MANAGEMENT AND SYSTEM OBJECTIVES CONTROLS METHODOLOGY
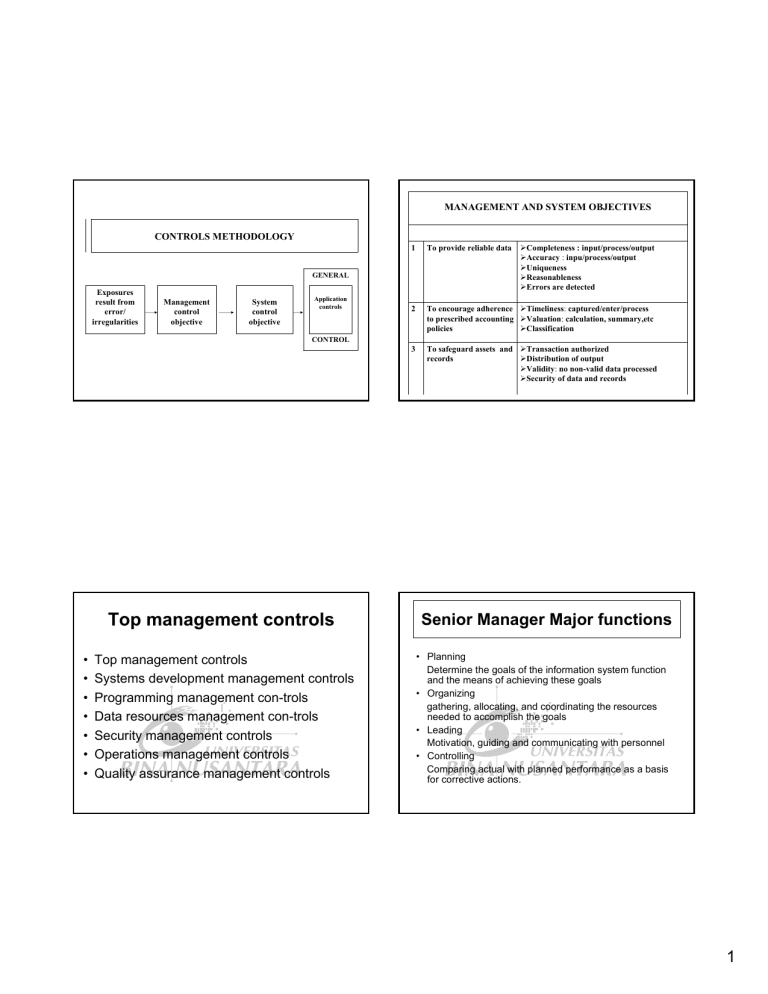
CONTROLS METHODOLOGY
Exposures result from error/ irregularities
Management control objective
System control objective
GENERAL
Application controls
CONTROL
MANAGEMENT AND SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
1 To provide reliable data ¾ Completeness : input/process/output
¾ Accuracy : inpu/process/output
¾ Uniqueness
¾ Reasonableness
¾ Errors are detected
2 To encourage adherence to prescribed accounting policies
¾ Timeliness : captured/enter/process
¾ Valuation : calculation, summary,etc
¾ Classification
3 To safeguard assets and records
¾ Transaction authorized
¾ Distribution of output
¾ Validity : no non-valid data processed
¾ Security of data and records
Top management controls
• Top management controls
• Systems development management controls
• Programming management con-trols
• Data resources management con-trols
• Security management controls
• Operations management controls
• Quality assurance management controls
Senior Manager Major functions
• Planning
Determine the goals of the information system function and the means of achieving these goals
• Organizing gathering, allocating, and coordinating the resources needed to accomplish the goals
• Leading
Motivation, guiding and communicating with personnel
• Controlling
Comparing actual with planned performance as a basis for corrective actions.
1
Manager
Data Processing
Manager
Systems Analysis
Manager
Programming
Manager
Data Entry
Manager
Operations
Production
Control
Development Maintenence Development Maintenence
Computer
Operations
Network
Operations
Librarian
Accounting
Applications
Engineering
Applications
Accounting
Applications
Engineering
Applications
FIGURE 3-4 Traditional data processing organization structure
Vice President
Information System
Manager
IS and IT
Planning
Manager
Information
Tecnology
Services
Manager
Quality
Assurance
Manager
End-User
Support
Manager
Corporate
Systems
Integration
Manager
Contracts and
Outsourcing
Manager
Operations
Facilities
Manger
Administration
Applications
Development
Standards
Development
Data
Administration
Corporate
Modeling
Applications
Maintenance
Database
Administration
FIGURE 3-5 More recent information system department organizational structure
Tugas
• Dari kasus (contoh boleh ditugaskan ke mahasiswa, atau komputerisasi di
Universitas Bina Nusantara), mahasiswa diharapkan dapat melakukan identifikasi kelemahan pengendalian intern ( general controls ) yang ada serta memberikan saran perbaikan .
Pengendalian umum
• Pengendalian organisasi &prosedur
• Pengendalian Dokumentasi
• Pengendalian perangkat keras
• Pengendalian keamanan fisik
• Pengendalian keamanan data dan fasilitas pengolahan
• Pengendalian sistem komunikasi data
2
Insurance
• Insurance sometimes can be used to mitigate losses that arise when disasters eventuate. Policies usually can be obtained to cover the following resources
Operations Management
Controls
• Responsible for the daily running of computer facilities
• Production application systems can accomplish
• Development staff can design, implement and maintain application systems.
Operations Management
Operations Management Responsible for :
• Computer Operations
• Communications Network Control
• Data Preparation and Entry operation
• Production Control
• File Library/Documentation and Program Library
• Help Desk / Technical Support
• Capacity Planning and Performance Monitoring
• Outsourced Operations
Computer Operations
• Operations Controls
Comply to standard operating procedure
• Schedule Controls
Computers are used for authorized purposes
• Maintenance Controls
Preventive and repair maintenance
3
Network Operations
• Wide area network controls
→ Control over : Network control terminals, that provides access to specialized systems software.
• Local area network controls
→ Control over : File servers
Product control
• Receipt/Dispatch Input/Output
• Input is accepted from authorized
• Output provided to authorized, timely basis
• Job Scheduling
• Production jobs are executed
• Management of Service–Level Agreements
• Monitor compliance
• Transfer Pricing / Chargeout Control
• Responsible for billing users
• Acquisition of Computer Consumables
• Responsible for acquiring and managing consumables
File Library
• To ensure that removable storage media are stored securely in a clean environment.
• To ensure that storage media are used only for authorized purposes.
• To maintain storage media in good working order.
• To locate storage media appro-priately at either on–site or off–site facilities.
Documentation and Program
Library
• To maintain the documentation needed to support computer operations and managing the inventory of acquired or licensed software.
• Documentation should be kept up–to –date and be used only by authorized parties.
• Acquired or licensed software should be carefully manages, so it or it’s documentation is not lost or stolen, illegal copies of the software are not made, and use of the software complies with the terms and conditions of the licensing agreement and suitable backup is maintained
4
Help Desk / Technical Support
• To assist end users
• To provide technical support for production systems by assisting with problem resolution.
• To function effectively and efficiently, it must be staffed by competent and trustworthy personnel and be supported by a logging and reporting mechanism to help manage users queries and complaints.
Capacity Planning/Performance
Monitoring
• To ensure that systems are executing efficiently, an acceptable response time or turnaround time is being achieved, and an acceptable level of uptime is occuring.
• Performance statistics is used to determine :
• Unauthorized activities are occuring.
• Systems performance is acceptable.
• More hardware and software resources are needed.
Management of Outsourced
Operations
• On going evaluation of the financial viability of the outsourcing vendor.
• Ensuring compliance with the outsourcing contract’s term and conditions.
• Ensuring the on going reliability of controls in the outsourcing vendor’s operations.
• Maintaining procedures for disaster recovery with the outsourcing vendor .
QUALITY ASSURANCE
– Quality assurance management controls
– Pentingnya peranan quality assurance (QA)
– Kwalifikasi QA
– Fungsi QA
– Problem rekruitmen QA
– QA dan system development
– Hubungan QA audit internal dan audit eksternal indipenden
5
Motivations Toward The QA Role
• Increasing organizations are producing Safety–Critical
Systems.
• Users more demanding in the quality
• Organizations are undertaking more ambitious information systems projects that have more stringent quality requirements.
• Organizations are more concerned about their liabilities if they produce and sell defective software.
• Poor control over the production, implementation, operation and maintenance of software can be costly
• Improving the quality of software is part of a worldwide trend among organization to improve the quality of the goods and services they sell
Quality Assurance Personnel
Perform 6 Major Functions
• Develop quality goals for the information systems function overall and to assist in the development of quality goals for specific information systems.
• Develop, promulgate, and maintain information system standards.
• Monitoring compliance with standards
• Identify areas for improvement
• Report to management
• Regular reports on compliance with general/specific standards.
• Train all other information systems personnel
Programming Management
Controls
Objectives
• To produce or acquire and to implement high quality programs.
• High quality programs :
• Perform their functions correctly and completely.
• Have a high-quality user interface.
• Work efficiently.
• Well designed and well documented.
• Easy to maintain.
• Robust under abnormal conditions.
Pengendalian Aplikasi
• Pengendalian Aplikasi ialah sistem atau mekanisme yang didesain untuk mendeteksi kemungkinan kesalahan/ kelalaian atau penyalahgunaan, dan aturan itu hanya berla-ku khusus untuk sistem aplikasi tertentu saja.
• Misalnya cek-konsistensi antara Nomor-Kartu-
ATM dengan PIN untuk sistem aplikasi penarikan uang tunai bank dari ATM. Sistem lain mungkin tidak perlu PIN
6
Input Controls
• Yaitu mekanisme yang didesain untuk mendeteksi agar tidak ada data salah atau disalahgunakan, yang masuk ke file komputer.
• Pada tahap penangkapan data pada pengisian dokumen input (data capturing)
• Pada tahap pemasukan data (data entry) maupun pengecekan terprogram ( data validation )
Pengendalian proses
• Processing logic check
• Run-to-run check
• File and program check
• Audit trail linkage
Pengendalian Hasil keluaran
• Mekanisme yang didesain dengan tujuan agar informasi komputer sampai kepada yang berhak, tepat sasaran, tepat waktu, dan akurat
(tidak salah data).
• Keluaran akurat dan sesuai dengan yang dibutuhkan
• Keluaran tepat sasaran kepada yang berhak
• Keluaran sesuai jadwal waktu atau saat diperlukan
Pengendalian Data/ File/
Database
• Access controls
• Application/ program controls
• Cryptographic controls
• File handling controls
• Audit-trail xontrols
• Existence controls
7
Studi Kasus
Anggap suatu Tim Auditor mencoba mengidentifikasi sistem pengendalian intern suatu perusahaan (contoh: prosedur nonton bioskop) :
• Pemisahan tugas kasir dengan petugas penjaga pintu
• Pemegang karcis yang belum dijual adalah manajer
• Semua petugas memakai seragam.
• Karcis bernomor tercetak (pre-numbered ) dan kode
Dinas Pajak DKI
• Laporan kasir pada akhir jam kerja malam itu..
• Adanya petugas khusus pencatatan pembukuan
• Pemeriksaan fisik atas roll film
• Verifikasi oleh pihak ketiga (Dinas Pajak)
8