Procedure to Answer 5 Marks Questions
advertisement

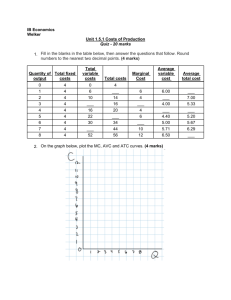
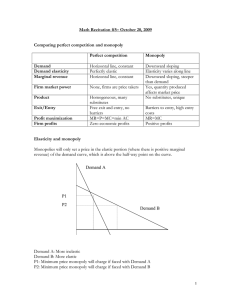
Procedure to Answer 5 Marks Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Add graph or diagram if necessary. Explain with examples wherever possible. Ensure you have a proper start and conclusion to your answers. Add tables wherever necessary. There must be a flow between each sentence. Random, yet meaningful sentences can cause you to lose marks if they are not connected to one another. 6. Make sure there is clear demarcation between each question for 5 marks. Note: 1. It isn’t necessary that you should write 1 page for each 5 marks question. According to PU board, the answer must have at least 5 sentences. 2. In 5 marks questions, your knowledge is tested. 3. The following questions (next page) are the only ones according to the blue print which can be asked for 5 marks. Micro-Economics Introduction to Micro Economics 1. Explain the main types of economic system 2. Is economics positive or normative? Discuss. 3. Explain the various limitations of microeconomics. Theory of Consumer Behavior 1. 2. 3. 4. What are the differences between cardinal and ordinal approach to utility analysis? Distinguish between total utility and marginal utility with the help of example. Explain the concept of budget line and budget set with the help of an example. Explain any five properties of indifference curves. Demand Analysis 1. 2. 3. 4. Why does the demand curve slope downwards? Explain How does the demand curve shift? Explain with diagram. Explain the factors determining the price elasticity of demand. What is income elasticity? Calculate income elasticity of demand when income of a consumer increases from Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 12,000 and demand for rice increases from 30 to 40 kg. Production and Cost 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain the concepts of TP, AP and MP. Discuss various types of short-run costs. Explain long run cost with the help of diagram. Explain various economies and diseconomies of scale. Perfect Competition 1. AR and MR curves of a firm in perfect competition take shape of a horizontal line. Explain this with a diagram. 2. Explain the average revenue and marginal revenue of a firm. 3. Explain diagrammatically, the total revenue, average revenue and marginal revenue of a perfect competitive market. 4. Derive the long run supply curve of a firm. 5. Explain the law of supply with the help of a schedule and diagram. Imperfect Competition 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Explain the features of a monopoly. Draw the demand curve of a monopoly market. What is total revenue? Draw a rough sketch of total revenue curve of a monopoly firm. Write down the features of monopolistic competition. What is oligopoly market? Write down the characteristics of oligopoly market. Macro-Economics Introduction to Macro Economics 1. Explain the circumstances for the emergence of macro-economic study. 2. ‘Although macro-economic has gained maximum popularity, yet it is not free from limitations.’ Justify this statement. 3. Briefly explain the scope of macro-economics. National Income Accounting 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Describe the circular flow of income in a simple economy. Explain the macroeconomic identities GDP, NDP, GNP and NNP. Write a note on nominal national income, real national income. Explain any five problems in measuring national income. Describe relationship between national income and welfare. Money and Banking 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Explain the primary functions of money. Write a note on the supply of money. Explain the quantitative methods of monetary policy of RBI. Explain the qualitative methods of monetary policy of RBI. Explain the objectives of monetary policy. Explain the primary functions of commercial banks. Consumption and Investment 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain the types of investment. Explain Keynes consumption function. Explain the investment function of Keynes. Briefly explain the concept of multiplier of Keynes. Government Budget and the Economy 1. 2. 3. 4. Mention any four objectives of the government budget. Distinguish between surplus budget and deficit budget. Differentiate between direct and indirect tax. What are the major components of non-plan revenue expenditure of the government in developing countries? 5. What are the uses of the tax system as an instrument of fiscal policy in India? 6. Name any four objectives of fiscal policy. Open Economy 1. Explain the structure of balance of payments. 2. Explain the theories of determination of exchange rate. 3. What are the exchange rate systems?