26.7 267.9 100.0 1,659 3,189 3,238 2,071 ‐23,522 ‐1,271 16.4 11.6 6.4 2.4 ‐8.6 ‐1.8 20.2 22.3 23.8 23.7 20.5 21.9 58.7 77.4 87.9 94.2 97.8 ‐6,821 ‐11,097 ‐32,806 ‐334,252 ‐1,751,573 41.3 22.6 12.1 5.8 2.2 4,941 5,808 9,470 42,265 264,054 1.8 5.0 11.0 26.9 35.4 10.7 19.9 60.8 176.5 99.5 ‐1,871 ‐7,104 ‐26,737 ‐307,473 ‐1,689,562 ‐1.4 ‐3.7 ‐7.9 ‐17.4 ‐21.5 23.3 22.2 20.0 17.9 17.9 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0411‐2). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 21.0 Proposal: 0.0 * Less than 0.05 ** Insufficient data (1) Since we conducted this analysis, the Cain campaign has said tax units could claim a deduction on the individual flat tax to mitigate the effects on households below the poverty level Despite several requests for clarification, the campaign has not defined clearly how that deduction would work. This analysis therefore does not include a poverty deduction. Including a poverty deduction would reduce taxes for households claiming the deduction but would require either higher tax rates or a broader tax base in order to raise the same amount of revenue as the version of the plan without poverty relief. (Footnote added November 10, 2011) (2) Baseline is 2013 current law. Proposal replaces the individual income tax, corporate income tax, payroll tax and estate tax with presidential candidate Herman Cain's 9‐9‐9 Plan. The fully phased in proposal is evaluated at 2013 income levels and all amounts are expressed in 2013 dollars. For a detailed description of TPC's interpretation of the 9‐9‐9 Plan, see www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/Cain‐9‐9‐9‐plan.cfm. For a description of TPC's current law and current policy baselines, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/T11‐0270 (3) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (4) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2011 dollars): 20% $17,909; 40% $37,090; 60% $64,531; 80% $111,344; 90% $160,377; 95% $227,314; 99% $592,985; 99.9% $2,682,143. (5) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (6) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (7) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0373 Herman Cain's "9‐9‐9" Tax Reform Plan without Poverty Deduction 1 Baseline: Current Law 2 Fully Phased in Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Detail Table Percent of Tax Units 5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income6 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Under the Proposal Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 2.8 6.1 15.9 32.6 70.9 21.0 90.4 93.7 84.1 67.4 29.1 77.0 ‐17.0 ‐13.0 ‐7.7 ‐3.0 12.2 2.3 ‐34.1 ‐56.9 ‐50.1 ‐26.7 267.9 100.0 1,659 3,189 3,238 2,071 ‐23,522 ‐1,271 436.8 107.5 36.7 11.1 ‐29.6 ‐7.4 2.8 4.9 4.8 3.6 ‐16.1 0.0 3.4 8.8 15.0 21.4 51.2 100.0 16.4 11.6 6.4 2.4 ‐8.6 ‐1.8 20.2 22.3 23.8 23.7 20.5 21.9 58.7 77.4 87.9 94.2 97.8 41.3 22.6 12.1 5.8 2.2 1.8 5.0 11.0 26.9 35.4 10.7 19.9 60.8 176.5 99.5 ‐1,871 ‐7,104 ‐26,737 ‐307,473 ‐1,689,562 ‐5.6 ‐14.2 ‐28.3 ‐49.3 ‐54.5 0.3 ‐0.8 ‐3.6 ‐12.0 ‐6.9 14.6 9.7 12.4 14.6 6.7 ‐1.4 ‐3.7 ‐7.9 ‐17.4 ‐21.5 23.3 22.2 20.0 17.9 17.9 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 2 by Cash Income Percentile, 2013 Tax Units5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Pre‐Tax Income After‐Tax Income 6 Federal Tax Burden Percent of Total Percent of Total Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Number (thousands) Percent of Total 43,362 37,681 32,699 27,208 24,067 166,272 26.1 22.7 19.7 16.4 14.5 100.0 10,122 27,586 50,739 87,197 272,779 72,381 3.7 8.6 13.8 19.7 54.6 100.0 380 2,966 8,815 18,634 79,526 17,091 0.6 3.9 10.1 17.8 67.4 100.0 9,742 24,621 41,924 68,563 193,254 55,290 4.6 10.1 14.9 20.3 50.6 100.0 3.8 10.8 17.4 21.4 29.2 23.6 12,130 5,919 4,805 1,213 124 7.3 3.6 2.9 0.7 0.1 136,031 193,370 338,609 1,767,267 7,871,135 13.7 9.5 13.5 17.8 8.1 33,513 50,000 94,594 624,137 3,098,549 14.3 10.4 16.0 26.6 13.6 102,517 143,370 244,015 1,143,130 4,772,586 13.5 9.2 12.8 15.1 6.5 24.6 25.9 27.9 35.3 39.4 Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Percent of Total Average (dollars) Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0411‐2). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 21.0 Proposal: 0.0 * Less than 0.05 (1) Since we conducted this analysis, the Cain campaign has said tax units could claim a deduction on the individual flat tax to mitigate the effects on households below the poverty level. Despite several requests for clarification, the campaign has not defined clearly how that deduction would work. This analysis therefore does not include a poverty deduction. Including a poverty deduction would reduce taxes for households claiming the deduction but would require either higher tax rates or a broader tax base in order to raise the same amount of revenue as the version of the plan without poverty relief. (Footnote added November 10, 2011) (2) Baseline is 2013 current law. Proposal replaces the individual income tax, corporate income tax, payroll tax and estate tax with presidential candidate Herman Cain's 9‐9‐9 Plan. The fully phased in proposal is evaluated at 2013 income levels and all amounts are expressed in 2013 dollars. For a detailed description of TPC's interpretation of the 9‐9‐9 Plan, see www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/Cain‐9‐9‐9‐plan.cfm. For a description of TPC's current law and current policy baselines, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/T11‐0270 (3) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (4) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2011 dollars): 20% $17,909; 40% $37,090; 60% $64,531; 80% $111,344; 90% $160,377; 95% $227,314; 99% $592,985; 99.9% $2,682,143. (5) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (6) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (7) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0373 Herman Cain's "9‐9‐9" Tax Reform Plan without Poverty Deduction 1 Baseline: Current Law Fully Phased in Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size 2 Detail Table Percent of Tax Units 5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income6 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Under the Proposal Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 2.8 2.2 9.5 25.7 71.4 21.0 89.2 97.5 90.3 74.3 28.6 77.0 ‐21.6 ‐14.4 ‐9.0 ‐4.1 11.6 2.3 ‐34.3 ‐52.8 ‐53.2 ‐35.8 276.4 100.0 2,012 3,215 3,406 2,474 ‐19,045 ‐1,271 1,915.3 139.3 47.9 15.6 ‐28.7 ‐7.4 2.8 4.5 4.9 4.2 ‐16.5 0.0 2.9 7.3 13.2 21.3 55.2 100.0 21.3 13.0 7.6 3.3 ‐8.3 ‐1.8 22.5 22.4 23.5 24.1 20.5 21.9 60.3 77.4 86.6 92.7 97.7 39.7 22.6 13.4 7.3 2.3 1.2 4.9 10.2 26.8 35.6 7.5 22.2 61.8 185.0 104.8 ‐1,022 ‐6,085 ‐21,462 ‐266,527 ‐1,494,257 ‐3.6 ‐14.3 ‐26.8 ‐49.6 ‐54.9 0.6 ‐0.9 ‐3.6 ‐12.6 ‐7.3 15.8 10.7 13.5 15.1 6.9 ‐0.9 ‐3.7 ‐7.4 ‐17.4 ‐21.6 23.3 22.1 20.2 17.7 17.8 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 2 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Pre‐Tax Income After‐Tax Income 6 Federal Tax Burden Percent of Total Percent of Total Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Number (thousands) Percent of Total 36,065 34,713 33,034 30,538 30,666 166,272 21.7 20.9 19.9 18.4 18.4 100.0 9,430 24,668 44,764 76,122 230,715 72,381 2.8 7.1 12.3 19.3 58.8 100.0 105 2,308 7,106 15,834 66,366 17,091 0.1 2.8 8.3 17.0 71.6 100.0 9,325 22,360 37,658 60,288 164,348 55,290 3.7 8.4 13.5 20.0 54.8 100.0 1.1 9.4 15.9 20.8 28.8 23.6 15,414 7,701 6,085 1,466 148 9.3 4.6 3.7 0.9 0.1 115,967 165,716 289,779 1,533,122 6,917,786 14.9 10.6 14.7 18.7 8.5 28,051 42,628 79,971 537,321 2,722,897 15.2 11.6 17.1 27.7 14.2 87,916 123,088 209,807 995,800 4,194,889 14.7 10.3 13.9 15.9 6.8 24.2 25.7 27.6 35.1 39.4 Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Percent of Total Average (dollars) Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0411‐2). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 21.0 Proposal: 0.0 * Less than 0.05 (1) Since we conducted this analysis, the Cain campaign has said tax units could claim a deduction on the individual flat tax to mitigate the effects on households below the poverty level. Despite several requests for clarification, the campaign has not defined clearly how that deduction would work. This analysis therefore does not include a poverty deduction. Including a poverty deduction would reduce taxes for households claiming the deduction but would require either higher tax rates or a broader tax base in order to raise the same amount of revenue as the version of the plan without poverty relief. (Footnote added November 10, 2011) (2) Baseline is 2013 current law. Proposal replaces the individual income tax, corporate income tax, payroll tax and estate tax with presidential candidate Herman Cain's 9‐9‐9 Plan. The fully phased in proposal is evaluated at 2013 income levels and all amounts are expressed in 2013 dollars. For a detailed description of TPC's interpretation of the 9‐9‐9 Plan, see www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/Cain‐9‐9‐9‐plan.cfm. For a description of TPC's current law and current policy baselines, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/T11‐0270 (3) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (4) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2011 dollars): 20% $12,690; 40% $24,714; 60% $41,203; 80% $67,700; 90% $97,816; 95% $138,772; 99% $358,601; 99.9% $1,621,178. (5) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (6) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (7) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0373 Herman Cain's "9‐9‐9" Tax Reform Plan without Poverty Deduction 1 Baseline: Current Law Fully Phased in Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size 2 Detail Table ‐ Single Tax Units Percent of Tax Units 5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income6 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Under the Proposal Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 3.2 2.9 14.7 36.8 77.3 19.2 86.0 96.6 85.1 63.2 22.7 77.2 ‐14.4 ‐10.2 ‐6.8 ‐2.0 14.6 2.0 ‐48.3 ‐71.1 ‐62.0 ‐20.0 301.6 100.0 1,017 1,775 1,917 834 ‐15,349 ‐606 241.0 102.1 35.9 7.1 ‐34.4 ‐7.0 3.8 5.7 5.6 3.0 ‐18.1 0.0 5.2 10.6 17.7 22.9 43.4 100.0 13.6 9.3 5.7 1.5 ‐10.2 ‐1.6 19.3 18.4 21.6 23.1 19.5 20.6 71.4 82.8 84.1 90.3 97.8 28.5 17.2 15.9 9.8 2.2 4.1 8.7 13.2 35.4 46.9 26.9 35.7 70.1 168.8 89.8 ‐2,571 ‐7,481 ‐19,145 ‐226,170 ‐1,316,070 ‐12.2 ‐23.3 ‐33.5 ‐57.4 ‐60.9 ‐0.9 ‐1.9 ‐4.2 ‐11.2 ‐6.0 14.6 8.9 10.5 9.5 4.4 ‐3.1 ‐6.3 ‐9.5 ‐21.9 ‐26.5 22.2 20.8 18.8 16.2 17.0 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 2 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Pre‐Tax Income After‐Tax Income 6 Federal Tax Burden Percent of Total Percent of Total Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Number (thousands) Percent of Total 23,198 19,587 15,802 11,719 9,604 80,622 28.8 24.3 19.6 14.5 11.9 100.0 7,467 19,069 33,699 54,610 150,063 39,043 5.5 11.9 16.9 20.3 45.8 100.0 422 1,739 5,347 11,790 44,630 8,637 1.4 4.9 12.1 19.8 61.6 100.0 7,045 17,329 28,352 42,819 105,433 30,407 6.7 13.9 18.3 20.5 41.3 100.0 5.7 9.1 15.9 21.6 29.7 22.1 5,116 2,332 1,790 365 33 6.4 2.9 2.2 0.5 0.0 83,160 118,552 202,277 1,033,246 4,968,941 13.5 8.8 11.5 12.0 5.3 21,007 32,161 57,181 393,929 2,162,383 15.4 10.8 14.7 20.7 10.4 62,152 86,391 145,096 639,317 2,806,558 13.0 8.2 10.6 9.5 3.8 25.3 27.1 28.3 38.1 43.5 Average (dollars) Percent of Total Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0411‐2). * Less than 0.05 (1) Since we conducted this analysis, the Cain campaign has said tax units could claim a deduction on the individual flat tax to mitigate the effects on households below the poverty level. Despite several requests for clarification, the campaign has not defined clearly how that deduction would work. This analysis therefore does not include a poverty deduction. Including a poverty deduction would reduce taxes for households claiming the deduction but would require either higher tax rates or a broader tax base in order to raise the same amount of revenue as the version of the plan without poverty relief. (Footnote added November 10, 2011) (2) Baseline is 2013 current law. Proposal replaces the individual income tax, corporate income tax, payroll tax and estate tax with presidential candidate Herman Cain's 9‐9‐9 Plan. The fully phased in proposal is evaluated at 2013 income levels and all amounts are expressed in 2013 dollars. For a detailed description of TPC's interpretation of the 9‐9‐9 Plan, see www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/Cain‐9‐9‐9‐plan.cfm. For a description of TPC's current law and current policy baselines, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/T11‐0270 (3) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (4) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2011 dollars): 20% $12,690; 40% $24,714; 60% $41,203; 80% $67,700; 90% $97,816; 95% $138,772; 99% $358,601; 99.9% $1,621,178. (5) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (6) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (7) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0373 Herman Cain's "9‐9‐9" Tax Reform Plan without Poverty Deduction 1 Baseline: Current Law Fully Phased in Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size 2 Detail Table ‐ Married Tax Units Filing Jointly Percent of Tax Units 5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income6 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Under the Proposal Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 3.9 2.0 3.3 16.3 68.3 28.5 90.7 97.9 96.7 83.7 31.7 71.0 ‐28.8 ‐16.8 ‐11.1 ‐5.3 10.8 4.0 ‐7.7 ‐15.2 ‐27.7 ‐26.3 177.1 100.0 4,015 5,256 5,476 3,918 ‐21,085 ‐3,976 5,361.4 138.1 62.0 20.7 ‐27.0 ‐11.9 1.0 2.2 4.5 5.6 ‐13.4 0.0 1.1 3.6 9.8 20.7 64.7 100.0 28.6 15.0 9.4 4.2 ‐7.7 ‐3.0 29.2 25.8 24.5 24.5 20.8 22.1 53.1 74.9 88.0 93.6 97.7 46.8 25.1 12.0 6.4 2.3 0.1 3.9 9.5 24.9 33.4 0.2 12.0 39.8 125.0 70.5 ‐56 ‐5,473 ‐22,760 ‐275,698 ‐1,527,658 ‐0.2 ‐11.5 ‐25.0 ‐47.7 ‐53.4 2.1 0.1 ‐2.8 ‐12.7 ‐7.4 17.4 12.6 16.1 18.6 8.3 0.0 ‐2.9 ‐6.9 ‐16.4 ‐20.6 23.7 22.4 20.6 18.0 17.9 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 2 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Pre‐Tax Income After‐Tax Income 6 Federal Tax Burden Percent of Total Percent of Total Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Number (thousands) Percent of Total 4,398 6,664 11,624 15,415 19,298 57,802 7.6 11.5 20.1 26.7 33.4 100.0 14,027 35,110 58,324 93,246 274,004 132,789 0.8 3.1 8.8 18.7 68.9 100.0 75 3,806 8,836 18,898 78,019 33,359 0.0 1.3 5.3 15.1 78.1 100.0 13,952 31,304 49,488 74,348 195,984 99,430 1.1 3.6 10.0 19.9 65.8 100.0 0.5 10.8 15.2 20.3 28.5 25.1 9,190 5,048 4,018 1,042 106 15.9 8.7 7.0 1.8 0.2 135,542 188,768 331,401 1,686,659 7,429,691 16.2 12.4 17.4 22.9 10.3 32,197 47,791 91,006 578,469 2,859,912 15.4 12.5 19.0 31.3 15.7 103,344 140,977 240,394 1,108,191 4,569,779 16.5 12.4 16.8 20.1 8.4 23.8 25.3 27.5 34.3 38.5 Average (dollars) Percent of Total Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0411‐2). * Less than 0.05 (1) Since we conducted this analysis, the Cain campaign has said tax units could claim a deduction on the individual flat tax to mitigate the effects on households below the poverty level. Despite several requests for clarification, the campaign has not defined clearly how that deduction would work. This analysis therefore does not include a poverty deduction. Including a poverty deduction would reduce taxes for households claiming the deduction but would require either higher tax rates or a broader tax base in order to raise the same amount of revenue as the version of the plan without poverty relief. (Footnote added November 10, 2011) (2) Baseline is 2013 current law. Proposal replaces the individual income tax, corporate income tax, payroll tax and estate tax with presidential candidate Herman Cain's 9‐9‐9 Plan. The fully phased in proposal is evaluated at 2013 income levels and all amounts are expressed in 2013 dollars. For a detailed description of TPC's interpretation of the 9‐9‐9 Plan, see www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/Cain‐9‐9‐9‐plan.cfm. For a description of TPC's current law and current policy baselines, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/T11‐0270 (3) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (4) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2011 dollars): 20% $12,690; 40% $24,714; 60% $41,203; 80% $67,700; 90% $97,816; 95% $138,772; 99% $358,601; 99.9% $1,621,178. (5) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (6) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (7) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0373 Herman Cain's "9‐9‐9" Tax Reform Plan without Poverty Deduction 1 Baseline: Current Law Fully Phased in Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size 2 Detail Table ‐ Head of Household Tax Units Percent of Tax Units 5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income6 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 1.2 0.6 5.9 26.9 74.0 8.4 97.5 99.4 93.9 73.1 26.0 91.0 ‐28.2 ‐18.6 ‐8.6 ‐3.0 8.2 ‐9.5 38.4 50.7 21.2 6.0 ‐16.4 100.0 3,758 5,079 3,512 1,745 ‐10,448 3,190 ‐469.2 215.0 41.1 10.7 ‐21.9 50.5 14.3 13.0 ‐1.6 ‐7.5 ‐18.2 0.0 10.2 24.9 24.5 20.8 19.6 100.0 30.0 17.1 7.1 2.3 ‐6.0 8.0 23.6 25.0 24.5 23.9 21.3 23.8 70.1 81.1 78.5 94.7 97.4 29.9 19.0 21.5 5.3 2.6 2.4 5.2 7.7 25.0 34.6 ‐2.0 ‐1.7 ‐3.5 ‐9.1 ‐5.0 ‐2,005 ‐6,013 ‐15,193 ‐220,176 ‐1,353,710 ‐7.3 ‐15.3 ‐22.3 ‐45.9 ‐52.9 ‐5.4 ‐2.5 ‐3.8 ‐6.4 ‐3.3 8.7 3.2 4.1 3.6 1.5 ‐1.8 ‐3.9 ‐5.7 ‐16.2 ‐20.9 22.9 21.7 19.9 19.0 18.6 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 2 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Pre‐Tax Income After‐Tax Income 6 Federal Tax Burden Percent of Total Percent of Total Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Number (thousands) Percent of Total 8,232 8,034 4,869 2,769 1,263 25,256 32.6 31.8 19.3 11.0 5.0 100.0 12,526 29,745 49,199 75,439 175,207 39,986 10.2 23.7 23.7 20.7 21.9 100.0 ‐801 2,363 8,538 16,282 47,675 6,311 ‐4.1 11.9 26.1 28.3 37.8 100.0 13,327 27,382 40,661 59,157 127,531 33,675 12.9 25.9 23.3 19.3 18.9 100.0 ‐6.4 7.9 17.4 21.6 27.2 15.8 814 230 186 33 3 3.2 0.9 0.7 0.1 0.0 111,657 154,037 266,330 1,361,869 6,471,563 9.0 3.5 4.9 4.5 1.9 27,609 39,378 68,177 479,425 2,558,687 14.1 5.7 7.9 10.1 4.8 84,048 114,659 198,153 882,443 3,912,875 8.0 3.1 4.3 3.5 1.4 24.7 25.6 25.6 35.2 39.5 Average (dollars) Percent of Total Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0411‐2). * Less than 0.05 (1) Since we conducted this analysis, the Cain campaign has said tax units could claim a deduction on the individual flat tax to mitigate the effects on households below the poverty level. Despite several requests for clarification, the campaign has not defined clearly how that deduction would work. This analysis therefore does not include a poverty deduction. Including a poverty deduction would reduce taxes for households claiming the deduction but would require either higher tax rates or a broader tax base in order to raise the same amount of revenue as the version of the plan without poverty relief. (Footnote added November 10, 2011) (2) Baseline is 2013 current law. Proposal replaces the individual income tax, corporate income tax, payroll tax and estate tax with presidential candidate Herman Cain's 9‐9‐9 Plan. The fully phased in proposal is evaluated at 2013 income levels and all amounts are expressed in 2013 dollars. For a detailed description of TPC's interpretation of the 9‐9‐9 Plan, see www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/Cain‐9‐9‐9‐plan.cfm. For a description of TPC's current law and current policy baselines, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/T11‐0270 (3) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (4) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2011 dollars): 20% $12,690; 40% $24,714; 60% $41,203; 80% $67,700; 90% $97,816; 95% $138,772; 99% $358,601; 99.9% $1,621,178. (5) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (6) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (7) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0373 Herman Cain's "9‐9‐9" Tax Reform Plan without Poverty Deduction 1 Baseline: Current Law Fully Phased in Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size 2 Detail Table ‐ Tax Units with Children Percent of Tax Units 5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income6 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Under the Proposal Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 0.7 0.7 4.3 22.2 73.6 18.1 93.1 99.3 95.7 77.8 26.4 80.5 ‐31.7 ‐19.2 ‐9.9 ‐3.8 10.5 ‐0.2 900.1 1,248.6 957.1 579.6 ‐3,593.4 100.0 4,580 5,941 4,908 2,990 ‐22,093 104 ‐416.1 194.8 44.6 13.1 ‐24.9 0.5 4.2 5.8 4.4 2.6 ‐17.0 0.0 3.2 8.8 14.4 23.2 50.3 100.0 34.3 17.5 8.1 3.0 ‐7.4 0.1 26.1 26.5 26.2 25.6 22.3 24.1 62.3 81.0 90.1 96.2 98.3 37.6 19.0 9.9 3.8 1.7 1.2 4.5 9.6 25.2 33.5 ‐118.6 ‐282.7 ‐831.0 ‐2,361.1 ‐1,273.9 ‐1,385 ‐7,327 ‐26,837 ‐317,025 ‐1,860,503 ‐3.5 ‐12.4 ‐23.8 ‐44.7 ‐51.3 ‐0.6 ‐1.4 ‐3.9 ‐11.1 ‐6.0 15.1 9.3 12.3 13.6 5.6 ‐0.9 ‐3.3 ‐6.8 ‐16.1 ‐20.3 24.6 23.4 21.9 20.0 19.3 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 2 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Pre‐Tax Income After‐Tax Income 6 Federal Tax Burden Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Number (thousands) Percent of Total 10,088 10,789 10,009 9,950 8,349 49,418 20.4 21.8 20.3 20.1 16.9 100.0 13,356 33,957 60,740 101,182 298,935 93,026 2.9 8.0 13.2 21.9 54.3 100.0 ‐1,101 3,050 11,001 22,868 88,778 22,303 ‐1.0 3.0 10.0 20.6 67.3 100.0 14,456 30,907 49,739 78,314 210,157 70,723 4.2 9.5 14.2 22.3 50.2 100.0 ‐8.2 9.0 18.1 22.6 29.7 24.0 4,396 1,981 1,589 382 35 8.9 4.0 3.2 0.8 0.1 154,877 221,864 392,402 1,966,324 9,174,185 14.8 9.6 13.6 16.4 7.0 39,479 59,124 112,658 710,074 3,627,809 15.8 10.6 16.3 24.6 11.6 115,399 162,740 279,744 1,256,250 5,546,377 14.5 9.2 12.7 13.7 5.6 25.5 26.7 28.7 36.1 39.5 Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0411‐2). * Less than 0.05 Note: Tax units with children are those claiming an exemption for children at home or away from home. (1) Since we conducted this analysis, the Cain campaign has said tax units could claim a deduction on the individual flat tax to mitigate the effects on households below the poverty level. Despite several requests for clarification, the campaign has not defined clearly how that deduction would work. This analysis therefore does not include a poverty deduction. Including a poverty deduction would reduce taxes for households claiming the deduction but would require either higher tax rates or a broader tax base in order to raise the same amount of revenue as the version of the plan without poverty relief. (Footnote added November 10, 2011) (2) Baseline is 2013 current law. Proposal replaces the individual income tax, corporate income tax, payroll tax and estate tax with presidential candidate Herman Cain's 9‐9‐9 Plan. The fully phased in proposal is evaluated at 2013 income levels and all amounts are expressed in 2013 dollars. For a detailed description of TPC's interpretation of the 9‐9‐9 Plan, see www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/Cain‐9‐9‐9‐plan.cfm. For a description of TPC's current law and current policy baselines, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/T11‐0270 (3) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (4) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2011 dollars): 20% $12,690; 40% $24,714; 60% $41,203; 80% $67,700; 90% $97,816; 95% $138,772; 99% $358,601; 99.9% $1,621,178. (5) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (6) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (7) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 18‐Oct‐11 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T11‐0373 Herman Cain's "9‐9‐9" Tax Reform Plan without Poverty Deduction 1 Baseline: Current Law Fully Phased in Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size 2 Detail Table ‐ Elderly Tax Units Percent of Tax Units 5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After‐Tax Income6 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Under the Proposal Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 2.8 2.3 5.9 15.2 56.8 15.6 92.1 97.6 94.1 84.8 43.2 83.5 ‐12.4 ‐11.4 ‐11.5 ‐7.3 15.7 4.3 ‐7.9 ‐23.8 ‐40.4 ‐31.5 203.4 100.0 1,175 2,269 4,343 4,419 ‐26,391 ‐2,420 1,564.7 619.9 182.2 48.9 ‐40.8 ‐17.0 1.6 5.0 9.0 8.7 ‐24.3 0.0 1.7 5.6 12.8 19.6 60.2 100.0 12.3 11.2 10.8 6.3 ‐11.3 ‐3.4 13.1 13.1 16.8 19.3 16.4 16.7 37.9 61.2 80.9 91.0 98.7 62.1 38.8 19.1 9.0 1.4 ‐0.4 5.6 13.9 34.5 43.4 ‐1.3 13.0 47.4 144.3 78.4 365 ‐6,657 ‐27,305 ‐302,721 ‐1,604,042 1.8 ‐19.7 ‐39.1 ‐60.0 ‐62.2 2.7 ‐0.4 ‐5.5 ‐21.1 ‐11.7 14.6 10.9 15.1 19.7 9.7 0.4 ‐4.4 ‐10.3 ‐21.9 ‐25.6 19.1 17.8 16.0 14.6 15.5 Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 2 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2013 Tax Units5 Cash Income Percentile 3,4 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Pre‐Tax Income After‐Tax Income 6 Federal Tax Burden Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total Average Federal Tax Rate 7 Number (thousands) Percent of Total 5,988 9,396 8,334 6,402 6,913 37,068 16.2 25.4 22.5 17.3 18.7 100.0 9,531 20,198 40,053 69,759 232,751 71,055 2.2 7.2 12.7 17.0 61.1 100.0 75 366 2,383 9,043 64,617 14,265 0.1 0.7 3.8 11.0 84.5 100.0 9,456 19,832 37,669 60,716 168,134 56,790 2.7 8.9 14.9 18.5 55.2 100.0 0.8 1.8 6.0 13.0 27.8 20.1 3,175 1,753 1,557 427 44 8.6 4.7 4.2 1.2 0.1 105,683 152,604 266,474 1,382,440 6,274,992 12.7 10.2 15.8 22.4 10.4 19,828 33,855 69,807 504,551 2,577,217 11.9 11.2 20.6 40.8 21.4 85,855 118,749 196,667 877,888 3,697,775 13.0 9.9 14.6 17.8 7.7 18.8 22.2 26.2 36.5 41.1 Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Average (dollars) Addendum 80‐90 90‐95 95‐99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban‐Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0411‐2). * Less than 0.05 Note: Elderly tax units are those with either head or spouse (if filing jointly) age 65 or older. (1) Since we conducted this analysis, the Cain campaign has said tax units could claim a deduction on the individual flat tax to mitigate the effects on households below the poverty level. Despite several requests for clarification, the campaign has not defined clearly how that deduction would work. This analysis therefore does not include a poverty deduction. Including a poverty deduction would reduce taxes for households claiming the deduction but would require either higher tax rates or a broader tax base in order to raise the same amount of revenue as the version of the plan without poverty relief. (Footnote added November 10, 2011) (2) Baseline is 2013 current law. Proposal replaces the individual income tax, corporate income tax, payroll tax and estate tax with presidential candidate Herman Cain's 9‐9‐9 Plan. The fully phased in proposal is evaluated at 2013 income levels and all amounts are expressed in 2013 dollars. For a detailed description of TPC's interpretation of the 9‐9‐9 Plan, see www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxtopics/Cain‐9‐9‐9‐plan.cfm. For a description of TPC's current law and current policy baselines, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/T11‐0270 (3) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (4) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2011 dollars): 20% $12,690; 40% $24,714; 60% $41,203; 80% $67,700; 90% $97,816; 95% $138,772; 99% $358,601; 99.9% $1,621,178. (5) Includes both filing and non‐filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (6) After‐tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (7) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income.