Types of Writing Information Paragraph (Expository/Explanatory)
advertisement

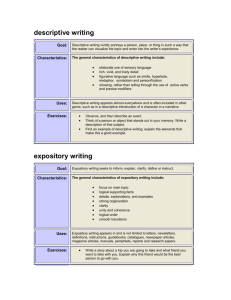
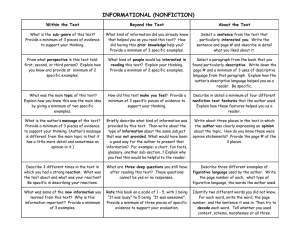
Types of Writing Information Paragraph (Expository/Explanatory) - used to clarify, define, or explain something to the reader that he/she may not know -exposition involves presenting facts, details, and examples to support the main idea and explain it to a specific audience - the writer’s personal opinions and value judgments are not usually part of expository writing - exposition demands more than simply answering who, what, when, where, why, and how - three forms of expository writing: i) explanation – tells how or why something happens, explains the connections between a cause and effect ii) précis – a summary of a written passage – states the main point of the original passage iii) research report – present information from outside sources, facts must first be gathered EXAMPLES: News Report Information Paragraph Summary (explanatory) Research (explanatory) Process Analysis Narrative - the word narrative means storytelling; a narrative is a story based on a series of events - a narrative establishes characters, setting, plot, and theme - a narrative paragraph doesn’t merely tell the readers what happens: it recreates the experience for the reader so they can hear, see, and feel exactly what the experience is like -three forms of narrative writing: i) autobiographical ii) short story (fictional) iii) script (fictional) EXAMPLES: Short Story Autobiography Persuasive - persuasive writing is writing with a purpose, aiming to encourage the reader to support a point of view, idea, or cause - the art of persuasion involves creating logical, clear arguments - persuasive writing is an effective means of getting your message heard - two forms of persuasive writing: i) comparison (to identify similarities and differences) ii) advertisement (meant to sell a product, create an image,or promote a company or brand name) EXAMPLES: Letter to an Editor Opinion Paragraphs Descriptive - the word description means word picture - descriptive writers select details and words that create a single strong impression of a person, event, feeling, or idea - often descriptive passages are found within a longer piece of writing - descriptive writers use figurative language techniques, such as simile or metaphor, and plenty of adjectives to describe a place, person or thing - three forms of descriptive writing: i) poetry ii) profile (short biography focusing on a single aspect of a person’s background or experience) iii) event description (facts and descriptive details combined) EXAMPLES: Profile Event Description Character Sketch