Pertemuan < 23 > Government Regulation Chapter 17 Matakuliah

Matakuliah
Tahun
Versi
: J0434 / Ekonomi Managerial
: 01 September 2005
: revisi
Pertemuan < 23 >
Government Regulation
Chapter 17
Learning Outcomes
Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : menganalisis mengenai regulasi pemerintah, bentuk organisasi dan rancangan mekanisme
(C4)
Outline Materi
• Government Regulation
• Market Performance, Market Conduct, and
Market Structure
• Condition of Entry
• Market Concentration
Government Regulation
• Corporations are legal entities which exist only because governments allow them to exist.
• Governments impose many restrictions on firms: mergers, patents, licensing, or subsidies.
• The stated intention of governments is set restrictions that promote social welfare, but they sometimes benefit particular groups or individuals.
2002South-Western Publishing
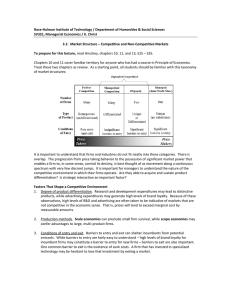
Market Performance, Market Conduct, and Market Structure
Market basic supply and demand conditions
Feedback
Effects
MARKET STRUCTURE
MARKET CONDUCT
MARKET PERFORMANCE
Good Market Performance
Depends on:
• Efficient resource allocation
• Technologically progressive
• Promote full employment
• Equitable distribution of income
Market Conduct
• Pricing behavior
• Product policy
• Sales promotion and advertising
• R&D and innovation strategies
• Legal tactics with regard to entry
Market Structure
• Seller and buyer concentration in a market. With one buyer we have monopsony power of buyers.
• Product differentiation . A market structure of highly differentiated products may be monopolistically competitive.
• Conditions surrounding entry conditions .
The ease of entry and exit are market structure determinants.
Condition of Entry open
1. Demand conditions.
2. Control over input supplies.
3. Legal barriers.
4. Scale Economies.
5. Large capital requirements
6. Technological barriers. closed
Contestable Markets
• Economists have thought that structure influences conduct and performance in an industry .
– This is the central paradigm in the economic field known as industrial organization.
• The idea of contestable markets is applied in markets with scale economies.
– A perfectly contestable market has many
"potential entrants" with the same cost functions as the incumbent firms.
– They enter or not depending on the incumbent's price, which causes the incumbent firms to set prices equal to marginal costs
Market Concentration
• The market or industry concentration ratio sum the market shares of the largest 4, 8, 20, 50 firms.
– A four-firm concentration ratio (4CR) of 80 says that the top for firms comprise 80% of the sales in the industry.
• Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) is:
HHI =
S i
2 , which is the sum of the squares of the market shares of all firms in the industry.
• With small market shares, HHI is small. With large market shares, HHI is large.
• If two firms with 50% market shares each HHI = 50 2 +50 2 =
5,000. With 100 firms of 1% each, HHI only 100.
Summary
• Corporations are legal entities which exist only because governments allow them to exist.
• Governments impose many restrictions on firms: mergers, patents, licensing, or subsidies.
• The stated intention of governments is set restrictions that promote social welfare, but they sometimes benefit particular groups or individuals.