10.3: Acid-Base Stoichiometry and Titrations Terminology ____________________________________ –
advertisement

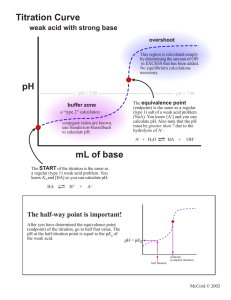
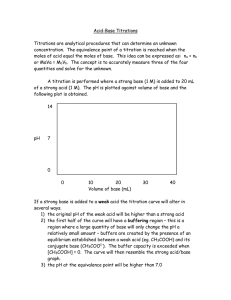
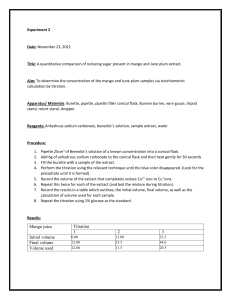
10.3: Acid-Base Stoichiometry and Titrations Terminology • Titration – a laboratory process that is ________________________________________________ ____________________________________ by reacting it with a solution of a known concentration. • Titrant – the ____________________________ during a titration. Concentration is _____________ **In an acid base titration, one solution is _________________, the other solution is ____________. We want to see the exact moment when _________________________ occurs. We use an indicator and gradually add one solution to the other until a ___________________________ colour change is observed. • Equivalence point – the point during a titration at which the ______________________________ ______________________________is stoichiometrically equal to the _______________________ ___________________________________. • • pH changes extremely quickly and sharply! Endpoint – the point during a titration when the ___________________________________. What’s the difference? • EQUIVALENCE POINT is ________________________________ • ENDPOINT is _________________________________ • The goal is to do the titration very carefully and precisely so that your ________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Titration Setup and Results The pH changes VERY drastically at the equivalence point. Just 1 drop of titrant can change the pH from 3 to 11! Titration Labware • Volumetric Flask – used to _______________________________________________ (the solution of _________________ concentration). • Glass funnel – the standard solution is _____________________________________________ by pouring through the funnel. • Burette – a calibrated tube used to dispense very ________________________________________ _________________________________________________ into the flask below. The rate of flow is adjusted with a stopcock near the bottom. • Pipette – used to _________________ precise and accurate volumes of the _________________ _________________________________________ to the Erlenmeyer flask. • Erlenmeyer flask – the ________________________________________________ is placed in this. Titration Procedure • Follow pg 479-480 in textbook Titration Calculations 1. Collect data from at least 3 trials! (see table) 2. Calculate average volume of titrant used (convert to L). 3. Write balanced equation for reaction. Fill in chart for values that you have. 4. Use stoichiometry to determine the concentration of your acid. Trial # Initial burette reading (mL) Final burette reading (mL) Volume of base (titrant) added (mL) 1 2 3