Initial IPX Configuration and Troubleshooting on Contents Introduction
advertisement

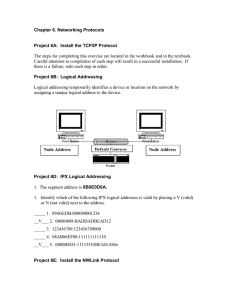
Initial IPX Configuration and Troubleshooting on Cisco Router and Novell Netware Server Document ID: 19165 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Related Information Introduction This document outlines the steps necessary to successfully configure a Cisco router to communicate with a locally attached (Ethernet or Token Ring) Netware server in an effort to route IPX. The general configuration steps are as follows: 1. Determine the desired IPX network number for the local segment. 2. Configure IPX routing on the router. 3. Configure the local routed interface for the correct IPX network number and encapsulation (frame type). Before You Begin Conventions For more information on document conventions, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions. Prerequisites There are no specific prerequisites for this document. Components Used This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions. The information presented in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If you are working in a live network, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command before using it. Configure In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document. Note: To find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the IOS Command Lookup tool Network Diagram This document uses the network setup shown in the diagram below. Configurations This document uses the configurations shown below. 1. Configure IPX routing on the router. 2. Configure the router interface and Novell server IPX network number. Configure IPX routing on the router Router#config t Router(config)#ipx routing Router(config)#exit Router# Note: After issuing the ipx routing command in configuration mode on your router, you may get the following error message: % Invalid input detected at '^' marker. If you get this message, the software image running on your router does not support IPX. Upgrade your router with the software image that supports IPX routing. !−−− Verify the IPX servers and IPX routes on the router. Router#show ipx servers <no output> Router#show ipx route Codes: C − Connected primary network, c − Connected secondary network S − Static, F − Floating static, L − Local (internal), W − IPXWAN R − RIP, E − EIGRP, N − NLSP, X − External, A − Aggregate s − seconds, u − uses, U − Per−user static/Unknown, H − Hold−down 0 Total IPX routes. Up to 1 parallel paths and 16 hops allowed. No default route known. Router#show IPX interface brief Interface IPX Network Encapsulation Status IPX State Ethernet0 unassigned not config'd up n/a Serial0 unassigned not config'd administratively down n/a Serial1 unassigned not config'd administratively down n/a At this point, IPX routing is enabled. However, no routes or servers are showing up. The router interface that connects to the Netware servers segment needs to be configured with an IPX network address. It is essential that the router interface IPX network number match the local Netware server external IPX network address. The next configuration shows what happens if a fake IPX network address for the router interface Ethernet 0 is created. Configure the router interface and Novell server IPX network number !−−− The IPX address is assigned to the interface. Router#config t Router(config)#interface ethernet 0 Router(config−if)#IPX network 123 Router#show IPX interface brief Interface Ethernet0 Serial0 Serial1 IPX Network Encapsulation Status IPX State 123 NOVELL−ETHER up [up] unassigned not config'd administratively down n/a unassigned not config'd administratively down n/a !−−− The IPX address 123 shows up as a directly connected route. Router#show ipx route Codes: C − Connected primary network, c − Connected secondary network S − Static, F − Floating static, L − Local (internal), W − IPXWAN R − RIP, E − EIGRP, N − NLSP, X − External, A − Aggregate s − seconds, u − uses, U − Per−user static/Unknown, H − Hold−down 1 Total IPX routes. Up to 1 parallel paths and 16 hops allowed. No default route known. C 123 (NOVELL−ETHER), Et0 !−−− Although the IPX address is configured, the !−−− router does not show any SAPs/servers. Router#show IPX servers <no output> At this point, the Novel server will log console messages indicating that there is a network addressing mismatch. The routers Ethernet interface must match the local Netware servers external IPX network number and frame type. Refer to the following document for an explanation on the difference between a NetWare servers internal and external IPX network numbers: Understanding Internal and External Network Numbers on Novell Server. The servers external IPX network(s) can be easily determined by accessing the Netware server and issuing the command config. This command can be issued via the servers console or rconsole utility. Note: There are two IPX networks bound to the servers NIC. IPX external network number 00000333 is bound via frame type 802.3, and IPX external network number 00000222 is bound via frame type 802.2 Note: Refer to the following document for details on Novell encapsulation (frame type) and IPX encapsulation naming conventions: Novell Encapsulation and IPX Encapsulation Naming Conventions. The Cisco default IPX frame type is 802.3 (encapsulation novell−ether) . The Cisco default IPX frame type is 802.3 (encapsulation novell−ether). !−−− Configure this command under the !−−− interface connecting to the router. Router(config−if)#IPX network 333 encapsulation novell−ether Note: encapsulation novell−ether is the default command. Therefore, it is not necessary to issue the ipx network command. It is also not necessary to add the leading zeros in the IPX network address !−−− With this servers current configuration, we could alternatively !−−− use IPX network 00000222 and frame type 802.2, as shown below. Router#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#interface ethernet 0 Router(config−if)#IPX network 222 encapsulation ? arpa IPX Ethernet_II hdlc HDLC on serial links novell−ether IPX Ethernet_802.3 novell−fddi IPX FDDI RAW sap IEEE 802.2 on Ethernet, FDDI, Token Ring snap IEEE 802.2 SNAP on Ethernet, Token Ring, and FDDI Router(config−if)#ipx network 222 encapsulation sap Router#show running−config interface e0 interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.1.44 255.255.255.0 ipx network 222 encapsulation SAP no cdp enable end Router# !−−− The show ipx routecommand now displays the updated !−−− IPX network configuration. The encapsulation designator in !−−− the route now shows SAP. Router#show ipx route Codes: C − Connected primary network, c − Connected secondary network S − Static, F − Floating static, L − Local (internal), W − IPXWAN R − RIP, E − EIGRP, N − NLSP, X − External, A − Aggregate s − seconds, u − uses, U − Per−user static/Unknown, H − Hold−down 1 Total IPX routes. Up to 1 parallel paths and 16 hops allowed. No default route known. C 222 (SAP), Et0 !−−− The show ipx servers command now displays !−−− the local server. Router#show ipx servers Codes: S − Static, P − Periodic, E − EIGRP, N − NLSP, H − Holddown, + = detail U − Per−user static 5 Total IPX Servers Table ordering is based on routing and server info P P P P P Type 4 107 26B 278 64E Name LS1 LS1 LANSWITCHING_________ LANSWITCHING_________ ES1!!!!!!!!!!!!A5569B Net Address Port 3C0124BD.0000.0000.0001:0451 3C0124BD.0000.0000.0001:8104 3C0124BD.0000.0000.0001:0005 3C0124BD.0000.0000.0001:4006 1.0000.0000.0001:4000 Route Hops Itf 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 It is possible to route for multiple IPX networks on the same segment. It is necessary to associate each network with a different encapsulation type as referenced above. For example, we will add a new server, LS2, to the Ethernet that requires a different IPX network (444). This will require us to configure a second IPX network statement on Ethernet 0, specifying the correct encapsulation (novell−ether, 802.3) and the trailing keyword secondary. Router(config)#interface ethernet 0 Router(config−if)#ipx network 444 encapsulation ? arpa IPX Ethernet_II hdlc HDLC on serial links novell−ether IPX Ethernet_802.3 novell−fddi IPX FDDI RAW sap IEEE 802.2 on Ethernet, FDDI, Token Ring snap IEEE 802.2 SNAP on Ethernet, Token Ring, and FDDI Router(config−if)#ipx network 444 encapsulation novell−ether ? secondary Make this network a secondary network <cr> Router(config−if)#ipx network 444 encapsulation novell−ether secondary Router(config−if)#end Router#show running−config int e0 interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.1.44 255.255.255.0 ipx network 222 encapsulation SAP ipx network 444 encapsulation NOVELL−ETHER secondary no cdp enable end !−−− Note the new output of the show ipx route !−−− and show ipx servers commands. Router#show Codes: C − S − R − s − ipx route Connected primary network, c − Connected secondary network Static, F − Floating static, L − Local (internal), W − IPXWAN RIP, E − EIGRP, N − NLSP, X − External, A − Aggregate seconds, u − uses, U − Per−user static/Unknown, H − Hold−down 2 Total IPX routes. Up to 1 parallel paths and 16 hops allowed. No default route known. C c 222 (SAP), 444 (NOVELL−ETHER), Et0 Et0 Router#show ipx servers Codes: S − Static, P − Periodic, E − EIGRP, N − NLSP, H − Holddown, + = detail U − Per−user static 9 Total IPX Servers Table ordering is based on routing and server info P P P P P P P P Type 4 107 26B 278 4 107 26B 278 Name LS1 LS1 LANSWITCHING_________ LANSWITCHING_________ LS2 LS2 LANSWITCHING_________ LANSWITCHING_________ Net Address Port 3C0124BD.0000.0000.0001:0451 3C0124BD.0000.0000.0001:8104 3C0124BD.0000.0000.0001:0005 3C0124BD.0000.0000.0001:4006 3C7E85D0.0000.0000.0001:0451 3C7E85D0.0000.0000.0001:8104 3C7E85D0.0000.0000.0001:0005 3C7E85D0.0000.0000.0001:4006 Route Hops Itf 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 2/01 1 Et0 If it is appropriate to change the Novell servers external IPX address, use the inetcfg utility. The console or rconsole command is load inetcfg. Use the graphics below for further examples. Select Bindings and press Enter. Select the desired entry. Make the desired changes and follow the prompts to save and exit. Down and restart the server, or issue the reinitialize system command for the change to take effect: Verify There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration. Troubleshoot There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration. Related Information • Cisco IOS AppleTalk and Novell IPX Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 • Novell / IPX (Novell Internetwork Packet Exchange) Routing Support Page • Technical Support & Documentation − Cisco Systems Contacts & Feedback | Help | Site Map © 2014 − 2015 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions | Privacy Statement | Cookie Policy | Trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. Updated: Sep 01, 2005 Document ID: 19165