exploring transformations of parent functions
advertisement

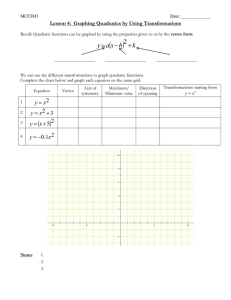
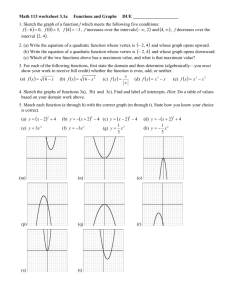
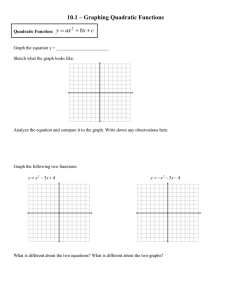
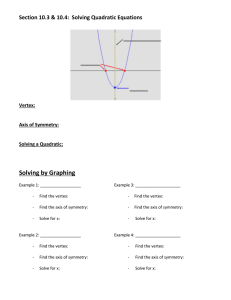
MCR3U1 U2L6 EXPLORING TRANSFORMATIONS (of the Parent Functions) PART A ~ REVIEW OF TRANSFORMATIONS (QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS) Sketch the graph of y = x2: y ordinate differences: the differences in the y-coordinates V(0,0) OD: 1, 3, 5, … x The graph of y = x2 can be transformed as follows: 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝑎(𝑥 − 𝑑)2 + 𝑐 vertical stretch (|a| > 1) vertical compression (0 < |a| < 1) reflection (x-axis) (a < 0) Example horizontal translation (+) move left (–) move right vertical translation (+) move up (–) move down vertex: (d,c) axis of symmetry: x = d max (a < 0) or min (a > 0) value: y = c Describe the transformations that have occurred to 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 to obtain the function 𝑓(𝑥) = −3(𝑥 − 2)2 + 5. MCR3U1 U2L6 Example Sketch each of the following functions: a) 𝑓(𝑥) = 2(𝑥 − 3)2 − 5 vertex: ____________________ axis of symmetry: ____________________ direction of opening: ____________________ max/min value: ____________________ range: ____________________ y x y 1 b) 𝑓(𝑥) = − (𝑥 + 1)2 + 3 2 vertex: ____________________ axis of symmetry: ____________________ direction of opening: ____________________ max/min value: ____________________ range: ____________________ Example a) xx Write an equation for each of the following quadratic functions: HT left 6 units VT up 2 units VC by a factor of ½ reflected in the x–axis b) HOMEWORK: Sketch a graph of each of the following quadratic functions: a) 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 4)2 1 d) 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 + 2 2 b) 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 + 3)2 − 4 e) 𝑓(𝑥) = −3(𝑥 − 2)2 c) 𝑓(𝑥) = 2(𝑥 − 3)2 + 1 f) 𝑓(𝑥) = −(𝑥 + 1)2 − 2 MCR3U1 U2L6 PART B ~ REVIEW OF THE FIVE PARENT FUNCTIONS LINEAR FUNCTION 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 y QUADRATIC FUNCTION 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 2 y x RECIPROCAL FUNCTION 1 𝑓(𝑥) = y 𝑥 ABSOLUTE VALUE FUNCTION 𝑓(𝑥) = | 𝑥 | y x SQUARE ROOT FUNCTION 𝑓(𝑥) = √𝑥 x y x x