Document 14435824
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mathematics
Lab/Recitation #3 – Quadratic Equations
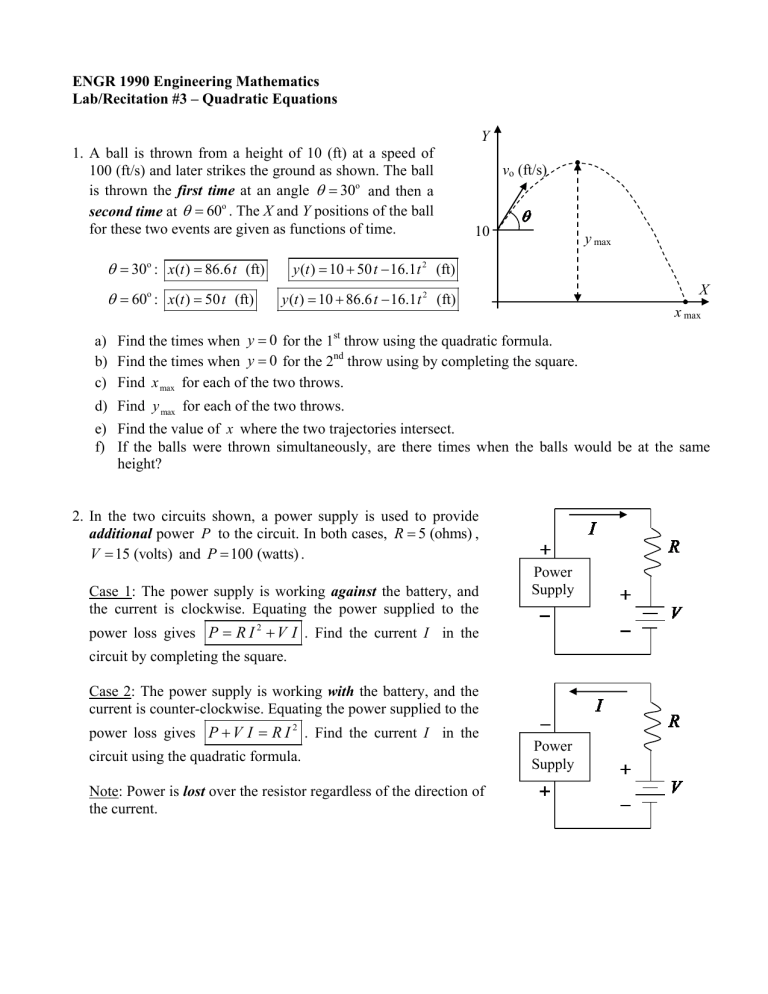
1. A ball is thrown from a height of 10 (ft) at a speed of
100 (ft/s) and later strikes the ground as shown. The ball is thrown the first time at an angle
30 o
and then a second time at
60 o
. The X and Y positions of the ball for these two events are given as functions of time.
30 o
: ( )
86.6 (ft) y t
t
t
2
( ) 10 50 16.1 (ft)
Y
10 v o
(ft/s) y
max
60 o
: ( )
50 (ft) y t
t
t
2
( ) 10 86.6
16.1 (ft)
X x
max a) Find the times when y
0 for the 1 st
throw using the quadratic formula. b) Find the times when y
0 for the 2 nd
throw using by completing the square. c) Find x for each of the two throws. max d) Find y for each of the two throws. max e) Find the value of x where the two trajectories intersect. f) If the balls were thrown simultaneously, are there times when the balls would be at the same height?
2. In the two circuits shown, a power supply is used to provide additional power P to the circuit. In both cases, R
5 (ohms) ,
V
15 (volts) and P
100 (watts) .
Case 1: The power supply is working against the battery, and the current is clockwise. Equating the power supplied to the
Power
Supply power loss gives P
R I
2
V I . Find the current I in the circuit by completing the square.
Case 2: The power supply is working with the battery, and the current is counter-clockwise. Equating the power supplied to the power loss gives P V I
R I
2
. Find the current I in the circuit using the quadratic formula.
Note: Power is lost over the resistor regardless of the direction of the current.
Power
Supply