Document 14405747
advertisement
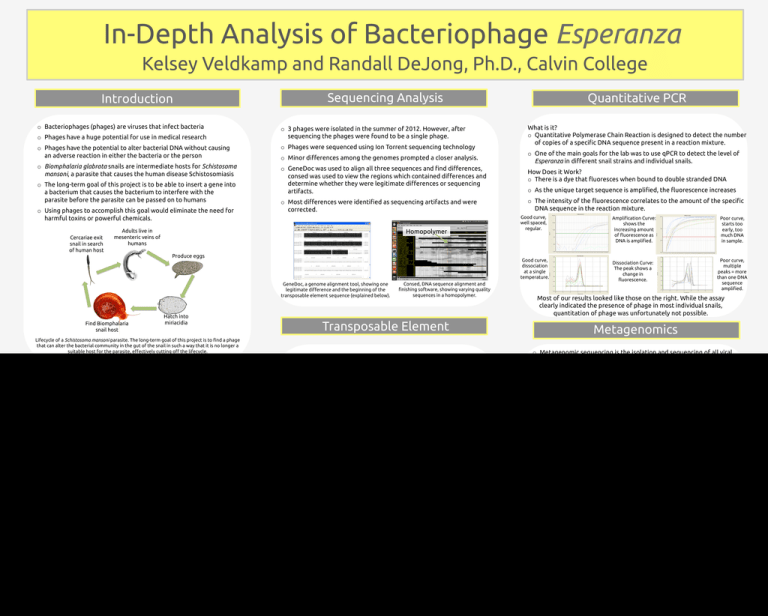
In-Depth Analysis of Bacteriophage Esperanza Kelsey Veldkamp and Randall DeJong, Ph.D., Calvin College Sequencing Analysis Introduction o Bacteriophages (phages) are viruses that infect bacteria o 3 phages were isolated in the summer of 2012. However, after sequencing the phages were found to be a single phage. o Phages have a huge potential for use in medical research o Phages have the potential to alter bacterial DNA without causing an adverse reaction in either the bacteria or the person o Phages were sequenced using Ion Torrent sequencing technology o Biomphalaria glabrata snails are intermediate hosts for Schistosoma mansoni, a parasite that causes the human disease Schistosomiasis o GeneDoc was used to align all three sequences and #nd di"erences, consed was used to view the regions which contained di"erences and determine whether they were legitimate di"erences or sequencing artifacts. o Minor di"erences among the genomes prompted a closer analysis. o The long-term goal of this project is to be able to insert a gene into a bacterium that causes the bacterium to interfere with the parasite before the parasite can be passed on to humans o Most di"erences were identi#ed as sequencing artifacts and were corrected. o Using phages to accomplish this goal would eliminate the need for harmful toxins or powerful chemicals. Cercariae exit snail in search of human host Adults live in mesenteric veins of humans Homopolymer What is it? o Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction is designed to detect the number of copies of a speci#c DNA sequence present in a reaction mixture. o One of the main goals for the lab was to use qPCR to detect the level of Esperanza in di"erent snail strains and individual snails. How Does it Work? o There is a dye that $uoresces when bound to double stranded DNA o As the unique target sequence is ampli#ed, the $uorescence increases o The intensity of the $uorescence correlates to the amount of the speci#c DNA sequence in the reaction mixture. Good curve, well spaced, regular. Ampli#cation Curve: shows the increasing amount of $uorescence as DNA is ampli#ed. Poor curve, starts too early, too much DNA in sample. Produce eggs Good curve, dissociation at a single temperature. GeneDoc, a genome alignment tool, showing one legitimate di"erence and the beginning of the transposable element sequence (explained below). Find Biomphalaria snail host Quantitative PCR Hatch into miriacidia Consed, DNA sequence alignment and #nishing software, showing varying quality sequences in a homopolymer. Most of our results looked like those on the right. While the assay clearly indicated the presence of phage in most individual snails, quantitation of phage was unfortunately not possible. Transposable Element Lifecycle of a Schistosoma mansoni parasite. The long-term goal of this project is to #nd a phage that can alter the bacterial community in the gut of the snail in such a way that it is no longer a suitable host for the parasite, e"ectively cutting o" the lifecycle. o DNA Master revealed an extra gene in one copy of the genome o The added gene was a Transposable Element (TE); a sel#sh bit of DNA that is able to move around within and between genomes. Esperanza: A Quick Look Transposable Element o Isolated from Citrobacter sp. and Enterobacter sp. residing in the gut of a Biomphalaria glabrata snail o The genome was sequenced using Ion Torrent technology Poor curve, multiple peaks = more than one DNA sequence ampli#ed. Dissociation Curve: The peak shows a change in $uorescence. Metagenomics o Metagenomic sequencing is the isolation and sequencing of all viral particles in a sample. o Eliminates the need to culture the bacterial hosts to #nd phages o Presents an opportunity to #nd phages whose bacterial hosts are un-cultivatable o The technique uses ultracentrifugation and a CsCl gradient to separate the viral particles by density. o Viral particles at the target density are removed from the tube, and their DNA is isolated and sequenced. o Esperanza has a conventional genome structure, with structural genes grouped at the beginning of the genome. o Genome length: 33.1kb (34.2kb with transposable element) o Contains 50 genes (51 with transposable element) DNA Master showing the 921 bp Transposable Element present in one copy of the Esperanza genome. o Includes 12 genes of unknown function o Has an integrase gene, and therefore is able to incorporate itself into its host’s DNA o Myoviridae phage (has contractile tail) o TE’s typically have direct and inverted repeats in their DNA sequences o We found both types of repeats in our TE. CCCTTGACTGG CTTTGTTGAATAAATC ACCAAAAT GG AGATTTCGGGTAAGTCTCCCCCGTAGCGGGTTGTGTTTTCAGGCAATACGCACGCT TTCAGGCATACCTGCTTTCGTCATTTTGTTCAGCGCTCGTACCAGGCCATAGCCTCCGCAACCTGACCATCGTAGTCACGCAGCGTCAGTGAACCCCCGAACAGCTGTTTTACCCGGTA CATCGCCGTTTCCGCTATCGAGCGACGGTTGTAATCTGTTGTCCATTTCCACCGCGCATTACTCCCGGTCATTCGCTGATTAGCCACTGCACGGTTACGGTCTGCATATTCACCGGGCCA GTAACCCGCACCTTTTCGGGGAGGGATAAGCGCGCTGATTTTCTTACGCCGCAGTTCATCGTGACATAGCCGGGTATCGTAAGCGCCATCGGCGGCGGCTGACCTGATTTTCCGGTGG GTTTGCCGGATTAACCCGGGGAAGGCCTCTGAGTCCGTAACGTTGTTCAGCGACAGGTCAGCGCAGATGATTTCATGTGTTTTACTGTCAACGGCGAGATGCAGCTTACGCCAGATAC GGCGGCGTTCCTGGCCATGCTTTTTGACTTTCCACTCGCCTTCACCGAAGACCTTCAGCCCGGTGGAATCAATTACCAGGTGTGCGATTTCACCCCGGGTGGGCGTTTTGAAACTGAC ATTAACCGACTTTGCCCGCCTGCTGACACAGCTGTAATCCGGGCAGCGTAGCGGAACGTTCATCAGAGAAAAAATGGAATCAATAAAGCCCTGCGCAGCCCGCAGGGTCAGCCTGAA TACGCGTTTAATGACCAGCACAGTAGTGATGGCAAGGTCAGAATAGCGCTGAGGTCTGCCTCGTGAAGAAGGTGTTGCTGACTCATACCAGGCCTGAATAGCTTCATCATCCAGCCAG AAAGTTATGGAGCCACGGTTGATGAGGGCTTTATTGTAGGTGGGCCAGTTGGTGATTTTGAACTTTTGCTTTGCCACGGAACGGTCTGCGTTGTCGGGAAGATACGTGATCTGATCCTT GATTTATTCAACAAAGCCCTTGACTGGTATAAATATTTATACCATTATGTTTTTCAC CAACTCAGCAAAAGTTC EM image of Esperanza taken at Michigan State University Biomphalaria glabrata snail The sequence of the Transposable Element in Esperanza’s genome. The direct repeat is shown with green text and arrows and the inverted repeat is shown with blue text and arrows. The second sequence of the inverted repeat must be complemented and read from right to left in order for it to match. Step 1: Biomphalaria glabrata snails are dissected, and their guts are homogenized. Step 2: The snail gut homogenate is loaded onto a CsCl gradient and spun at very high speeds to separate particles by density. Step 3: The layer with the target density is removed, and the DNA is extracted from those viruses. Step 4: The extracted DNA is then sequenced and analyzed. o Samples are currently being processed for Biomphalaria snails, Helisoma snails, and termites. References & Acknowledgements o Calvin College Biology Department o Michigan State University o Lori Keen o Van Andel Institute o Jansma Family Research Fellowship o Thurber, R. V., Haynes, M., Breitbart, M., Wegley, L., & Rohwer, F. (2009, October 19). Laboratory procedures to generate viral metagenomes. Nature Protocols, 4(4), 470-483





