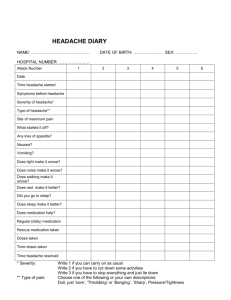
Evaluation and Diagnosis 61 YES
advertisement
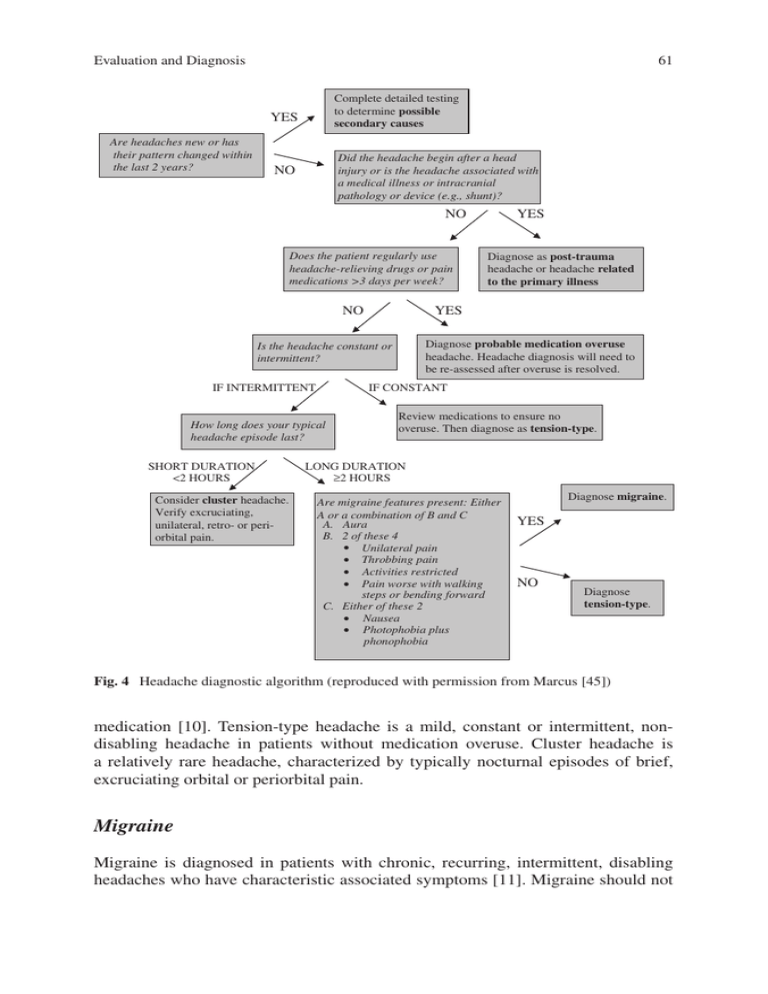
Evaluation and Diagnosis 61 Complete detailed testing to determine possible secondary causes YES Are headaches new or has their pattern changed within the last 2 years? Did the headache begin after a head injury or is the headache associated with a medical illness or intracranial pathology or device (e.g., shunt)? NO NO Does the patient regularly use headache-relieving drugs or pain medications >3 days per week? NO Diagnose probable medication overuse headache. Headache diagnosis will need to be re-assessed after overuse is resolved. IF CONSTANT How long does your typical headache episode last? SHORT DURATION <2 HOURS Consider cluster headache. Verify excruciating, unilateral, retro- or periorbital pain. Diagnose as post-trauma headache or headache related to the primary illness YES Is the headache constant or intermittent? IF INTERMITTENT YES Review medications to ensure no overuse. Then diagnose as tension-type. LONG DURATION ≥2 HOURS Are migraine features present: Either A or a combination of B and C A. Aura B. 2 of these 4 • Unilateral pain • Throbbing pain • Activities restricted • Pain worse with walking steps or bending forward C. Either of these 2 • Nausea • Photophobia plus phonophobia Diagnose migraine. YES NO Diagnose tension-type. Fig. 4 Headache diagnostic algorithm (reproduced with permission from Marcus [45]) medication [10]. Tension-type headache is a mild, constant or intermittent, nondisabling headache in patients without medication overuse. Cluster headache is a relatively rare headache, characterized by typically nocturnal episodes of brief, excruciating orbital or periorbital pain. Migraine Migraine is diagnosed in patients with chronic, recurring, intermittent, disabling headaches who have characteristic associated symptoms [11]. Migraine should not