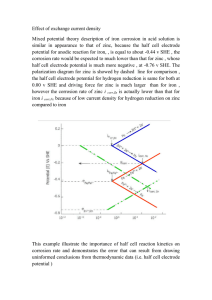
19 Iron, Copper, and Zinc T.S. Dharmarajan, Srinivas Guptha Gunturu, and C.S. Pitchumoni
advertisement

Iron, Copper, and Zinc 19 T.S. Dharmarajan, Srinivas Guptha Gunturu, and C.S. Pitchumoni Questions and Answers 1. Which one of the following has highest bioavailable iron content? a. Chicken liver b. Spirulina c. Spinach d. Almonds Answer: a Heme iron has better bioavailability than non-heme iron; absorption of non-heme iron is subject to food component interactions, such as phytates in greens. Although spirulina has highest non-heme iron content, its bioavailability is less compared to chicken liver heme-iron. Spinach and almonds are low in iron (below 5 mg per 100 g of food). 2. What is the role of hepcidin? a. It promotes iron absorption b. It inhibits iron absorption c. Its role depends on the iron stores in the body d. All of the above Answer: b Hepcidin is a 25-amino acid peptide produced by hepatocytes; production is dependent on iron status, inflammation, hypoxia, and erythropoietin activity; this regulation of iron absorption is termed the “gut–liver axis.” Hepcidin inhibits iron absorption; its level is upregulated in the presence of inflammation and iron overload and is downregulated in the presence of hypoxia, anemia, and erythropoietic activity. 3. An 80-year-old female comes to the clinic for weakness, decreased exercise tolerance, irritability, decreased taste sensation, and loss of appetite. She is obese and has had a gastric bypass procedure. Routine lab: Hb: 8 g/dL, Hct: 24, MCV 70 fL. Her ferrokinetics demonstrate transferrin saturation to be 7%, ferrtin level 12 ng/mL. EGD, colonoscopy, small bowel series, hemoglobin electrophoresis, and sickle screen are negative. What is the best modality of replacing her iron? a. Oral iwron b. Iron sucrose c. Iron dextran d. All of the above Answer: b The patient has iron deficiency anemia. Using Ganzoni’s formula: body weight [kg] × (target hemoglobin-actual hemoglobin) [g/dL] × 2.4 + depot iron [mg], her total iron deficit is [13.5–8 g/dL × 2.4 + 0.5 g] 13.7 g of iron. Oral iron will be poorly absorbed with a history of gastric bypass, and her anemia is severe. In this situation the best option is parenteral iron. Iron dextran has a risk of anaphylactic reactions, life threatening in 1% of the patients exposed, so this may not be an ideal choice today. Intravenous iron sucrose can be given up to 1,000 mg in a 2-week period, and replenish iron stores in weeks. 4. A 70-year-old female with diabetes, hypertension, and systemic lupus erythematosis has anemia. Lab values: Hb: 10 g/dL, Hct: 33%, transferrin saturation is 14%, ferritin: 100 ng/mL. B12 and folate levels are in normal limits. She has history of total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-ophorectomy. She denies any history of menorrhagia or post-menopausal bleeding. Her lupus flares up 2–3 times a year. She had EGD, colonoscopy, and small bowel series, without detecting any source of bleeding. She was started on oral iron preparations 6 months earlier, but there was no improvement. What is the cause of treatment failure? a. Compliance issues b. Chronic inflammation with increase in hepcidin activity, interfering with iron reutilization c. Both d. None of the above C.S. Pitchumoni and T.S. Dharmarajan (eds.), Geriatric Gastroenterology, DOI 10.1007/978-1-4419-1623-5_19, © Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2012 189 190 Answer: b This patient has anemia of chronic disease, as a result of ongoing inflammatory activity, which increases hepcidin production in the liver. The higher hepcidin levels will decrease gut iron absorption and decrease iron reutilization from macrophages leading to less functional iron availability for erythropoiesis. 5. Copper absorption can be decreased by a. Iron salts b. Zinc salts c. Both d. None Answer: c Divalent metals such as copper, zinc, molybdenum, cobalt, cadmium, nickel, and lead are competitively absorbed at divalent metal ion transporter (DMT1) receptor in the enterocytes. When dietary zinc is excessive or large amounts of zinc are administered over prolonged periods, copper deficiency can result. While zinc induces T.S. Dharmarajan et al. intestinal metallothionein (MT), copper has greater affinity for MT than zinc and displaces zinc, getting trapped. Supplemental iron provided as ferrous form (more so than ferric form) also has an inhibitory effect on zinc absorption; the basis is competition for uptake at the receptor level. 6. True statements about zinc deficiency include a. Loop diuretics can cause zinc deficiency b. Chronic oral iron therapy may cause zinc malabsorption c. Zinc deficiency can result in loss of taste or altered taste d. All of the above Answer: d Loop diuretics decrease zinc absorption at the loop of Henle; chronic administration of oral iron supplements in diabetes mellitus can cause zinc loss in the urine, mechanisms not clear. Iron supplementation for prolonged periods will decrease gut zinc absorption through competitive action. Taste disturbances (aguesia and dysguesia) may result from zinc deficiency.