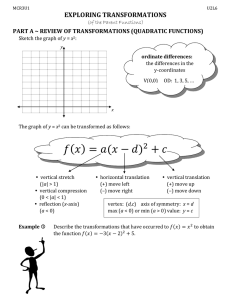
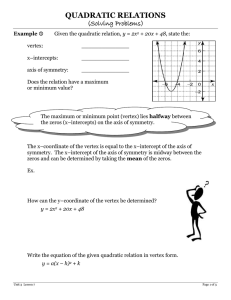
Document 14470952
advertisement
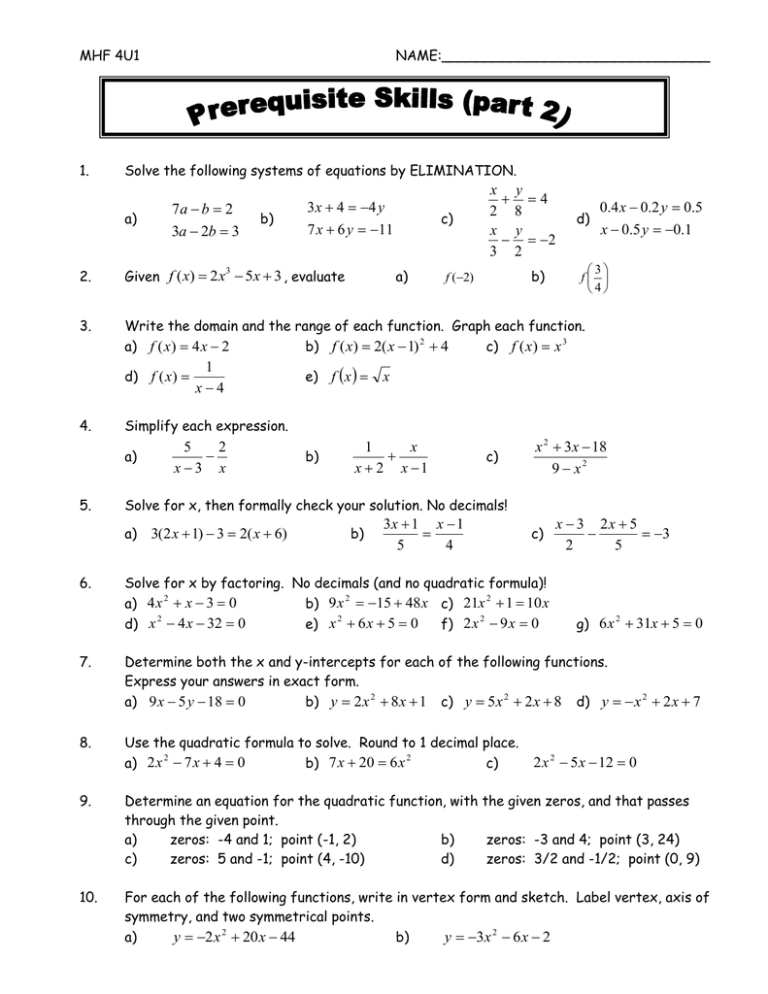
MHF 4U1 1. NAME:_______________________________ Solve the following systems of equations by ELIMINATION. a) 7a b 2 3a 2b 3 b) 3 x 4 4 y 7 x 6 y 11 c) x 2 x 3 y 4 8 y 2 2 d) 3 f 4 2. 3 Given f ( x) 2 x 5x 3 , evaluate 3. Write the domain and the range of each function. Graph each function. a) f ( x) 4 x 2 b) f ( x) 2( x 1) 2 4 c) f ( x) x 3 d) f ( x ) 4. x 5 2 x3 x b) 1 x x 2 x 1 c) x 2 3x 18 9 x2 Solve for x, then formally check your solution. No decimals! a) 6. e) f x b) f (2) Simplify each expression. a) 5. 1 x4 a) 0.4 x 0.2 y 0.5 x 0.5 y 0.1 3(2 x 1) 3 2( x 6) b) 3x 1 x 1 5 4 c) Solve for x by factoring. No decimals (and no quadratic formula)! a) 4 x 2 x 3 0 b) 9 x 2 15 48 x c) 21x 2 1 10 x d) x 2 4 x 32 0 e) x 2 6 x 5 0 f) 2 x 2 9 x 0 x 3 2x 5 3 2 5 g) 6 x 2 31x 5 0 7. Determine both the x and y-intercepts for each of the following functions. Express your answers in exact form. a) 9 x 5 y 18 0 b) y 2 x 2 8 x 1 c) y 5 x 2 2 x 8 d) y x 2 2 x 7 8. Use the quadratic formula to solve. Round to 1 decimal place. a) 2 x 2 7 x 4 0 b) 7 x 20 6 x 2 c) 2 x 2 5 x 12 0 9. Determine an equation for the quadratic function, with the given zeros, and that passes through the given point. a) zeros: -4 and 1; point (-1, 2) b) zeros: -3 and 4; point (3, 24) c) zeros: 5 and -1; point (4, -10) d) zeros: 3/2 and -1/2; point (0, 9) 10. For each of the following functions, write in vertex form and sketch. Label vertex, axis of symmetry, and two symmetrical points. a) b) y 2 x 2 20 x 44 y 3x 2 6 x 2 Answers 1 15 ,b 11 11 1. a) a 2. a) -3 3. a) x Ry R 1 2 b) x 2, y b) 3x 6 x( x 3) b) 5. a) x 3 b) 6. a) 1, 3 4 b) x 2 3x 1 ( x 2)( x 1) x c) 9 7 c) c) 1 1 , 7 3 g) -5, d) 8, -4 1 6 8. a) x 0.7 or x 2.8 b) x 1.3 or x 2.5 9. a) y ( x 4)( x 1) 1 3 c) y 2( x 1)( x 5) b) y 4( x 3)( x 4) 10. a) b) x 5 c) no x-intercepts ; y 8 a) x 2, y x Ry R c) ( x 6) x3 4 14 , y 1 2 d) x 1 2 2 , y 7 7. no solution e) x R x 0 y R y 0 1 ,5 3 9 f) 0, 2 e) -5, -1 b) x R y R y 4 a) d) x 6, y 8 3 32 d) x R, x 4 y R y 0 4. c) 18 5 b) x d) y 3(2 x 1)( 2 x 3) y 2( x 5) 2 6 ; vertex (5,6) ; axis of symmetry x 5 ; points (4, 4) & (6, 4) y 3( x 1) 2 1 ; vertex (-1, 1) ; axis of symmetry x 1 ; points (-2, -2) & (0, -2) a) b) 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 -2 -4 -6 -8 -10 4 6 8 10 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 -2 -4 -6 -8 -10 4 6 8 10