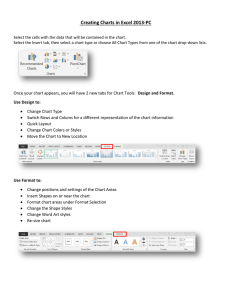
Module 4
Diverse Cognitive Styles in Teams
PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
Five Key Aspects of Work Situations
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
Figure 4.1
4–2
Personal Work Styles
• Four activities that every worker has to do each
day are:
Meeting with others
Generating information
Making decisions
Choosing priorities
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–3
Personal Work Styles (cont’d)
• Meeting with others
This activity also called managing relationships
Two approaches for managing relationships:
Extroverted
Introverted
• Generating information
Two aspects of gathering information:
Sensing
Intuition
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–4
Personal Work Styles (cont’d)
• Making decisions
Two options for dealing with information that has been
gathered:
Thinking
Feeling
• Choosing priorities
Choices must be made in how to allocate time
Priorities are:
Getting more facts (sensing) or ideas (intuition)
Making decisions (thinking or feeling)
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–5
Personality Preferences
Extrovert
——— Establishing Relations
———
Introvert
Sensing
——— Generating Information ———
Intuitive
Thinking
———
Judgmental ———
Making Decisions
Choosing Priorities
———
Feeling
——— Perceptive
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–6
Establishing Relationships:
Extrovert Approach
• Will often think things out by talking them through
• Enjoys meeting other people and often seeks
social gatherings
• Enjoys a variety of tasks and activities
• Stimulated by unanticipated interruptions
• When speaking publicly will often talk impromptu
• Likely to contribute a lot at meetings
• Can be impulsive
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–7
Establishing Relationships:
Introvert Approach
• Prefers to think things out before speaking
• Does not have a high need to meet regularly with
others
• Likes to concentrate on a few tasks at a time
• Dislikes unanticipated interruptions
• When speaking publicly will prepare in depth and
speak to a plan
• May be more quiet at meetings
• More likely to consider things before acting
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–8
Generating Data: Sensing Approach
• Prefers practical problems
• Prefers systems and
methods
• Likes to work with tested
ideas
• Likes to work with real
things
• Patient with routine detail
• Will test established facts
• Pays attention to facts and
detail
• Wants to see detailed
parts
• Likes schedule of working
• Searches for standard
problem-solving approach
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–9
Generating Data: Intuitive Approach
• Enjoys ambiguous
problems
• Gets bored with routine
problems
• Regularly floats new ideas
• Sees possibilities and
implications
• Frequently jumps beyond
the facts
• May get facts wrong
• Has creative vision and
insight
• Follows inspirations
• Searches for the new;
innovation
• Likes complexity and
searches for creative
approaches
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–10
Making Decisions: Thinking Approach
• Tries to establish objective
decision criteria
• Measures decisions
against payoffs
• Can be seen as detached
and cold
• Believes in deciding
according to situation
• Is likely to be flexible
depending on situation
• Negotiates on the
evidence
• Has concern for fairness
based on the rules
• Likes analysis and clarity
• Sets objectives and beliefs
follow
• Task orientated
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–11
Making Decisions: Feeling Approach
• Has personal subjective
decision criteria
• Measures decisions
against beliefs
• Can be seen as
overcommitted to a point
of view
• Believes in deciding on
personal considerations
• Is likely to be nostalgic,
holding to traditional ways
• Negotiates on rights and
wrongs of the issues
• Believes fairness relates
to values and beliefs
• Likes harmony based on
common values
• Objectives emerge from
beliefs
• Principles orientated
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–12
Establishing Priorities:
Judging Approach
• Likes clarity and order
• Concerned with resolving
matters
• Dislikes ambiguity
• Very orderly
• May rush to quick
decisions
• Can be somewhat
inflexible once judgment is
made
• Concerned to work to a
plan
• Emphasizes decision
making over information
getting
• Concerned with
implementation
• Likes to get things
resolved and operating
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–13
Establishing Priorities:
Perceptive Approach
• Enjoys searching and
finding
• May procrastinate in
search of even better
information
• Can tolerate ambiguity
• Concerned to know, not
organized
• Takes in lots of data—
maybe too much
• Open minded and curious
• Works according to the
requirements of the data
• Emphasis on diagnosing
over concluding and
resolving
• Concerned with
knowledge
• Likes to find out as much
as possible before action
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
4–14
Combinations of Preference Alternatives
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
Figure 4.2
4–15
Organizational Preferences
of Different Types
The Press: Mapping Managerial Styles
Copyright © 2005 South-Western. All rights reserved.
Table 4.1
4–16