- appeared, showing not only the ...
advertisement

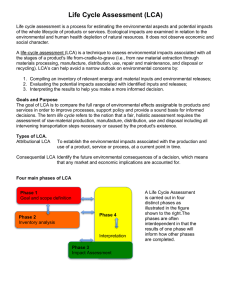
Product Life Cycle Assessment and Environmental Efficiency Assessment Yu-hua Cao 1,2,Guo-zhang Chen 3 ,Guo-ning Qi 1,Xin-jian Gu 1 ,Hong-guang Peng 2 2 1 Institute of Contemporary Manufacturing Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hang zhou , China School of Economics and Management Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, Hang zhou, China 3 Jiang xi Vocational College of Mechanical Electrical Technology ,Nanchang, China (caoyuhua921@126.com) Abstract - With growing human demand for a variety of economic, resources and environment exerting a profound human impact on the environment, in order to deal with economic, resource and environment relationship, life cycle assessment (LCA) and environmental efficiency evaluation are widely used. In order to more accurately conduct the environmental assessment of the product, it is needed to rationally utilize life cycle assessment and environmental efficiency evaluation, put accurate environmental load data into effective use of the evaluation of environmental efficiency, in which environmental efficiency indicators and the performance factor index correctly reflects the value of the product enhancement and mitigation of environmental load. Keywords - LCA, environmental efficiency, performance factor I. INTRODUCTION Project funding: National Science and Technology Support Program(2011BAB02B01 ) Zhejiang Provincial Education Department 2010 annual research projects(Y201018445) Zhejiang Provincial Education Department 2010 annual research projects (Y201119364) Hangzhou Special Information Research Technology Development Plan (Z0100434M07) effect came out combining the economic benefits and the environment benefits then the ecological efficiency II. LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT (LCA) The life cycle assessment first appeared in the US. Though the development of a few years LCA has been the main technique to evaluate the product’s environment factors and potential impact, and also used in product design, product development and improvement, pollution perfection, strategic planning, evaluate and improve the environmental laws, personal and organization’s purchasing, environmental label, the strategy of market development, environmental management system and so on. International organization for standardization (ISO) gives the definition of LCA. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a method developed to evaluate the mass balance of inputs and outputs of systems and to organize and convert those inputs and outputs into environmental themes or categories relative to resource use, human health and ecological areas. LCA contain four parts: Goal and scope definition, Inventory analysis, Impact assessment, and Interpretation as illustrated in the figure 1. Goal and Scope Definition Inventory Analysis Interpretation With the international market issued by the WEEE Directive, ROHS Directive and the EUP Directive, more and more foreign enterprises take the initiative to provide its product life cycle environmental information, such as product carbon footprint, water footprint, product ecology files. At present, all of the environmental engineering research must support the report of the life cycle assessment, according to framework program 7 in EU Science Plan in order to ensure that it will not cause the transfer of the environment problems when solving environment problems. Therefore, life cycle assessment has been the key of research in the field of international sustainable development and the protection of the environment, the main is to research the relationship between the industry activity and the environment impact. Since the human being was in a complex economicenvironment-sociality system, in order to reflect more clearly the relationship of the economic, resources and environment, the new concept named environmental appeared, showing not only the impact of the research object but also evaluation the economic value. Then the way of environment efficiency also become the key to research. At present, the countries and company all over the world are trying their best to find the way of how to use the life cycle assessment to know the product life cycle caused environment carrying capacity in every moment, try to use the data of environment carrying capacity to evaluate the environment efficiency though the environment efficiency index and the performance factor to reflect the improvement of the product or service and the efficiency of the devolution of environment carrying capacity. Impact Assessment Fig.1 LCA framework Applications: -product development and improvement -Strategic Planning -marketing -Public policy formulation At present, the way of inventory analysis is ripe. But the impact assessments are on the stage of study and exploration, and the way to research the interpretation are seldom. So the key problems of life cycle assessment are the definition of product; data changing with different time and space in life cycle impact assessment, data’s reliability problems, and the comprehensive evaluation weights problem and so on. In a word, the life cycle assessment can evaluate all the part of the product life cycle, but it is hard to evaluate the product value. Therefore, the ISO organization promoting the standardization of environmental efficiency and make it helpful to the economic-environment-society. III. ENVIRONMENTAL EFFICIENCY Environmental efficiency based on environment and economic activities of the social system led or realize enterprise management is one of the foundation, it is the product of the environment load determination standards, and is the flexible use of sales strategy management index, it is to improve product or the value of services upward and reduce the effectiveness of the environment load index, meanwhile it is to promote the product or service environment harmonious performance indispensable for communication tools. WBCSD (World Business Council for Sustainable Development) in Earth Summit in Rio held in 1992 proposed the definition of environmental efficiency, which is the ratio of the value of the products or services to the environment load, namely the value generating by unit environment load. The production activities by the environment load is small, the economic value created is larger, and environmental efficiency is higher Japanese industry management association gives the framework of environmental efficiency, as shown in figure 2. From figure 1 and figure 2 we can see the main differences between the LCA and the environmental efficiency that the LCA give the explanation in each stage ,but the environmental efficiency only give the explanation to the result of the environment load and the value evaluation. Goal and scope definition Environmental load Product value Calculation of eco-efficiency results Interpretation Applications: -product development and improvement -strategic planning -budgeting -investment analysis -pubic policy making -marketing -green purchasing -awareness raising Fig.2 Phases of an eco-efficiency assessment Domestic and overseas scholars have researched widely from the different area such as country, region, and enterprise, such as the foreigner Sturm and Landmark’s research[1,2], regional ecological efficiency research[3-5], the business enterprise research[6-9] and industrial research[10-13], but there are a little research on environmental efficiency assessment. With the in-depth study of the environmental efficiency evaluation method at home and abroad, international developed countries has proposed more detailed evaluation index for environmental efficiency. Germany WUPPERTAL research institute suggested that in order to realize the sustainable development of social economy, developed countries should improve the productivity of resources(the unit of the facility resources products, services output) for 10 times in the next 50 years. In 1999 Japan announced the environment white paper, which on building the sustainable development of the economy and society about the direction of industrial activity, introduced the “10 factors” and made a positive activity requirements for the enterprise. From then on many big research institutions and manufacture enterprises, especially the electronic enterprise took part in the discussion and technical development of environmental efficiency and performance and employed them for customers to easily compare conservation of resources of new products with the old. Thought the national development and reform commission jointly with relevant departments drawn up《Evaluation index system of circular economy》, but the system was made up from the macroscopic level and industrial park respectively, rather than the detailed evaluation index; It focused on resources and energy output, consumption of resources, comprehensive utilization and the waste in the emissions, rather than the bad impact on the environment. The implement of environmental impact assessment from technical guideline in 2012 has some guiding index, not including the detailed evaluation index. IV. PRODUCT ENVIRONMENTAL EFFICIENCY ASSESSMENT In order to do the product eco-efficiency assessment better, it is needed to prepare the accurate life cycle assessment resources data and the environment impact data, make full use of environmental efficiency evaluation model analysis, determine product environmental efficiency and performance factor. Environmental efficiency index characterizes the ratio of the value of the product or service improvement to the reducing environmental impact. Therefore environmental efficiency evaluation formula is as follows: Eco efficiency= functional value of the product (1) environmental impact of the product Eco-efficiency= (fundament function)(utility duration) amount of greenhousegas emissions over the life cycle of the product (2) Common factor= eco - efficiency of the evaluated product eco - efficiency of the same type (3) of product for the reference year As the table showed, this article utilized the resources consumption of oil-immersed transformer, which was announced by Japanese manufacturing enterprises. After conducting environmental efficiency evaluation, we got table 2. M E T Table 1 Environment data reference product 2725 kg (1)product weight iron 1790 Kg cuprum 2 kg aluminum 207 kg resin (regeneration) 0 Kg resin(Non-renewable) 0 kg other 726 kg 664 Kg (2)weight of the regeneration material 0 kg (3)weight of recycled components 664 kg (4)weight of the 3R material《(2)+(3)》 Kg (5)resource consumption 2061 《(1)-(4)》 2665 kg (6)Can 3R weight 60 kg (7)Can not 3R weight《 (1)-(6)》 Consumption of electric 4.853 kwh power Chromium weight 74 g evaluated product 3808 kg 2256 Kg 965 kg kg 0 Kg 0 kg 587 kg 905.4 Kg 0 kg 905.4 kg 2902.6 Kg 3733 75 kg kg 2 kwh 0 g B A*B M E T 1990year 1 1 1 RA-T 2006year 1.4 0.426 0 RA-TS (1/ environmental load of evaluated product)/(1/ environmental load of reference product) (evaluated Product value)/( reference product value) (evaluated Product value/ environmental load of evaluated product)/( reference product value/ environmental load of reference product) Product environment load calculation method by the Japanese company simplified the life cycle assessment method. In order to accurately calculate more natural resource consumption and global warming environment load, the life cycle assessment by Japan Seizo Kato in Sweden EPS method based on the development of NETS method, the accurate numerical formula is as follows: n (5) Ecl ( Lf i * x i) i 1 ALi * Ri (6) Lf i pi Ecl: is the environment load value or any industry process of the whole life cycle caused by the environment load value ; Lf i :the basic environment load factor; : i the whole process of the first a processes input or output the raw material and a number of pollutants; p i :considering the bearing capacity of the earth capacity, x the output of the measurement, such as fossil fuel reserves and CO2 emissions, etc; AL :the earth can load value; i R i :the weight factor. V. CONCLUSION Table 2 Eco-efficiency assessment environmental load reference product evaluated product A environment load calculation is according to the formula (4) to calculate. 2 2 2 Product environmental load= M E T (4) Product value 1.732 1 1.463 1.184 1.184 1 1.184 In table 2 the environment load is reflected index. Among them Material (M): the consumption; Energy(E):energy consumption; (T) :hazard substances. Therefore, the by MET resource Toxicity product Through the environmental efficiency evaluation of transformer product manufactured by Japanese enterprises, the transformers’ environmental efficiency and performance factors are calculated to facilitate the consumers understanding products’ performance, and to promote the products or services’ environmental coordination. The research on the eco-efficiency pays attention to the country, region and enterprise in our country, focusing on environment impact, other than the product. In order to operate the economic-environment-society system, we need to draw lessons from Japan’s experience, make suitable environmental efficiency index and performance factor index fitting China’s national conditions. Total life cycle assessment and environmental efficiency evaluation should proceed from product design stage. In order to make products consume the least resources, impact the environment and achieve the highest value in the whole life cycle, the products which can’t meet the requirements should be renewed for the environmental design. REFERENCES [1] Sturm A,Waekernage M. Winners and Losers in Global Competition: Why Eco-efficiency Reinforces Competitiveness[M].West Lafayette USA: Purdue University Press, 2003 [2] L indmarkM, V ikstrmP. Lobar convergence in productivity A distance function app roach to technical change and efficiency improvement [R] .Paper for conference Catching up growth and techno logy transfers in Asia and Western Europe Groningen, 2003( 10) : 17-18. [3] . S eppala J, M elanenM, M aenpaaI. How can the eco- efficiency of a region be measured and monitored [J] Journal of Industrial Ecology, 2005( 9) : 117-130. [4] Ma Yu jun, Huang Xian jin, Xiao Si si,Wang SHu. efficiency of ecological environmental protection based on the model of data envelopment analysis(DEA)-A case study of Suzhou city ,Jiangsu province.Resources and Environment in the Yangtze basin. 2007.16(6):769-774. (in china) [5] Wang Jun neng,Xu Zhen cheng,Hu Xi bang,Peng Xiao chun,Zhou Yang. Analysis of environmental efficiencies and their changes in China based on DEA theory. China Environmental Science. 2010.30 ( 4 ) :565 - 570. ( in china) [6] Björn S. A road to sustainable industry: How to promote resource efficiency in companies [M]. Düsseldorf: WBCSD, 2001. [7] Tyteca D. On the measurement of the environmental performance of firms-A literature review and a productive efficiency perspective [J].Journal of Environmental Management, 1996,46(3):281-308. [8] Pekka J K, Mikulas L. Eco-efficiency of power plants: An extension of data envelopment analysis [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2004,154(2):437-446. [9] Milka K, Timo K. Mearsuring eco-efficiency of production with data envelopment analysis [J]. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 2005,9(4):59-72. [10] Charles C R, Michael J G. Eco-efficiency analysis of an agricultural research complex [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2003,68(3):219-229. [11] Li Li, Han Li yuan. China industrial development’s efficiency evaluation based on energy-economyenvironment DEA [J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2008,28(5):93-95. (in china) [12] LI Jing, RAO Mei xian . China industry's Environmental efficiency and Rule Research[J]. Ecological and Economic, 2011.2:24-28. (in china) [13] Wang Bo, Zhang Qun. life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and environmental efficiency [J]. Beijing university of science and technology journal, 2000.22 ( 5 ) :400 - 403 ( in china) [14] . ZHi Chi Cheng ren . ISO14045 product of environmental efficiency evaluation principles ,requirements and guidance manual[J].Environmental Management. 2010.46(6):1419.(in japan) [15] ZHANG Jian ling. Resources, energy and environmental constraints efficiency evaluation index system[J]Science and Technology Management Research. 2009.11:164-168. (in china) [16] Wang SHou bing, Wang Ru song,Wu Qian hong. A new approach to calculate resource Depletion Potential and its Equivalency Factors in life cycle Assessment [J].FUDAN University Journal of Natural Science. 2001,40(5): 553-557. (in china)