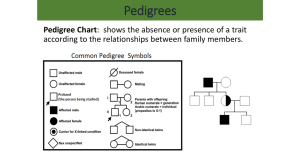
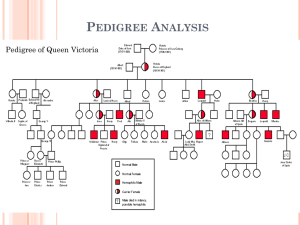
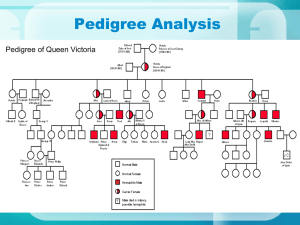
12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica chromosome 1 localization
advertisement

12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: complement component C1q A chain deficiency autosomal dominant 120550 clinical findings of systemic lupus erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. complement component C1s deficiency autosomal dominant 120580 clinical findings of systemic lupus erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. dementia nonspecific type autosomal dominant degenerative dementia. Potentially paternally imprinting. diphenylhydantoin defect in hydroxylation autosomal dominant fetal hydantoin syndrome autosomal recessive no genetic fetal maternal lupus syndrome autosomal dominant neurological disturbance, ataxia, nystagmus, mental blunting after administration of diphenylhydantoin due to defect on its hydroxylation. pre-postnatal growth deficiency, trigonocephaly, midface hypoplasia, nail/terminal phalanges hypoplasia, hypospadias, ocular anomalies, single umbilical artery, other defects. Ganglioneuroblastoma lymphoma tendency. bradycardia detected in utero, heart block, skin discoid lupus, rash in the newborn. leukemia-associated phosphoprotein p18 sporadic undefinable lupus erythematous systemic supposed autosomal dominant supposed multifactorial methylmalonicacidemia homocystinuria 1 autosomal recessive methylmalonicacidemiahomocystinuria 2 autosomal recessive myopathy with lactic acidosis mitochondrial supposed autosomal recessive chromosome 1 localization acute leukemia of various types with increased cellular levels of an 18-kD cytosolic phosphoprotein (p18) mapping on chromosome 1p. fever, weight loss, cutaneous lesions, erythematous butterfly rash of the face, maculopapular rash after sunlight exposure, alopecia, symmetric arthritis, myalgia, renal disease, peripheral neuropathy, immunological disorders; occasionally fetal myocardittis/heart block. first months onset; failure to thrive, neurologic manifestations, spasticity, delirium, seizures, lethargy, megaloblastosis/macrocytic anemia, with normal serum cobalamin and folate concentrations. failure to thrive, neurologic manifestations, spasticity, delirium, seizures, lethargy, megaloblastosis/macrocytic anemia with normal serum cobalamin and folate concentration. weakness, cramps, severe acidosis, mitochondrial abnormalities, sideroblastic anemia. Hum.Mol.Genet.4,162 5-1628,1995 600795 132810 261720 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 559 B.D.Encyclopedia 2112 p.177 Prenat.Diagn.21,143145,2001 151442 152700 601690 277400 277410 255125 chromosome 1p localization acute insuline response modified type autosomal dominant variation in insulin secretion in response to a glucose challenge. Genomics 39,227230,1997 601676 acute myeloid leukemia 2 sporadic acute myeloid leukemia. 600210 Genomics 23,425432,1994 Genus Clinical Database chromosome 1p localization 1 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency medium chain autosomal recessive mitochondrial adenosine monophosphate deaminase1 deficiency. supposed autosomal dominant intermittent hypoglycemia, lethargy, coma, fatty liver, hyperammonemia, sudden death. nonprogressive myopathy, exerciserelated weakness, cramps, hypotonia. adrenal hyperplasia II autosomal recessive agranulocytosis infantile autosomal recessive Albers-Shonberg dominant type autosomal dominant amaurosis congenita Leber II autosomal recessive atrioventricular septal defect multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant Auburger syndrome autosomal dominant Bartter syndrome infantile type autosomal recessive Bartter syndrome type 3 autosomal recessive breast cancer ductal-2 autosomal recessive cardiomyopathy dilated-1A autosomal dominant mitochondrial supposed genetic heterogeneity carnitine palmitoyltransferase II autosomal recessive deficiency lethal form mild virilization, hypospadias, male pseudohermaphroditism, salt loss. congenital neutropenia, severe recurrent infections. bones fragility, dental abscess, osteomyelitis, sandwich appearance of the vertebral bodies, 'bone within bone' appearance of the long bones, high level of acid phosphatase without anemia. keratoconus, pigmentary changes resembling retinitis pigmentosa, mental retardation, neuropsychiatric disorders. isolated failure of separation of the ventricular inlet, inducing cyanosis, congestive failure. Bibliography[OMIM]: 201450 102770 201810 202700 166600 204100 Am.J.Med.Genet. 47,437-438,1993 600309 Genomics 31,9094,1996 601042 Pediat.Nephrol.1,491premature birth, postnatal poliuria, dysmorphic face, hypokalemic alkalosis, 497,1987 occasionally sensorineural deafness. 602522 renal salt-wasting inducing hypotension, Nature Genet.17,171178,1997 hypokalemic alkalosis, hypercalciuria, nephrocalcinosis leading to renal failure, 602023 other clinical data. Prenat.Diagn.19,671673,1999 frequently bilateral multifocal breast 211420 cancer in premenopausal women or in 176705 males. 188825 115200 cardiac arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, conduction defect, sudden death, great variability of age of onset. episodic paroxysmal choreoathetosis, spasticity, ataxia. lethal neonatal form of hypoketotic hypoglycemia, cardiac arrhythmia, lethargy. New Eng.J.Med. 325.1862-1864,1991 600649 115665 cataract congenital Volkmann type X-linked dominant congenital cataract.Eye isolated anomalies. cataract posterior polar autosomal dominant ceroid lipofuscinosis infantile Finnish type autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth motor sensory neuropathy IIA autosomal dominant complement component C1q A chain deficiency autosomal dominant congenital type of cataract. Occasionally posterior lenticonus. Eye isolated anomaly. first months of age onset; microcephaly, seizures, ataxia, retinal degeneration, optic atrophy, psychomotor decline, loss of speech; pathologic inclusion body. peroneal muscular atrophy, pes cavus, decreased median neve conduction, motor-sensory neuropathy neuronal form. clinical findings of systemic lupus erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. complement component C1q B chain deficiency autosomal dominant 120570 clinical findings of systemic lupus erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. complement component C8 deficiency type I autosomal dominant infections recurrent, meningitis meningococcal. 120950 complement component C8 deficiency type II autosomal dominant recurrent infections, meningitis meningococcal. 120960 Genus Clinical Database chromosome 1p localization 116600 256730 Prenat.Diagn.19,559562,1999 118210 120550 2 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: corneal dystrophy Schnyder type autosomal dominant deafness neurosensorial autosomal dominant-2 autosomal dominant Early life onset. Bilateral corneal central part oval/annular clouding. Sometimes associated with premature corneal arcus and limbal girdle of Vogt. Eye isolated anomaly. noncongenital sensorineural deafness. deafness progressive high tone autosomal dominant neural type genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive dihydropyrimidineautosomal recessive dehydrogenase deficiency Ehlers-Danlos VI-A supposed autosomal recessive Ehlers-Danlos VI-B supposed autosomal recessive Ehlers-Danlos VI-C supposed autosomal recessive elliptocytosis-1 autosomal dominant enolase deficiency autosomal dominant epiphyseal dysplasia multiple 2 autosomal dominant erythrokeratodermia variabilis autosomal dominant Freeman syndrome autosomal recessive fucosidosis I autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database high frequencies hearing loss. unusual severe reaction to fluorouracil administration, stomatitis, leucopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, ataxia, other neurologic symptoms. severe scoliosis, recurrent joint dislocations, stretchable skin, floppiness amyotonic-like, premature rupture of fetal membranes, ocular manifestations including choroidoretinal changes, absent hydroxylysine, low lysylhydroxylase activity. severe scoliosis, recurrent joint dislocations, stretchable skin, floppiness, amyotonic-like premature rupture of fetal membranes, ocular manifestation including choroidoretinal changes, normal hydroxylysine, low lysyl hydroxylase activity. severe scoliosis, recurrent joint dislocations, stretchable skin, floppiness amyotonic-like, premature rupture of fetal membranes, ocular manifestations including choroidoretinal changes, normal hydroxylysine, normal lysyl hydroxylase activity. mild-severe chronic anemia, hemolysis, splenomegaly, childhood/infancy onset, poikilocytic erythrocytes. spherocytosis with mild or absent hemolysis. knee and ankle pain in infancy.Prominent joints, epiphyseal changes involving mainly the knees, without deformities of the spine and chest. infancy early, clyhdhood onset, sharply outlined geographical areas of erythrokeratodermia, symmetric hyperkeratotic plaques resembling psoriasis or pityriasis rubra pilaris, sparing the trunk, hypertrichosis, hyperpigmentation, erythema, varying from timme to time and in site. psychotic symptoms, catatonia, catalepsy, hallucinations, vascular thrombosis without skeletal/ocular hallmarks of homocystinuria disease. progresive cerebral degeneration in the first year, weakness, hypotonia, spastic quadriplegia, thick skin, abundant sweating, cardiomegaly, sodium and chloride increased in sweat, gallbladder function defects, corneal cloudiness, other ocular defects, lummbar kyphosis. chromosome 1p localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 121800 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.239 Genomics 41,7074,1997 600101 124800 274270 225400 225400 225400 130500 172430 Am.J.Hum.Genet.55,6 78-684,1994 600204 133200 236250 230000 3 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: fucosidosis II Inheritance: Synthesis: autosomal recessive psychomotor retardation, angiokeratomas, dwarfism, coarse face resemblig mucopolysaccharidoses, spasticity, contractures, peripheral neuropathy, choroidoretinal changes, corneal clouding, amyotrophy, skeletal anomaly, respiratory infections, thickened skiin. hepatomegaly, vomit, failure to thrive, mental retardation, deafness, aminoaciduria in the severe form, asymptomatic in the mild form. congenital glaucoma. galactose epimerase deficiency autosomal recessive glaucoma primary infantile B autosomal recessive glycogenosis III autosomal recessive hydroxymethyl-glutaricaciduria autosomal recessive mitochondrial hypophosphatasia 1 congenital autosomal recessive hypophosphatasia 2 childhood type autosomal recessive hypophosphatasia adult type autosomal dominant leukemia acute T-cell lymphocytic supposed multifactorial undefinable supposed autosomal dominant supposed multifactorial autosomal recessive macular degeneration senile maple syrup urine disease 2 melanoma malignant supposed autosomal dominant undefinable myopathy metabolic carnitine mitochondrial palmitoyltransferase deficiency supposed autosomal recessive I myopathy metabolic carnitine autosomal recessive palmitoyltransferase deficiency mitochondrial II Genus Clinical Database massive hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, muscle weakness, wasting, bleeding tendency, ketoacidosis, short stature. impressive hypoglycemia, hypotonia, convulsions, dehydration, coma, lethargy, cerebral atrophy, infections, other clinical findings, nonketotic acidosis. Leucine metabolism defects. bone formation defects, almost complete lack of mineralization, intrauterin fractures, increased urinary phosphatides. Bibliography[OMIM]: 230000 230350 Hum.Molec.Genet.5,11 99-1203,1996 600975 232400 246450 241500 Prenat.Diagn.19,755757,1999 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 392 241510 failure to thrive, irritability, hypotonia, severe skeletal deformity, mineralization defects of metaphyses and skull, premature loss of deciduous teeth, occasionally nephrocalcinosis, phosphoethanolaminuria. 146300 premature loss of teeth, bowed legs resembling rickets, beaten-copper appearance of skull, paraspinous ligaments calcification. 187040 infantile acute lymphocytic leukemia. macular degeneration late onset, familial. Eye isolated anomaly. 153800 clinical features similar to MSUD1, due to deficiency of E2 protein subunit (transacylase or aryltransferase). cutaneous melanoma, developing in congenital giant nevocellular nevus. 248610 adult onset; myopathy with cramps and myoglobinuria due to deficiency of carnitine palmitoyl transferase II in muscle and leukocytes, with normal CPT I activity. 255110 Genomics 22,243244,1994 600134 155600 190020 116806 123829 attacks of myoglobinuria, muscular pain, 255120 weakness. chromosome 1p localization 4 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: neuroblastoma supposed autosomal recessive 256700 600613 paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis sporadic suprarenal-adrenal medulla/posteromediastinal mass with calcifications, hypertension, fever, sweating, abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, other cutaneous-neurovisceral findings, characteristic laboratory data. Occasionally it occurs prenatally. encephalomyelitis, sensory neuropathy associated with small-cell lung cancer. pheochromocytoma autosomal dominant isolated adrenal medullary tumor, tachycardia, sweating, hypertension, albuminuria, renal artery stenosis. bullous lesions on the sun-exposed areas, ulcerations, scarring, scleroderma-like lesions, liver disease, hemosiderosis, hepatocarcinoma/autoimmune diseases tendency. clinical features similar to the porphyria cutanea tarda familial. 171300 porphyria cutanea tarda familial autosomal dominant porphyria cutanea tarda sporadic supposed autosomal dominant ptosis congenital ptosis epicanthus autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-18 autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-19 autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa-20 autosomal recessive rhabdomyosarcoma-2 autosomal recessive Schwartz-Jampel-Aberfeld syndrome autosomal recessive Stargardt disease-1 autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity Stickler syndrome III autosomal dominant thyrotropin deficiency autosomal recessive urate oxidase deficiency autosomal dominant uridine monophosphate kinase deficiency autosomal recessive Usher IIB syndrome autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database eyelids ptosis at birth. Eye isolated anomaly. Bibliography[OMIM]: 168360 176100 176090 178300 178300 eyelids ptosis with epicanthus. Eye isolated anomaly. autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. 601414 Hum.Molec.Genet.5,11 93-1197,1996 Genomics 40,142childhood onset; night blindness, 146,1997 peripheral scattered pigmentation, choroidal atrophy. Eye isolated anomaly. 601718 180069 severe childhood-onset retinal dystrophy, affecting rod and cone photoreceptors. 268220 childhood onset; embrional tumor involving connective-muscular tissue, J.Med.Genet.20,303with a locus suggested on chromosome 312, 1983 2. 255800 myotonia, skeletal deformities, fixed facial expression, eye anomalies Smith's Recognizable including juvenile cataract. Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 218 degeneration of the macular area with 248200 flecks, central retinitis pigmentosa, onset in first 2 decades. Eye isolated anomaly. Am.J.Hum.Genet. clinical data resembling Stickler 59(suppl.):A17,1996 syndrome I. 275100 symptoms not suggestive of thyroid disease, such as dizziness, weakness, hypometabolism, constipation, angina pectoris, other associated findings. 191540 asymptomatic. Occasionally hyperuricemia with symptoms of gout. 191710 immunodeficiency due to UMPK deficiency. moderate/severe congenital deafness, occasionally cataract, retinitis pigmentosa in late teens. chromosome 1p localization 276905 5 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: Zellweger syndrome 2 autosomal recessive 170995 Prenat.Diagn.20,520521,2000 Zellweger syndrome variant type autosomal recessive dysmorphic face, hypotonia, seizures,hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, heart defects, primary glaucoma, stippled chondral calcification, other clinical data, resembling Zellweger syndrome. type II of Zellweger syndrome, suggested by complementation studies; ocular/neurovisceral changes, stippled chondral calcification. Genomics 34,198204,1996 600759 301220 214110 chromosome 1q localization Alzheimer type 4 autosomal dominant genomic imprinting late onset dementia. amyloidosis cutaneous familial X-linked dominant apolipoprotein A-II defect autosomal dominant arthropathy-camptodactylypericarditis syndrome autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity breast cancer ductal-1 sporadic undefinable in man diarrhea, respiratory infections, photophobia, skin hypopigmentation, ocular changes; in female:skin hyperpigmentation (linear streaks). familial apolipoprotien A-II deficiency, with normal lipid/lipoprotein profiles and without occurrence of coronaropathy. arthropathy, congenital flexion contractures early infancy onset, synovial changes, constrictive pericarditis. frequently bilateral multifocal breast cancer in premenopausal women or in males. cardiomyopathy dilated right ventricular-2 autosomal dominant cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, juvenile sudden death. cardiomyopathy dilated-2 autosomal dominant variability of age of onset; dilated cardiomyopathy, congestive heart failure, sudden death. 107670 208250 211410 176705 188825 Hum.Mol.Genet.4,215 1-2154,1995 600996 Circulation 92,33873389,1995 601494 115195 cardiomyopathy hypertrohpic-2 autosomal dominant hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. cataract zonular pulverulent 1 autosomal dominant Chediak-Higashi syndrome autosomal recessive complement component C3b defect autosomal dominant congenital type of cataract. Eye isolated 116200 anomaly. 214500 hair skin hypopigmentation, choroidoretinal changes, corneal clouding, bacterial infections, anomalous leukocytic granulations formed by fusion of lysosomes. 120620 lupus systemic. complement component C3d defect autosomal dominant infections recurrent pyogenic. complement component H defect autosomal dominant 134370 occasionally vasculitis, thrombocytopenia, IgA nephropathy with proteinuria and renal failure, recurrent infections, depressed serum H (factor beta-1H) and C3 levels. 105120 cranial neuropathy, adult onset corneal dystrophy , thickening of the skin. Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.234 premature closure of sutures, leading to 123100 abnormally shaped head, including brachycephaly, oxycephaly, plagiocephaly,turricephaly/acrocephaly, cloverleaf skull. corneal dystrophy lattice type II autosomal dominant sporadic craniosynostosis type 1 Genus Clinical Database autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive chromosome 1q localization 120650 6 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: deafness neurosensorial autosomal dominant-7 autosomal dominant progressive high-frequencies neurosensorial deafness. Dejerine-Sottas disease autosomal dominant dysautonomia II autosomal recessive elliptocytosis-2 autosomal dominant epidermolysis bullosa atrophicans Herlitz-Pearson type autosomal recessive childhood onset, weakness, areflexia, palpable enlargement of peripheral nerves, stocking-glove sensory loss, cranial nerve involvement, other neurological defects, ataxia, pes cavus, ocular changes. impaired pain/temperature perception, with normal tactile sensitivity, unexplained fever, irritability, truncal anhydrosis, self-mutilation, presence of the fungiform papillae. chronic hemolytic anemia, elliptocytosis due to congenital red cell membrane disorder, Rhesus-unlinked. congenital ulcerations/erosions, congenital hands/feet blisters sparing later; hemidesmosome defects. epidermolysis bullosa Disentis type supposed autosomal recessive adult, atrophic form of the disease with reduced hemidesmosomes. epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica inversa autosomal recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex Koebner type autosomal dominant Factor V deficiency autosomal recessive factor V Leiden defect autosomal recessive factor XIII-B subunit deficiency supposed autosomal recessive fumaric aciduria autosomal recessive mitochondrial Gaucher acute cerebral type supposed autosomal recessive Gaucher juvenile cerebral type supposed autosomal recessive Gaucher juvenile noncerebral type autosomal recessive glaucoma juvenile autosomal dominant autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity glycogenosis IB autosomal recessive blistering/skin atrophy on the trunk, neck, thighs legs, and sparing hands/feet; oral-esophageal-perianal involvement. generalized serous non-scarring blisters, increasing in the warm season, mainly involving soles/toes, fingers, heels; normal teeth and nails, onset at birth or first months of life. mild congenital hemorrhagic disorder, prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time prolonged, reduced level of Factor V. familial thrombosis-bleeding due to activated protein C (APC) resistance. bleeding tendency due to deficiency of B subunit of factor XIII. failure to thrive, hypotonia, mild lactic acidemia, microcephaly, cerebral/liver disease, other defects. hepatosplenomegaly, head retroflexion, strabismus, dysphagia, choking spells, hypertonicity. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. Death during the first 3 years of life. Onset: birth to 14th year of life; hepatosplenomegaly, ataxia, spastic paraplegia, seizures, ophthalmoplegia, dementia. hepatosplenomegaly, pain joints/bones, fractures, aseptic necrosis, scleral pingueculae, abnormal pigmentations. congenital primary glaucoma with late onset, or open/closen angle glaucoma with early onset. Eye isolated anomaly. hypoglycemia, seizures, hepatomegaly, ketoacidosis, growth retardation, bleeding tendency, leucopenia, abcesses tendency. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 1q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: Hum.Molec.Genet.5,11 87-1191,1996 601412 145900 601097 256800 130600 226700 600805 Prenat.Diagn.17,343354,1997 226650 226450 131900 Prenat.Diagn. 20,371377,2000 227400 Nature 369,64-67,1994 134580 136850 230900 Prenat.Diagn.20,340343,2000 231000 230800 137750 232220 7 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: granulomatous disease II autosomal recessive gray platelet syndrome supposed autosomal recessive hemolytic-uremic syndrome supposed autosomal recessive Higgins-Morton-Patronas syndrome autosomal recessive hyperparathyroidism-multiple ossifying jaw fibromas supposed autosomal dominant hyperproreninemia familial autosomal dominant hypertension essential multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant autosomal dominant at birth/young adulthood onset; severe frequent pyogenic infections/granulomas in any organs, osteomyelitis, due to 65kD neutrophil cytosol factor defect. bleeding disorder due to large platelet with few granules, due to marked decrease or absence of platelet-specific alpha-granule proteins. insidious/acute onset, from few months of age to third decade of life, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, acute renal failure, seizures, hypertension, cardiac failure. early childhood onset, severe ataxia, posterior columns of the spinal cord degeneration, achalasia, scoliosis, retinitis pigmentosa. parathyroid enlargement associated with maxillary and mandibular tumors histologically different from the typical 'brown tumors' of hyperparathyroidism. normotensive subjiects with normal plasma renin activities and high levels of prorenin. usually adult onset; primitive, high blood pressure values. hyperthermia malignant susceptibility 5 hyperthyroidism familial autosomal dominant ichthyosis vulgaris autosomal dominant immunoglobulin G receptor I deficiency autosomal dominant Kenny-Caffey syndrome autosomal recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity leukemia acute pre-B-cell transcription factor-1 supposed multifactorial undefinable lupus erythematous systemic supposed autosomal dominant supposed multifactorial lupus nephritis susceptibility autosomal dominant malaria vivax susceptibility no genetic measles susceptibility autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 233710 139090 235400 Neurology 49(6),17171720,1997 145001 NewEngl.J.Med.324,13 05-1311,1991 145500 malignant hyperthermia susceptibility related to a gene located on chromosome 1q. Hum.Molec.Genet.6,95 3-961,1997 601887 hyperthyroidism, due to overstimulation by inappropriate TSH secretion. first months of life onset; fine/white/adherent scales, more prominent at the calves and spares the neck, usually lessen in the summer, occasionally palmar hyperkeratosis, normal steroid sulfatase activity and serum cholesterol sulfate. Associated atopic disease in 50% of affected individuals. asymptomatic familial lack of phagocyte expression of CD64. 145650 acute lymphoblastic leukemia associated with t(1;19) chromosomal translocation. fever, weight loss, cutaneous lesions, erythematous butterfly rash of the face, maculopapular rash after sunlight exposure, alopecia, symmetric arthritis, myalgia, renal disease, peripheral neuropathy, immunological disorders; occasionally fetal myocardittis/heart block. hereditary susceptibility to lupus nephritis. susceptibility to malaria, due to presence of Duffy a or b antigen Fy. rubeola susceptibility due to modified measles virus receptor. chromosome 1q localization 146700 J.Immun.154,28962903,19995 244460 Genomics 54,1318,1998 176310 152700 601690 J.Clin.Invest.97,13481354,1996 110700 120920 8 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Mediterranean fever familial autosomal recessive MEN 2 syndrome autosomal dominant childhood/juvenile onset; recurrent episodes of fever, abdominal/chest pain, peritonitis, pleuritis, associated fingings, occasionally suggesting acute polyarthritis. bilateral pheochromocytoma, multifocal medullary thyroid carcinoma, other clinical data. methionine synthase deficiency autosomal dominant muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal dominant type 1B myopathy nemaline type autosomal dominant autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity nephrotic syndrome Fuchshuber type autosomal recessive paralysis periodic hypokalemic autosomal dominant supposed X-linked recessive Y-limited platelet storage pool deficiency autosomal dominant polycystic kidney medullary type autosomal dominant porphyria variegata autosomal dominant prostate cancer hereditary autosomal dominant pycnodysostosis autosomal recessive pyropoikilocytosis supposed autosomal recessive pyruvate kinase of erythrocyte deficiency autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database mental retardation, megaloblastic anemia, high folate activity. juvenile onset with slow progression; symmetric myopathy in the proximal limb muscles starting in lower-limb; cardiac defects including dilated cardiomyopathy. nonprogressive congenital myopathy, narrow high arched palate, weakness, hypotonia, slender extremities, enlongated expressionless face, cyanosis, kyphosis, other skeletal defects. early childhood onset; idiopathic nephrotic syndrome, resistance to steroid therapy. Bibliography[OMIM]: 249100 171400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 526 156570 Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,8 91-895,1997 161800 Hum.Molec.Genet.4,21 55-2158,1995 600995 juvenile onset; periodic attacks of flaccid 170400 quadriplegia, lasting several hours, 311700 usually in early morning, low serum potassium during attacks. Could be autosomal dominant with reduction in penetrance in females or Y limited (?) in some instances. bleeding diathesis, easy bruising, small 185050 and reduced platelets, due to deficiency of delta-granules/alpha-granules or both. 174000 chronic renal failure, due to corticomedullary/intramedullary cysts, occasionally hematuria, nephronophthisis, pyelonephritis; multiple pyramidal/calyceal calculi with ectatic medullary pyramidal changes. Small kidney by X-ray. Association with red/blond hair. 176200 photosensitivity, skin lesions, vesicles, bullae, erosion, scarring, hypertrichosis, chronic or acute attacks of peripheral/abdominal pain, motor paralysis, seizures, other neurological signs. 176807 early-onset prostate cancer. 601518 600020 265800 osteosclerosis, short distal phalanges, acro-osteolysis with wrinkled skin, dental Smith's Recognizable anomalies, hypodontia, fontanels Patterns of Human delayed closure, clavicle dysplasia, Malformation. 5th fractures, wormian bones, mental Edition pag. 406 retardation, deafness. 266140 hemolytic anemia at birth, microspherocytosis, unusual red cell, thermal sensitivity, spectrin defect. severe nonspherocytic chronic hemolytic 266200 anemia, splenomegaly, reticulocytosis. chromosome 1q localization 9 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: renal cell carcinoma papillary type autosomal dominant hereditary multiple papillary renal cell carcinoma. retinitis pigmentosa-12 autosomal recessive autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa Genomics 22,499504,1994 mapping on chromosoma 1q. 600105 rippling muscle disease-1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity myotonia, muscle hypertrophy/psudohypertrophy/rolling contractions/cramps. Rogers-Porter-Sidbury syndrome autosomal recessive Shy-Drager syndrome supposed autosomal dominant spectrin alpha-subunit defect autosomal dominant spherocytosis type III autosomal recessive T-cell antigen receptor (zeta subunit) deficiency autosomal dominant megaloblastic/sideroblastic anemia responded to thiamine, diabetes mellitus, deafness. orthostatic hypotension, bladder/bowel incontinence, anhidrosis, iris atrophy, amyotrophy, ataxia, rigidity, tremor, dopamine-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. elliptocytosis, congenital hemolytic anemia. severe hemolytic anemia, spherocytosis, spectrin deficiency in red cell membrane. failure to thrive, dirrhoea,respiratory infections. T-cell receptor-CD3 complex defect autosomal dominant thrombophilia due to AT-III deficiency autosomal dominant trimethylaminuria autosomal recessive Usher IIA syndrome autosomal recessive van der Woude syndrome 1 autosomal dominant Vohwinkel syndrome autosomal dominant palmoplantar keratoderma, elbows/knees linear keratoses, congenital deafness. achromatopsia autosomal recessive Crigler-Najjar I disease autosomal recessive epidermolysis bullosa BullNorins type autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant absence of cone function, normal rod function. Eye isolated anomaly. nonhemolytic persisten jaundice, unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, bilirubin encephalopathy, other neurologic sequelae of kernicterus infections. pyelonephrosis due to bilateral ureterovesical junction, stenosis/pyloric atresia, severe diffuse skin lesions. hemolytic anemia, recurrent respiratory infections, diarrhoea, failure to thrive, impaired immune humoral response. increased propensity to venous thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, with embolism at various sites in adulthood; pulmonary embolism. rotting fish odor in areas of active sweating,urine, breath due to excretion of large amounts of TMA. Depression. Severe hypertension after eating cheese. moderate/severe congenital deafness, occasionally cataract, retinitis pigmentosa in late teens. lower lip with depressions/paramedian fistulas or pits, secreting viscous saliva; cleft lip/cleft palate or lip-palate. Bibliography[OMIM]: 179755 Neurology 44,19151920,1994 600332 249270 146500 182860 270970 186780 186780 107300 136131 602079 276901 119300 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 238 124500 chromosome 2 localization Gilbert disease Genus Clinical Database chronic, fluctuating, mild unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, increasing with caloric deprivation or nicotinic acid administration, with normal transaminases. chromosome 2 localization 216900 218800 226730 Prenat.Diagn.20,7075,2000 143500 10 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: glaucoma juvenile open-angle supposed autosomal dominant 137760 Genomics 36,142150,1996 Leigh syndrome FrenchCanadian type autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity Primary glaucoma. Open angles of the anterior chamber inducing glaucoma, due to modified effect of corticosteroids on intraocular pressure. insidious or acute onset under 2years, weight loss, weakness, hypotonia, psychomotor defect, acidosis, optic atrophy, neurological involvement. 220111 chromosome 2p localization acrokeratoelastoidosis autosomal dominant palms /soles nodular yellow plaques. 101850 ACTH deficiency isolated supposed autosomal recessive 201400 Alstrom syndrome autosomal recessive aniridia 1 autosomal dominant Carney syndrome autosomal dominant cataract anterior polar 1 autosomal dominant cystinuria I autosomal recessive deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-9 autosomal recessive adrenocortical insufficiency due to isolated ACTH deficiency, attacks of hypoglycemia. retinal changes, cataract, optic atrophy, deafness, obesity, glucose intolerance, hypogenitalism. total or partial absence of iris. Occasionally, associated cataract and/or mental retardation.Eye isolated anomaly. Wilms tumor tendency. profuse cutaneous pigmented lesions, prominent in the summer months, subcutaneous myxoid neurofibromata resembling von Recklinghausen disease, atrial myxoma, ephelides, nevi, adrenocortical nodular dysplasia, Cushing disease, tumors predisposition. cataract anterior polar. dense white opacities of the central part of the anterior lens capsule.May be associated with other congenotal malformations of the anterior segment of the eye. Eye isolated anomaly. radio-opaque cystine calculi, renal/ureteral colic, hematuria, disuria, urinary tract infections, unconstant short stature, mental retardation, psychiatric disturbance. Normal aminoaciduria in heterozygotes. childhood onset neurosensory deafness. Doyne choroiditis autosomal dominant fetal maternal acute fatty liver autosomal recessive mitochondrial fructosuria autosomal recessive gingival fibromatosis supposed autosomal dominant glaucoma infantile autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database small round white retinal spots (drusen) usually identified after the second decade of life. May induce progressive visual loss. May be the same of choroiditis Hutchinson Tay tipe. Eye isolated anomaly. cardiomyopathy, myopathy, hypotonia, hypoglycemia, seizures, lactic aciduria, sudden death. asymptomatic defect; high blood fructose level after fructose administration, with normal glucose/galactose metabolism. childhood onset; generalized enlargement, involving all of the gengivae. infantile glaucoma. chromosome 2p localization 203800 106200 160980 115650 220100 Hum.Mol.Genet.5,155158,1996 601071 126600 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998, p.130 Am.J.Hum.Genet.58,9 79-988,1996 600890 Pediat.Res.40,393398,1996 229800 135300 Hum.Molec.Genet.6,64 1-647,1997 11 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: glaucoma primary infantile 1A autosomal recessive large ocular globe from intrauterin life. Eye isolated anomaly. gonadal dysgenesis XX autosomal recessive holoprosencephaly 2 autosomal dominant streak gonads resembling Turner syndrome, female external genitalia, normal mullerian development, 46,XX chromosome. Gonadoblastoma dysgerminoma tendency. 157170 mental retardation, microcephaly, cleft lip/palate, hypotelorism, antimongoloid slant, constipation, talipes varus, spinal anomalies, hernias. recurrent hypoglycemia, 143450 cardiomyopathy, seizures, liver damage, muscular atrophy. hydroxyacyl-CoA autosomal recessive dehydrogenase deficiency long mitochondrial chain hypercholesterolemia apo-B100 autosomal dominant defect apolipoprotein B defect; possible premature coronaropathy, angina, atherosclerosis, acanthocytosis. xanthoma tuberosum and tendinosum, ateromatosis, corneal arcus, other findings characteristic of hypercholesterolemia. reduced serum cholesterol and low density lipoprotein, acanthocytosis, unresponsiveness to local anesthesia, intolerance for fats/milk, diarrhea, neuromuscular disorders, ataxia, weakness, slight ocular pigmentary degeneration. 46,XY male, external genitalia resembling feminine in characters, perineal hypospadias with separate urethral and vaginal openings within urogenital sinus. Male limited disease. newborn period onset; prolonged neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, mixedema, hypothermia, bradycardia, respiratory distress, constipation, followed in infancy by macroglossia, hypotonia, dry skin, puffy facies, hoarse cry, mental retardation, other clinical finndings. hyperlipoproteinemia II supposed autosomal dominant hypobetalipoproteinemia supposed autosomal dominant hypospadias perineoscrotal pseudovaginal syndrome autosomal recessive hypothyroidism agoitrus autosomal recessive immunoglobulin kappa chain defect autosomal dominant diarrhea, respiratory infections. Leydig cell hypoplasia supposed autosomal recessive melanoma malignant supposed autosomal dominant undefinable sex reversal, 46,XY with female/ambiguous external genitalia, without female internal organs, occasionally labial fusion and urogenital sinus, palpable testes in inguinal canal. cutaneous melanoma, developing in congenital giant nevocellular nevus. Muir-Torre syndrome supposed autosomal dominant muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2A Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 231300 601771 233300 107730 144400 145950 264600 218700 601843 188450 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 614 147200 233440 Genomics 22,243244,1994 600134 155600 190020 116806 123829 158320 carcinomata of the colon-duodenumlarynx, keratoacanthomata of the face, multiple cutaneous sebaceous neoplasms. 253600 second decade onset; hip/shoulder proximal muscles weakness, difficulty climbing, stairs/holding hands above head, low back pain, occasionally cardiomyopathy/pseudohypertrophy/high serum creatine kinase levels. chromosome 2p localization 12 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2B supposed genetic heterogeneity muscular dystrophy Nonaka type supposed autosomal recessive orofacial cleft 1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity genomic imprinting multifactorial orofacial cleft 2 multifactorial orofacial cleft 2 genomic imprinting multifactorial paraplegia spastic hereditary-3 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity paraplegia spastic hereditary-4 Parkinson disease 3 autosomal dominant puberty precocious male-limited sex-limited, sex influence pulmonary alveolar proteinosis autosomal recessive thyroid hormonogenesis defect autosomal recessive IIA xanthinuria autosomal recessive Bibliography[OMIM]: muscular dystrophy milder than LGMD2A. Childhood onset with variable progression; late facial weakness and joint contractures; occasionally cardiac involvement. early adulthood onset; distal muscles involvement, especially tibialis anterior muscles, rapid clinic progression, typical histologic changes; high creatine kinase levels. complete or incomplete clefts of the upper lip, unilateral or bilateral, including posterior alveolar processes, and anteriorly alae nasi. Potentially paternal imprinting. 253601 complete or incomplete clefts of the upper lip, unilateral or bilateral, including posterior alveolar processes, and anteriorly alae nasi. Potentially paternal imprinting. variable age of onset, progressive spastic paraplegia. Genomics 50,299305,1998 602966 juvenile/adult onset. Weakness, progressive leg spasticity, occasionally sphincter incontinence. essential tremor, progressive akinetorigidity, shuffling gait, speech/language difficulties beginning in adult years. Occasionally, dysautonomia, dementia. sexual precocity in boys, characterized by rapid virilization, advanced spermatogenesis during the first years of age, due to gonadotropin-independent hypertestosteronemia. Male limited disease. respiratory distress due to alveolar obstruction with periodic-acid-Schiffpositive proteinaceous material. hypothyroidism, mental/growth/skeletal retardation, cretinoid facies, dry skin, low serum thyroxine. urinary tract stones tendency. 182601 254130 119530 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 236 182600 Nature Genet.18,262265,1998 602404 176410 265120 274500 278300 chromosome 2q localization acrogeria supposed autosomal recessive albinism oculocutaneous II autosomal recessive Albright osteodystrophy-3 autosomal dominant Alport syndrome recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity autosomal recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis juvenile type aneurysm intracranial Berry type Genus Clinical Database autosomal dominant hands and feet skin atrophy with old appearance, misdiagnosed as the Ehlers-Danlos IV syndrome. decreased skin/hair/eyes pigmentation, nystagmus, photophobia, choroidoretinal defects, iridal dyschromia, tyrosinase positive test. mental retardation, brachydactyly, brachymetacarpia. clinical features of Alport syndrome. juvenile onset; weakness, distal muscular atrophy, spasticity, fasciculations. cerebral aneurysm hereditary. chromosome 2q localization 201200 203200 Am.J.Hum.Genet.56,4 00-407,1995 600430 203780 205100 105800 13 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: abdominal aortic aneurism. 100070 Bjornstad syndrome multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive 262000 brachydactyly E genetic heterogeneity sensory neural hearing loss, alopecia, pili torti, hypogonadism. metacarpal/metatarsal shortening, mild short stature, round face. aortic aneurism abdominal cardiomyopathy dilated right ventricular-4 Bibliography[OMIM]: 113300 602087 Genomics 45,259263,1997 601286 Hum.Molec.Genet.5,69 9-703,1996 Medizinische Genetik 9,16,1997 601847 118800 cataract polymorphic congenital autosomal dominant congenital nonnuclear polymorphic cataract. Eye isolated anomaly. cholestasis progressive familial intrahepatic 2 autosomal recessive infancy onset; progressive intrahepatic cholestasis, intermittent jaundice, choreoathetosis paroxysmal autosomal dominant Cockayne I syndrome autosomal recessive paroxysmal attacks of choreoathetosis, lasting a few minutes and a few times a day, without unconsciousness. cachexia, growth/mental development reduced, loss adipose tissue, retinal degeneration, cataract, choroidoretinal changes, senile appearance, skin photosensitivity. craniofacial-deafness-hand syndrome supposed autosomal dominant desmin defect autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus II noninsulindependent autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus insulindependent 12 autosomal dominant flat face, hypertelorism, absent/small nasal bones with slit-like nares, small maxilla, hand ulnar deviation, sensorineural deafness. heterogenous disease, including distal myopathy late onset, congenital proximal myopathy, cardiomyopathy with ventricular hypertrophy, Mallory bodylike inclusions. late onset diabetes. Polyuria, polydipsia, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, obesity, microvascular complications, including neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, myocardiopathy, alterations in insulin behaviour. insulin-dependent diabetes. diabetes mellitus insulindependent 13 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus, insulin dependent. diabetes mellitus insulindependent 7 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus, insulin dependent. disaccharide intolerance II autosomal recessive disaccharide intolerance III autosomal recessive ectodermal dysplasia Jorgenson type supposed autosomal dominant failure to thrive, dehydration, fermentative diarrhea from birth, induced by lactose ingestion, but not with other carbohydrates. 223100 abdominal bloating, cramping, fermentative diarrhea after milk ingestion, childhood/adult life onset. 129490 mild hypotrichosis, mild hypodontia, reducted sweet. Ehlers Danlos X supposed autosomal recessive Ehlers-Danlos III supposed autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database mild skin changes, characteristic of E-D syndrome, defective collagen-induced platelet aggregation. marked joint hyperextensibility, without skeletal deformity, mild skin manifestations. chromosome 2q localization 216400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 144 122880 125660 601419 Hum.Genet.98,422429,1996 125853 601283 Hum.Mol.Genet.5,107 5-1080,1996 601388 Science 272,18111813,1996 601318 Nature Genet 9,8085,1995 600321 223000 225310 130020 14 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Ehlers-Danlos IV autosomal dominant autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive Ehlers-Danlos IV recessive type autosomal recessive elliptocytosis type 4 autosomal dominant fibromuscular dysplasia of arteries supposed autosomal dominant fibronectine deficiency autosomal dominant hyperammonemia I autosomal recessive ichthyosis lamellar type 2 autosomal recessive immunodeficiency due to selective T-cell defect autosomal recessive Klein-Waardenburg syndrome supposed autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes leukemia T-cell/lymphoma-4 autosomal dominant liver cancer-1 autosomal dominant liver cancer-2 autosomal dominant mesomelic dysplasia Kantaputra type autosomal dominant muscular dystrophy benign congenital supposed autosomal dominant mycobacteriosis familial autosomal recessive myopathy nemaline type autosomal recessive autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity nephronophthisis familial juvenile autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity Oguchi disease autosomal recessive oxalosis I autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 130050 arteries rupture/dissection, bowel perforation, very thin skin easily bruised. arteries rupture/dissection, bowel perforation, very thin skin easily bruised. elliptocytic red cells, hemolytic disease due to red cell membrane skeleton defect. reno-vascular severe hypertension, abdominal bruit, characteristic renal arteries appearance; arterial dissections. keloids at sites of surgery and burns. 225350 110750 135580 Lancet I,473-474,1986 respiratory distress, poor feeding, vomit, 237300 hypotonia, lethargy, pulmonary/intestinal hemorrhages. congenital lamellar ichthyosis. Hum.Molec.Genet.5,55 5-559,1996 601277 severe combined immunodeficiency due 176947 to protein tyrosine kinase deficiency. hypoplasia of musculoskeletal system, flexion contractures, carpal bones fusion, syndactyly, facial/ocular anomalies of Waardenburg syndrome including iridal dyschromia. leukemia with translocation between chromosome 2 and 8. familial primary cancer of the liver. 148820 186860 114550 liver cancer occurring in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. mesomelic dysplasia, bones bowing, carpal and tarsal synostosis. 142380 early childhood onset; slow progression, involving proximal limb muscles, sternocleidomastoid and anterior tibial muscles, without cardiomyopathy; high creatine kinase levels. atypical disseminated BCG infection after newborn inoculation inducing intestinal disturbance, osteomyelitis, macrophage defect. nonprogressive congenital myopathy, weakness, hypotonia, slender extremities, enlongated expressionless face, cyanosis, kyphosis, other skeletal signs. Cysts of 1-15 mm in diameter, located primarily at the corticomedullary junction. Childhood/juvenile onset; anemia, hypertension, chronic renal failure, uremia, symmetrical kidney destruction due to chronic sclerosing tubulo-interstitial nephropathy. stationary nightblindness, peculiar fundus discoloration, modified by dark adaptation. Eye isolated anomaly. progressive, bilateral oxalate urolithiasis, nephrocalcinosis, renal failure in childhood, oxalate external deposits in later stages. 158810 chromosome 2q localization 156232 209950 256030 256100 258100 259900 15 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: protein C deficiency autosomal dominant 176860 pulmonary hypertension primary autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive pyridoxine dependency autosomal recessive rhabdomyosarcoma-2 autosomal recessive syndactyly II autosomal dominant van der Woude syndrome 2 autosomal dominant various age onset from infant to later age; increased risk of lower extremities thrombosis/pulmonary embolism/ throbophlebitis, neonatal purpura fulminans. Occasionally associated PHPV. elevated pressures in the pulmonary artery and right ventricle, without structural anomalies of the heart/great vessels. seizures, prenatal/perinatal age onset, hyperirritability, hyperacusis, feeding difficulties, resistance to anticonvulsant drugs and control of seizures with pyridoxine. childhood onset; embrional tumor involving connective-muscular tissue, with a locus suggested on chromosome 2. syndactyly between 3rd/4th fingers, polydactyly of 4th fingers in the web, postaxial toes polydactyly. van der Woude syndrome Waardenburg I syndrome autosomal dominant deafness, dystopia canthorum, broad nasal bridge, synophrys, heterochromia irides, other ocular defects, white forelock, skin depigmentation. Waardenburg IIA syndrome supposed autosomal dominant 193500 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 248 193510 wrinkly skin syndrome autosomal recessive xanthomatosis cerebrotendinous autosomal recessive xeroderma pigmentosum II autosomal dominant deafness, broad nasal bridge, synophry, heterochromia irides, other ocular defects, white forelock, skin depigmentation, no dystopia canthorum; occasionally megacolon. 278250 present at birth; universal wrinkly hypoelastic skin, prominent venous pattern of the skin, increased palmar/plantar creases, mental retardation, microcephaly, ocular changes, hypotonia, spinal deformity, hip dysplasia, joint hyperextensibility. 213700 achilles tendon xanthomas, cataract, dementia, ataxia, other neurological disorders, atherosclerosis. clinical and cytobiological characteristics 133510 of both XP and Cockayne syndrome. 178600 266100 268220 J.Med.Genet.20,303312, 1983 186000 Hum.Genet.7,5,1994 chromosome 3 localization dementia nonspecific type autosomal dominant degenerative dementia. Potentially paternally imprinting. Hum.Mol.Genet.4,162 5-1628,1995 600795 histidine-rich glycoprotein autosomal dominant 142640 protein S deficiency autosomal dominant Small syndrome supposed autosomal recessive thyrotropin-releasing hormone deficiency autosomal recessive thrombosis recurrent, thrombophilia, embolisms, acute mesenteric infarction.due to prothrombotic effect of histidine-rich glycoprotein. venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism. weakness, mental retardation, myopatic facies, scoliosis, deafness, retinal changes. clinical findings of hypothyroidism, short stature. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 3 localization 176880 216350 275120 16 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: albinism ocular-lentiginesdeafness syndrome autosomal dominant albinism-deafness dominant type supposed autosomal dominant ocular albinism, iridal dyschromia, reduced visual acuity, photophobia, strabismus,choroidoretinal defects, deafness, lentigines. deaf-mutism, hypopigmented cutis without eyes involvement. Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 3 autosomal recessive Barroso syndrome autosomal dominant Bibliography[OMIM]: chromosome 3p localization carboxylase multiple deficiency autosomal recessive late onset cardiomyopathy dilated-2 with conduction defect autosomal dominant cardiomyopathy hypertrophic mid-cavity type 3 autosomal dominant carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency autosomal recessive mitochondrial cataract anterior polar 1 autosomal dominant chondrodysplasia punctata rhizomelic type 1 autosomal recessive chondrodysplasia punctata rhizomelic type 2 autosomal recessive colorectal familial cancer Lynch I supposed autosomal dominant undefinable colorectal familial cancer Lynch II autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database postaxial polydactyly, hypogonadism, obesity, mental retardation, pigmentary retinopathy. Chromosome 3p localization. acanthosis nigricans, diabetes mellitus, severe insulin resistance, hypertension. Gene map Locus: 3p25. seizures, hypotonia, ataxia, deafness, optic atrophy, skin rash, dermatitis, alopecia, organic aciduria, acidosis, lethargy; first weeks/months of age onset. dilated cardiomyopathy associated with conduction defect. variant of cardiac hypertrophy characterized by thickening of the midleft ventricular chamber; associated abnormal skeletal muscle. cardiac failure, weakness, respiratory distress, hepatomegaly, neurologic signs. cataract anterior polar. dense white opacities of the central part of the anterior lens capsule.May be associated with other congenotal malformations of the anterior segment of the eye. Eye isolated anomaly. rhizomelic dwarfism, microcephaly, flat face, cataract, optic atrophy, contractures, ichthyosis, alopecia. rhizomelic dwarfism, microcephaly, flat face, cataract, optic atrophy, contractures, ichthyosis, alopecia. No some biochemical defects typical of the type 1. site-specific colonic cancer changes in bowel habit, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, anemia, weight loss, onset before 40 years. May be the same of Lynch II. Associated endometrial carcinoma/atypical hyperplasia, uterine leiomyosarcoma, renal/bladder carrcinoma, gastric/biliary carcinoma. colonic cancer in association with other familial carcinomas, such as endometrium/ovary/pancreas. May be the same of Lynch I. chromosome 3p localization 103470 103500 Hum.Mol:Genet.3,133 1-1335,1994 600151 Nature 402,880883,1999 604367 601487 253260 J.Clin.Invest. 97,528532,1996 601154 Nature Genet.132,6369,1996 212138 115650 215100 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 390 222765 Prenat.Diagn.19,383385,1999 114500 190020 116806 114400 116806 17 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-6 autosomal recessive neurosensory deafness. epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica Pasini type autosomal dominant epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica pretibial supposed autosomal dominant first week life onset, generalized serous sanguineous blisters, leaving large red atrophic areas on the extremities, involving ears/face/buttocks, oral blistering, dystrophic nails. dermolysys limited to pretibial leg, childhood onset. epidermolysis bullosa Hallopeau-Siemens type autosomal recessive Fanconi pancytopenia type 4 autosomal recessive gangliosidosis GM1-I autosomal recessive glycogenosis IV autosomal recessive hemeralopia rhodopsin-related autosomal dominant HIV infection susceptibility/resistance autosomal recessive hyperglycinemia nonketotic II autosomal recessive Larsen syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive long QT syndrome 3 autosomal dominant abnormal prolungation of QT inducing attacks of syncope, other cardiac disturbance. lung cancer small-cell sporadic Marfan syndrome II autosomal dominant metaphyseal dysplasia Jansen type autosomal dominant small-cell cancer of the lung with precocious metastases. Sensitive to therapies. Occasionally paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis with sensory neuropathy. clinical features of Marfan syndrome, aortic dilatation, sudden death, no ocular abnormalities. dwarfism, metaphyseal dysplasia, contractural deformities, dysmorphic facies. myopathy mitochondrialexternal ophthalmoplegia 2 autosomal dominant mitochondrial Genus Clinical Database severe destructive skin lesions, at birth or in infancy, involving mucosal surfaces, fingers fusion, severe contractures, ocular changes. Fanconi syndrome due to complementation group D. mental/motor delay, seizures, dysmorphism, gingival hyperplasia, cherry red spots, long bones/vertebral anomalies, edema, deafness, other defects. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. cirrhosis, ascites, icterus in infancy, weakness, mental deterioration, neuromuscular abnormal glycogen accumulation. congenital night blindness.Eye isolated anomaly. variation im susceptibility/resistance to virus-1 infection. early infancy onset; mental retardation, hypotonia, seizures, lethargy; hyperglycinemia due to defect in enzyme of the glycine-cleavage system different from NKH1 and NKH3. flat facies with depressed nasal bridge, cleft palate, multiple congenital dislocations, cylindrical-nontapering fingers, multiple carpal ossification centers. myopathy, progressive external ophthalmoplegia. chromosome 3p localization Bibliography[OMIM]: Genome Res.5,305308,1995 600971 131750 Prenat.Diagn.20,618622,2000 131850 226600 227646 230500 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 450 232500 Nature Genet.9,358365,1996 Nature 381,661666,1996 238310 150250 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 286 Hum.Mol.Genet.4,160 3-1607,1995 600163 Prenat.Diagn.19,677680,1999 182280 190020 154705 156400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 386 Am.J.Hum.Genet.58,7 63-769,1996 601226 Prenat.Diagn.20,426431,2000 18 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: olivopontocerebellar III autosomal dominant Pallister-Hall syndrome supposed autosomal dominant ataxia, dysarthria, characteristic retinal changes, infancy/adult onset. hypothalamic hamartoblastoma, acidosis, lethargy, jaundice, ocular defects, hypogonadism, dysmorphism, multiple mouth frenula, imperforate anus, polydactyly. Occasionally increased nuchal translucency and hydrops. pituitary adenoma ACTHsecreting autosomal dominant pseudo-Zellweger syndrome autosomal recessive Refetoff syndrome autosomal recessive renal cell carcinoma-1 autosomal dominant thyroid carcinoma follicular supposed autosomal dominant thyroid hormone resistance autosomal dominant thyrotropin-releasing hormone deficiency autosomal recessive Turcot syndrome autosomal recessive von Hippel-Lindau syndrome autosomal dominant Waardenburg IIA syndrome supposed autosomal dominant Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome autosomal recessive xeroderma pigmentosum III autosomal recessive prenatal growth failure, severe hypotonia, feeding difficulties, convulsions, hepatomegaly, cerebral depression, cataract, single umbilical artery, other oculo-visceral anomalies. goiter, deafmutism, stippled epiphyses. Bibliography[OMIM]: 164500 146510 Prenat.Diagn.20,670672,2000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 186 Europ.J.Clin.Invest.25, 128-131,1995 261510 274300 144700 flank mass pain, hematuria, other symptoms. Occasionally congenital form. 188470 follicular thyroid carcinoma. goiter, without thyrotoxicosis, serum free 188570 thyroid hormone high levels, normal TSH. clinical findings of hypothyroidism, short 275120 stature. clinical evidence of brain tumor, such as, astrocytoma, medulloblastoma/glial cell tumor/pituitary adenoma, and intestinal adenomatous polyposis. retinal/cerebellar hemangioblastoma, spinal cord compression, ocular cysts, visceral cysts, angiomatosis, renal tumor, pheochromocytoma. deafness, broad nasal bridge, synophry, heterochromia irides, other ocular defects, white forelock, skin depigmentation, no dystopia canthorum; occasionally megacolon. alcoholic vulnerability, fibroblasts with transketolase defect. xeroderma pigmentosum type C, keratoacanthomas, particularly prone to malignant melanoma; occasionally cataract, corneal clouding. 276300 193300 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 511 193510 277730 278720 chromosome 3q localization alkaptonuria autosomal recessive atransferrinemia supposed autosomal recessive blepharophimosis-ovarian failure sex-limited, sex influence supposed contiguous genes supposed genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes blepharophimosis-ptosisepicanthus inversus 1 Genus Clinical Database brown/black standing urine, pigmentation of the sclerae/cartilages, sweet/cerumen dark, arthritis. total absence of transferrin, severe hypochromic anemia, severe hemosiderosis. blepharophimosis, epicanthus inversus, ptosis, premature ovarian failure. Female-limited disease. lid anomalies, blepharophimosis, ptosis, epicanthus inversus, distopia canthorum, other ocular defects, mild mental retardation, cardiac defects, hypotonia. chromosome 3q localization 203500 209300 110100 110100 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 232 19 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuronal type B autosomal dominant Am.J.Hum.Genet.57,8 53-858,1995 600882 cholinesterasis atypical autosomal dominant coproporphyria autosomal dominant Cornelia de Lange syndrome supposed autosomal dominant peroneal muscular atrophy, pes cavus, decreased median nerve conduction, motor-sensory neuropathy neuronal form. prolonged apnea lasting longer than 10 minutes after suxamethonium administration, during surgical anesthesia. acute attacks of abdominal pain, neurologic defects, paralysis, constipation, hallucinations, depression, photosensitivity. mental retardation, hirsutism, synophrys, microcephaly, long philtrum, anteverted nostrils, thin lips, limb defects, ocular changes. Dandy-Walker malformation autosomal recessive disaccharide intolerance I autosomal recessive Fanconi renotubular syndrome Aperia type autosomal recessive Flaujeac factor deficiency autosomal recessive glaucoma 1adult open-angle autosomal dominant glutathione peroxidase deficiency autosomal dominant histidine-rich glycoprotein autosomal dominant 142640 hypercalcemia benign autosomal dominant hyperglycinemia ketotic II autosomal recessive hyperparathyroidism severe neonatal supposed autosomal recessive hypertension essential multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant autosomal dominant thrombosis recurrent, thrombophilia, embolisms, acute mesenteric infarction.due to prothrombotic effect of histidine-rich glycoprotein. easy fatiguability, mild muscle weakness, unconstant other disturbance such as chondrocalcinosis, lipomas, pancreatitis, nephrolithiasis, peptic ulcer. infancy onset; vomiting, lethargy, hypotonia, failure to thrive, ketoacidosis. first weeks of life onset; failure to thrive, constipation, vomiting, anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, polydipsia, seizures, hypotonia, fractures, demineralization, renal calcinosis. usually adult onset; primitive, high blood pressure values. malignant hyperthermia susceptibility related to a gene located on chromosome 3q. Am.J.Hum.Genet.56,6 84-691,1995 600467 hyperthermia malignant susceptibility 4 Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 177400 121300 122470 Prenat.Diagn.19,70670,1999 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag.88 cystic enlargement of the fourth ventricle 220200 due to posterior fossa cyst continuous with the IV ventricle; agenesis of cerebellar vermis and Magendie/Luschka foramina; facultative hydrocephalus, bulging occiput, mental retardation. 222900 dehydration, failure to thrive, fermentative diarrhea with ingestion of sucrose, dextrin starch, but not occurring with monosaccharides or lactose. 227810 growth failure, poor appetite, distended abdomen, thin limbs, sparse subcutaneous fat, malabsorption, hyperaminociduria, acidosis, hypophosphatemia, rickets. 228960 asymptomatic deficiency of a procoagulant factor. 601682 adult onset glaucoma. Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,2 96-304,1997 138320 hemolytic syndromes with erythrocyte glutatione peroxidase deficiency. chromosome 3q localization 145980 232050 239200 145500 20 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: hypocalcemia benign familial autosomal dominant asymptomatic familial hypocalcemia, with normal phosphatemia and parathyroid hormone levels. hypoceruloplasminemiaaceruloplasminemia autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism familial isolated autosomal dominant retinal degeneration, blepharospasm, iron deposition in the basal ganglia, without neurologic symptoms in homozygous individuals. isolated familial hypoparathyroidism; occasionally cataract. leukemia acute pre-B-cell transcription factor-2 acute leukemia. 176311 Moebius syndrome 2 supposed multifactorial undefinable supposed autosomal dominant asymmetric weakness of facial muscle. Hum.Mol.Genet.5,136 7-1371,1996 601471 myelodysplasia syndrome 1 sporadic myelodysplasia inducing reduction in hemopoietic cell lines; occasionally evolving in leukemia. myelodysplasia--myeloid leukemia factor 1 sporadic supposed no genetic myelodysplastic syndrome and/or acute myeloid leukemia with NPM/MLF1 inframe fusion genes. Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.93, 1642-1647,1996 600049 Oncogene 12,265275,1996 601402 neutrophils lactoferrin deficiency autosomal recessive optic atrophy juvenile type oroticaciduria I autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity autosomal recessive recurrent infections due to defect of lactoferrin, a granulocyte iron-binding protein. Normal granulocyte count. early childhood/juvenile onset; progressive decreased visual acuity due to optic atrophy. Eye isolated anomaly. pemphigus benign familial autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa rhodopsin effect autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-4 autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-5 autosomal dominant thrombocytemia essential supposed autosomal dominant tremor essential autosomal dominant Usher III syndrome autosomal recessive megaloblastic anemia, crystalline orotic acid in the urine, unresponsive to vit.B12, responsive to pyrimidine replacement therapy; growth retardation, due to defect of two erythrocyte enzymes: orotidine-5-primepyrophosphorylase and orotidine-5prime-phossphate decarboxylase. Occasionally immunodeficiency and congenital malformations. chronic recurrent rash, vesicles, on erythematous base in the intertriginous areas axillar groins. decreased dim light vision, and constricted visual fields, with typical retinal changes. Eye isolated anomaly. decreased dim light vision, and constricted visual fields, with typical retinal changes. Eye isolated anomaly. so-called retinitis pigmentosa-5 is the same of retinitis pigmentosa-4. thrombohemorrhagic manifestation, high levels of platelets, increased megakaryocytes, sideroblastic anemia. hands/arms facial muscle/tongue tremors, enhancing with fatigue and emotion. retinitis pigmentosa, occasionally cataract, deafness at puberty, mental retardation. Bibliography[OMIM]: Nature Genet. 8,303307,1994 601198 117700 146200 245480 165500 258900 169600 180100 180380 180102 187950 190300 276902 chromosome 4p localization Genus Clinical Database chromosome 4p localization 21 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: achondroplasia autosomal dominant supposed germinal mosaicism cataract anterior polar 1 autosomal dominant chondrodysplasia punctata rhizomelic type 1 autosomal recessive rhizomelic micromelia, disproportionately large head, prominent forehead, depressed nasal bridge, trident hand, inverted interpedicular distance of the lumbar spine, protuberant abdomen. cataract anterior polar. dense white opacities of the central part of the anterior lens capsule.May be associated with other congenotal malformations of the anterior segment of the eye. Eye isolated anomaly. rhizomelic dwarfism, microcephaly, flat face, cataract, optic atrophy, contractures, ichthyosis, alopecia. chondrodysplasia punctata rhizomelic type 2 autosomal recessive craniosynostosis Adelaide type supposed autosomal dominant deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-6 autosomal dominant progressive in low-frequencies neurosensory deafness. Ellis-van Creveld syndrome autosomal recessive telomeric dwarfism, postaxial polydactyly, nail dysplasia, partial harelip, natal teeth, genu valgum, small thorax, upper lateral tibia hypoplasia, cardiac defects, cataract, mental retardation. Huntington disease autosomal dominant genomic imprinting hypochondroplasia genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive progressive choreic movements, usually 30-40 years onset, dementia, appearing indipendently of the movements disorders, first manifestations may be paranoia, emotional instability. Potentially paternal imprinting in juvenile form. short limbs, short/broad hands and feet, no trident deformity, no facial abnormality, occasionally cataract, X-ray changes milder than achondroplasia. hypodontia familial autosomal dominant mucopolysaccharidosis I autosomal recessive night blindness congenital stationary type 3 autosomal dominant phenylketonuria II autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database rhizomelic dwarfism, microcephaly, flat face, cataract, optic atrophy, contractures, ichthyosis, alopecia. No some biochemical defects typical of the type 1. craniosynostosis, other mild skeletal changes. congenital agenesis of one or more teeth, especially molars, in the permanent teeth. coarse facies, respiratory distress, herniae, joint stiffness, hepatosplenomegaly, mental retardation, ocular defects, other clinical data. congenital night blindness with normal fundi and visual acuity, without progressive retinal degeneration. Eye isolated anomaly. severe muscular hypotonia, seizures, mental retardation, other neurological disorders. chromosome 4p localization Bibliography[OMIM]: Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 346 100800 115650 215100 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 390 222765 Prenat.Diagn.19,383385,1999 Hum.Molec.Genet.4,68 1-683,1995 600593 Hum.Mol.Genet.4,196 7-1972,1995 600965 225500 Prenat.Diagn.18,504506,1998 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 374 143100 Prenat.Diagn.19,450457,1999 146000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 352 106600 252800 163500 180072 261630 22 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: pulmonary venous return anomalous supposed autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa autosomal recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity neonatal intense cyanosis, respiratory distress, hypoplastic right lung, due to abnormal pulmonary venous connections. infantile, juvenile, adult onset; retinitis pigmentosa. retinitis pigmentosa CNCG1 type autosomal recessive autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.92, 10177-10181,1995 Stargadt disease-4 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity degeneration of the macular area with flecks, onset in first 2 decades. Eye isolated anomaly. thanatophoric dwarfism autosomal dominant micromelic dwarfism, very short bones/ribs, H-shaped vertebral bodies, curved femurs resembling telephone receiver, no caudad narrowing of the spinal canal, no clover-leaf skull, occasionally macroencephaly. Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome chromosomic severe mental retardation, low birthweight, hypertelorism, microcephaly, nose with Greek helmet appearance, ocular defects, other anomalies, monosomy 4p. Wolfram syndrome autosomal recessive diabetes mellitus in infancy, optic atrophy, cataract, diabetes insipidus, deafness, neurological disorders, sideroblastic anemia. abetalipoproteinemia autosomal recessive albinism oculocutaneous II autosomal recessive alcoholism susceptibility genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked recessive autosomal dominant acanthocytes, steatorrea, ataxia, retinitis pigmentosa, beta-lipoprotein absence and very low serum cholesterol. decreased skin/hair/eyes pigmentation, nystagmus, photophobia, choroidoretinal defects, iridal dyschromia, tyrosinase positive test. increased risk of alcoholism and its pathologic effects. 106700 268000 180072 603786 Am.J.Hum.Genet.64,1 394-1399,1999 187600 Prenat.Diagn. 21,8995,2001 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 338 194190 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 38 222300 chromosome 4q localization alpha-fetoprotein hereditary persistence amelogenesis imperfecta hypocalcified I II supposed autosomal dominant amyloidosis VIII autosomal dominant analbuminemia autosomal dominant anterior segment mesenchymal autosomal dominant dysgenesis aspartylglycosaminuria autosomal recessive complement component C3 inactivator deficiency autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database 200100 203200 103780 126452 hereditary asymptomatic persistence of serum AFP. 104150 opaque/yellowish soft undercalcified enamel with normal thickness in both primary and secondary dentitions. chronic nephropathy, hypertension, hepatosplenomegaly, edema, weakness, visceral amyloidosis. edema in premenstrual period, high erythrocyte sedimentation, hypercholesterolemia. visual acuity reduced, corneal opacification, cataract, iridal changes. Eye isolated anomaly. pharyngeal tonsils enlarged, hernias, mental retardation, coarse facies, bone dysplasia, cataract. infections recurrent pyogenic, due to IF deficiency. 104500 chromosome 4q localization 105200 103600 107250 208400 217030 23 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: dentinogenesis imperfecta II autosomal dominant fibrinogen alpha-polypeptide chain variant autosomal dominant fibrinogen beta-polypeptide chain variant autosomal dominant fibrinogen gamma-polypetdide chain variant autosomal dominant Fletcher factor deficiency autosomal dominant glutaricaciduria IIC autosomal recessive hemophilia C autosomal recessive hyperthyroxinemia dysalbuminemic autosomal dominant interleukin-2 deficiency autosomal dominant iridogoniodysgenesis supposed autosomal dominant iris hypoplasia-glaucoma Landouzy-Dejerine dystrophy autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive autosomal dominant blue-gray/amber-brown teeth, bulbous crowns, narrow roots, small pulp chambers, readily splitting enamel. dysfibrinogenemia/hypofibrinogenemia due to fibrinogen alpha-subunit variant inducing abnormal bleeding/abnormal clotting. dysfibrinogenemia/hypofibrinogenemia due to fibrinogen beta-subunit variant inducing abnormal bleeding/abnormal clotting. dysfibrinogenemia/hypofibrinogenemia due to fibrinogen gamma-subunit variant inducing abnormal bleeding/abnormal clotting. coagulation defect without abnormal bleeding tendency inducing prolonged activated PTT with normal prothrombin time. variable age onset; hypotonia, visceral fatty degeneration, lethargy, coma, sudden death. Mild and severe cases occurring. both sexes affected by mild congenital hemorrhagic disease, usually following surgery/severe trauma, rarely spontaneous, due to reduced Factor XI activity. albumin variant and high tiroxine levels, in euthyroid subjects; occasionally conjunctival pinquecula. clinical findings of severe cellular/humoral immunodeficiency due to IL2 defect. hypoplastic, light in color iris, followed by glaucoma. Eye isolated anomalies. iris atrophy/hypoplasia, followed by glaucoma. Eye isolated anomalies. liver cancer-2 autosomal dominant long QT syndrome 4 autosomal dominant mannosidase-beta deficiency autosomal recessive mucolipidosis II autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database first two decades of life onset; facial weakness with characteristic mask-like expression, difficulty to smile, inability to close the eyes during sleep, shouldergirdle involvement. liver cancer occurring in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. abnormal prolungation of QT inducing attacks of syncope, other cardiac disturbances. coarse face, growth delayed, mental retardation, dystonia, irritability, performance changes, angiokeratoma, angioectasia. coarse facies, gum hyperplasia, joint contractures, kyphoscoliosis, lumbar gibbus, cardiomegaly, hepatomegaly, psychomotor retardation, ocular defects. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. Prenatal diagnosis reliably by electron microscopy of chorionic villlus tissue. chromosome 4q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 125490 134820 134830 134850 229000 231675 264900 103600 147680 137600 308500 158900 142380 Am.J.Hum.Genet.57,1 114-1122,1995 600919 Prenat.Diagn.19,677680,1999 248510 252500 Prenat.Diagn.19,252256,1999 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 452 24 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: mucolypidosis III Inheritance: Synthesis: autosomal recessive stifness, short stature, short trunk, coarse face, Hurler-like skeletal changes, multiple dysostosis, osteoporosis, corneal opacities, other ocular changes, normal liver/spleen, no acid mucopolysacchariduria. childhood/middle age onset; limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, weakness, scapular winging, high CPK, other laboratory data. 252600 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 454 essential tremor, progressive akinetorigidity, shuffling gait, speech/language difficulties beginning in adult years. Occasionally, dysautonomia, dementia. juvenile onset; progresive periodontal disease, characterized by chronic gengival inflammation leading to alveolar ridge resorption, premature loss of teeth. pigmentation defect on the face, on the body ventral surfaces, white forelock, iridal changes, other clinical data. adult type of polycystic kidney without linkage to markers on chromosome 16p. glomerular endotheliosis, hypertension, edema, proteinuria, eclampsia during pregnancy. unresponsiveness tyomineralocorticoids, limited mainly to the kidney. Clinical expression less severe than the most frequent autosomal recessive type. signs of a salt-wasting syndrome, without renal/adrenal disease, failure to thrive, anorexia, vomiting, dehydration, lethargy, collapse. Salt wasting due to target multiple organ unresponsiveness to mineral corticoids. iris/cornea dysgenesis, primary glaucoma, other ocular changes, incisors absence, flat midface, periumbilical skin persistance, other defects. 168600 601508 556500 muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2E genetic heterogeneity Bibliography[OMIM]: Nature Genet.11,266273,1995 600900 Parkinson disease multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant supposed mitochondrial periodontitis juvenile autosomal dominant piebald trait autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 2 autosomal dominant preeclampsia sporadic supposed autosomal dominant pseudohypoaldosteronism I autosomal dominant type autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity pseudohypoaldosteronism I recessive type autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity Rieger sequence-1 autosomal dominant sclerotylosis autosomal dominant skin scleroatrophic lesions, nails dysplasia, palmoplantar keratodermia, skin cancer and bowel cancer tendency. Cockayne I syndrome autosomal recessive cachexia, growth/mental development reduced, loss adipose tissue, retinal degeneration, cataract, choroidoretinal changes, senile appearance, skin photosensitivity. myelodysplasia--myeloid leukemia factor 1 sporadic supposed no genetic myelodysplastic syndrome and/or acute myeloid leukemia with NPM/MLF1 inframe fusion genes. Tay-Sachs disease AB variant autosomal recessive tyrosinemia III supposed autosomal recessive psychomotor delay, seizures, hypotonia, 272750 visual defect, choroidoretinal changes, apathy, exagerated responses to sound. 276710 mild mental deficiency, without hepatic dysfunction. 170650 172800 173910 189800 177735 264350 600761 600760 180500 601542 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 592 181600 chromosome 5 localization Genus Clinical Database chromosome 5 localization 216400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 144 Oncogene 12,265275,1996 601402 25 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: autosomal recessive xeroderma pigmentosum type C, keratoacanthomas, particularly prone to malignant melanoma; occasionally cataract, corneal clouding. 278720 chondrocalcinosis autosomal dominant 118600 complement component C6 deficiency autosomal recessive acute intermittent attacks of arthritis, calcium deposition in articular cartilage, and crystals in synovial fluids cartilage and periarticular soft tissue. infections recurrent neisserial. complement component C7 deficiency autosomal recessive infections recurrent neisserial. 217070 craniometaphyseal dysplasia dominant form genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive hypertelorism, mandibular enlargement, frontonasal swelling, cranial neuropathy, optic atrophy, deafness, nasal obstruction. hypospadias perineoscrotal pseudovaginal syndrome autosomal recessive methylcobalamin deficiency sporadic pituitary dwarfism Laron type sex-limited, sex influence supposed autosomal recessive Tildon disease supposed autosomal recessive 46,XY male, external genitalia resembling feminine in characters, perineal hypospadias with separate urethral and vaginal openings within urogenital sinus. Male limited disease. megaloblastic anemia, severe developmental delay, hypotonia, weakness, lethargy. normal length at birth, proportionate short stature, bone maturation/sexual development delayed, truncal obesity, high-pitched voice, small face, saddle nose, high hGH plasmatic levels. severe intermittent ketoacidosis due to succinyl-CoA:3-ketoacid CoAtransferase deficiency. 123000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 395 264600 xeroderma pigmentosum III Bibliography[OMIM]: chromosome 5p localization 217050 236270 262500 600946 245050 601424 chromosome 5q localization achondrogenesis IB autosomal recessive micromelia, bone ossification deficiency, Am.J.Hum.Genet.55,1 137-1145,1994 fractures. 600972 anemia macrocytic refractory contiguous genes supposed autosomal dominant anemia megaloblastic DHFR deficiency autosomal dominant refractory macrocytic anemia associated 153550 with chromosome 5q- in erythropoietic system. 126060 megaloblastic anemia due to dihydrofolate reductase deficiency. arthrogryposis multiple congenital neurogenic type autosomal recessive contractures and spinal motor neurons lesions. 208100 atelosteogenesis II supposed autosomal recessive Pediatr.Radiol.17,112118,1987 atopic IgE responsiveness autosomal dominant genomic imprinting multifactorial severe micromelia, spinal abnormalities, spondylo-humero-femoral hypoplasia, bowed long bones, abnormal pelvis with horizontal sacrum, cervical kyphosis with lumbosacral hyperlordosis; characteristic cartilage changes. May be the same of de la Capelle synndrome. increased risk of allergic manifestations, asthma, hay fever, eczema, due to exuberant IgE responses to minute amounts of antigen. Potentially maternal imprinting. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 5q localization 147050 600807 601690 26 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: atrial septal AV conduction defects autosomal dominant Avellino corneal dystrophy autosomal dominant atrial septal defect secundum or fossa ovalis type, and atrioventricular conduction defect. corneal dystrophy with both lattice and granular histologic features. Eye isolated anomaly. contractural-arachnodactyly autosomal dominant corneal dystrophy granular type autosomal dominant corneal dystrophy lattice type I autosomal dominant cutis laxa recessive type I autosomal recessive deafness low frequency I autosomal dominant desmoid disease autosomal dominant diastrophic dysplasia autosomal recessive eosinophilia familial autosomal dominant Gardner syndrome autosomal dominant glucocorticoid receptor deficiency autosomal dominant Hageman factor deficiency autosomal recessive Klippel-Feil IV syndrome supposed autosomal recessive Kok disease autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database Marfan-like/arthrogryposis features, multiple joints contractures, tall stature, long thin fingers, crumpled ears, kyphoscoliosis, ocular changes. hyaline degeneration in the corneal stroma, demarcated grayish-white simmetric opacities. Development in the first or second decades of life. Full penetrance of the gene. Eye isolated anomaly. hyaline degeneration in the stroma, recurrent ulceration. Eye isolated anomaly. multiple diverticula, pulmonary emphysema, aneurysms, herniae, other clinical findings suggesting generalized, severe elastolysis, bladder diverticula. sensorineural deafness, progressive lowfrequencies loss. abdominal mass due to infiltrative fibromatosis of the mesentery resembling Gardner disease, inducing bowel perforations, occlusions. APC gene mutations. short limbed dwarfism rhizomelic type, scoliosis, clubfeet, joint deformities, "hitchhiker" thumb, brachysymphalangism, ear chartilage calcification, ocular defects. asymptomatic, increased number of eosinophils, and mild ovalocytosis without recognized causes. multiple colorectal polyposis associated with various sorft- and hard- tissue tumors incuding, osteomas, dermoids, fibromas; dental growth defects, retinal changes, liver cysts; occasionally Horner syndrome. High likelihood of colorectal cancer. hypertension, atherosclerosis, polycystic ovarian due to hyperandrogenism, acne, hirsutism, other stigmata of hypercorticism. thromboembolic disease, normal bleeding time, without hemorrhagic disease and prolonged partial thromboplastin time. cervical, upper thoracic, lumbar vertebral fusion. hypertonia, muscular rigidity at birth, exaggerated startle response to unexpected acoustic/tactile stimuli, respiratory muscle spasm, inguinal/umbilical hernia. chromosome 5q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 108900 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.228 121900 121050 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 476 121900 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.226 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.232 122200 219100 124900 135290 222600 Prenat.Diagn.18,378383,1998 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 376 131400 175100 138040 234000 214300 149400 27 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: leukotriene C4 synthetase deficiency supposed autosomal recessive mucopolysaccharidosis VI autosomal recessive platelets with reduction of glutathione levels, due to leukotriene C4 synthetase deficiency. coarse facies, corneal clouding, deafness, joint stiffness, hepatosplenomegaly, lumbar kyphosis, X-ray changes, herniae. muscular atrophy intermediate type autosomal recessive muscular atrophy juvenile type autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant sexlimited, sex influence muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal dominant type 1A muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2A muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2F O'Rahilly syndrome supposed autosomal recessive undefinable polyposis entire gastrointestinal tract supposed autosomal dominant Reis-Bucklers corneal dystrophy autosomal dominant renal cell carcinoma-3 sporadic supposed autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa autosomal recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity retinitis pigmentosa PDE6A type autosomal recessive Sandhoff disease autosomal recessive schizophrenia-1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity multifactorial undefinable Tay-Sachs disease AB variant autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database first year onset; hypotonia, weakness with prolonged course, extending over several years, intermediate form between Werdnig-Hoffman syndrome and Kukelberg-Welander syndrome. after 2nd year or later onset; weakness, progressive muscular atrophy, starting in the proximal muscles resembling Duchenne type, fine tremor of outstretched arms. Males more severely affected. late onset; slow progression involving proximal limb muscles, sparing the face; high creatine kinase levels, linkage with the Pelger-Huet gene. second decade onset; hip/shoulder proximal muscles weakness, difficulty climbing, stairs/holding hands above head, low back pain, occasionally cardiomyopathy/pseudohypertrophy/high serum creatine kinase levels. severe muscular dystrophy, myopathy starting in lower limb. primary amenorrhea, obesity, hypogonadism, postprandial hypoglycemia, hypoinsulinemia. adenomatous polyposis involving entire gastrointestinal tract, bleeding, abdominal pain, diarrhea, early development of symptoms, cancer susceptibility. dusty opacity, rough map-like surface primarily in Bowman membrane. Eye isolated anomaly. flank mass pain, hematuria, other symptoms. Sporadic nonpapillary renal cell carcinoma. Occasionally congenital form. infantile, juvenile, adult onset; retinitis pigmentosa. Bibliography[OMIM]: 246530 253200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 468 253550 603011 253400 603011 159000 253600 Nature Genet.14,195198,1996 601287 600955 162150 175000 121500 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998, p.223 179760 190020 268000 180072 autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Nature Genet.11,468471,1995 268800 weakness, startle reaction, blindness, mental deterioration, coarse doll-like face, cherry red spots, macrocephaly, hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal changes, orthostatic hypotension. 181510 juvenile/adult onset; psychotic syndromes in previously normal subject, schizophrenic disorders, paranoid hebephrenic disturbance, hallucinations, delusions. psychomotor delay, seizures, hypotonia, 272750 visual defect, choroidoretinal changes, apathy, exagerated responses to sound. chromosome 5q localization 28 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: Treacher-Collins-Franceschetti syndrome autosomal dominant midface hypoplasia, downward slant of palpebral fissures, colobomata lower lips, microtia, micrognathia, deafness, ocular changes. Turcot syndrome autosomal recessive vitreoretinal degeneration Wagner type autosomal dominant clinical evidence of brain tumor, such as, astrocytoma, medulloblastoma/glial cell tumor/pituitary adenoma, and intestinal adenomatous polyposis. 143200 nightblindness, myopia, retinal dystrophy, presenile cataract, glaucoma, deafness. 154500 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 250 276300 chromosome 6 localization CHARGE syndrome supposed autosomal recessive choanal atresia, heart anomalies, ocular colobomas, choroidoretinal defects, mental retardation, growth deficiency, hypogenitalism, triangular shape of the concha. immunodeficiency late onset autosomal recessive narcolepsy autosomal dominant genomic imprinting pancreatic beta cell agenesisneonatal diabetes supposed autosomal recessive Infections tendency, normal B lymphocytes, lacking mechanism for plasma cell differentiation. Partial deletions of IgH genes (?) infancy or later onset; irresistible sleep episodes, occasionally sleep apnea, attacks of cataplexy, i.e. abrupt reversible loss of muscle tone. Potentially maternal imprinting. neonatal diabetes mellitus, severe organic acidemias. schizophrenia-3 autosomal dominant 214800 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 668 240500 161400 Diabetologia 36,352357,1993 600089 Genomics 43,1-8,1997 uvenile/adult onset; psychotic syndromes in previously normal subject, 600511 schizophrenic disorders, paranoid hebephrenic disturbance, hallucinations, delusions. chromosome 6p localization adrenal hyperplasia III autosomal recessive adrenal hyperplasia III late onset autosomal recessive adrenal hyperplasia V autosomal recessive agranulocytosis infantile autosomal recessive atrial septal defects autosomal dominant multifactorial Genus Clinical Database masculinization of the externa genitalia, female pseudohermaphroditism with ovaries and uterus and presence of a prostate, skin pigmentation around genitalia, salt loss, electrolyte disturbances. late childhood/puberty, virilization/somatic advance due to excessive secretion of adrenal androgens. mild hypertension, hypokalemic alkalosis, amenorrhea, absent sexual maturation, low plasma renin, ambiguous genitalia, prominent breast in males. congenital neutropenia, severe recurrent infections. isolated atrial septal defect, ostium primum or ostium secundum (fossa ovalis) type. chromosome 6p localization 201910 201910 202110 202700 108800 29 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 2 autosomal recessive postaxial polydactyly, hypogonadism, obesity, mental retardation, pigmentary retinopathy. Chromosome 16q localization. Bietti corneoretinal dystrophy autosomal recessive celiac disease multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive Char syndrome sporadic nightblindness, visual fields reduction, due to glistening intraretinal dots scattered over the fundus, retinal and choroidal vessels degeneration. Eye isolated anomaly. diarrhea, steatorrhea, wieght loss, abdominal distention, anemia, fecal electrolyte loss, dermatitis herpetiformis, small bowel mucosa flattened, remission on a gluten-free diet. connective tissue disorder characterized by cutis laxa, joint laxity, joint dislocations, sub-aortic stenosis, skeletal changes. cleidocranial dysplasia autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity persistently open skull sutures, bulging calvarium, clavicles hypoplasia, abnormal facility in apposing the shoulders, oligodontia, short stature, deafness, other anomalies. complement component C 4s deficiency autosomal dominant lupus systemic-like syndrome. complement component C2 deficiency autosomal recessive complement component C4f deficiency autosomal dominant complement C-2 defect occurring in wide variety of disease, such as renal disease, recurrent infections, skin rashes, autoimmune diseases. lupus systemic syndrome due to C4F deficiency. cone dystrophy 3 autosomal dominant central vision loss, color loss, cone dystrophy, photophobia. deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-13 autosomal dominant postlingual progressive deafness diabetes mellitus insulindependent 1 genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive dyslexia 2 autosomal dominant juvenile onset, polyuria, polydipsia, antibodies to pancreatic islet beta cells, ketoacidosis, vascular changes, increased in autoimmuno diseases. slow reading, reduced comprehension, words distortion or mission associated with behavioral and emotional dysfunctions congenital hemorrhagic disorder, umbilical cord bleeding, ecchymoses, hematomas, intracranial bleeding. multiple uniform yellow-white dots, congenital stationary night blindness. No macular involvement. Eye isolated anomaly. Factor XIII-A subunit deficiency autosomal dominant fleck retina fundus albipunctatus genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive glyoxalase II deficiency autosomal dominant asymptomatic enzymatic defect. hemochromatosis type 1 autosomal recessive adult onset; hypertrophic cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, melanodermia, articular pain with/without chondrocalcinosis, progressive infantilism, secondary gonadal atrophy, other findings, eventualyy to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 6p localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 209900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 590 210370 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.241 212750 Proc.Gr.Genet.Center 6,174-177,1987 169100 Circulation 99,30363042,1999 119600 600211 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 408 120810 217000 120820 602093 Hum.Mol.Genet.7,273277,1998 Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,7 58-764,1997 601868 222100 600202 Science 266,276279,1994 134570 136880 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.391 138760 235200 602254 30 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: hemolytic anemia Konrad type autosomal recessive hydronephrosis familial autosomal dominant immotile cilia syndrome Polynesian type autosomal recessive laryngeal paralysis adductor autosomal dominant macular dystrophy atypical vitelliform autosomal dominant macular dystrophy butterflyshaped pigmentary supposed autosomal dominant nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia, infancy and adult onset, spinocerebellar ataxia, reduced GSH in erythrocytes. congenital unilateral/bilateral hydronephrosis, megalo-idroureters, obstructive uropathy. respiratory infections, bronchiectasis due to defects in the motor mechanism of cilia. hoarsenes since birth, due to bilateral partial/complete paralysis of adductor vocal cord, without episodes of aspiration. small yellow lesions in the macula and peripapillary region. Eye isolated anomaly. bilateral macular pigment dystrophy, butterfly-shaped. Eye isolated anomaly. maple syrup urine disease 3 autosomal recessive methylmalonicaciduria MCM deficiency autosomal recessive molybdenum cofactor deficiency type A autosomal recessive myoclonus-epilepsy Janz type autosomal recessive Nance-Sweeney syndrome autosomal recessive nystagmus congenital autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive autosomal dominant olivopontocerebellar I orofacial cleft 1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity genomic imprinting multifactorial Paget syndrome supposed autosomal dominant polycystic kidney infantilejuvenile type autosomal recessive polycystic kidney perinatalneonatal type autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database clinical features similas to MSUD 1, due to E-1beta subunit deficiency. first months onset; failure to thrive, vomiting, dehydration, respiratory distress, hypotonia, acidosis, ketonuria, lethargy, coma. dysmorphism, psychomotor retardation, hypertonia, neonatal seizures, encephalopathy, lens dislocation. myoclonic epilepsy, juvenile onset, isolated myoclonic, jerks, usually in the morning. short-limbed dysplasia, dysmorphism, severe depressed nasal bridge, deafness, epi-metaphyseal changes, joint contractures. congenital nystagmus. Eye isolated anomaly. adult onset; progressive ataxia, dysarthria, tremors, involuntary choreic movements. complete or incomplete clefts of the upper lip, unilateral or bilateral, including posterior alveolar processes, and anteriorly alae nasi. Potentially paternal imprinting. progressive asymmetric enlargement skull/shins, severe bone pain, X-ray lucency/sclerosis, ocular defects, serum alkaline phosphatase elevated. infantile/juvenile onset; renal enlargement, renal failure, nephronophthisis, hypertension, heart failure, hepatic fibrosis, portal hypertension. perinatal/neonatal onset; oligohydramnios, Potter facies, massive palpable enlarged kidneys, nephronophthisis, distended abdomen, hematuria, oliguria, pulmonary hypoplasia, liver enlargement. chromosome 6p localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 230450 143400 242650 150270 153840 153860 248611 251000 252150 Prenat.Diagn.19,386388,1999 Prenat.Diagn.20,711,2000 254770 215150 164100 164400 601556 119530 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 236 167250 263200 263200 31 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: pseudohermaphroditism male internal autosomal recessive renal glycosuria autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa digenic autosomal dominant normal external genitalia and testes in males 46, XY, with uterus and falloppian tubes, prolapsing into inguinal hernia; cancer tendency in cryptorchid testes. glycosuria with normal oral glucose tolerance test, redused renal titration test. autosoma dominant retinitis pigmentosa due to RDS and ROM1 gene. retinitis pigmentosa-14 autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa-7 autosomal dominant sialidosis I supposed autosomal recessive sialidosis II supposed autosomal recessive spine ligament ossification undefinable spondylitis ankylosing autosomal dominant Stargardt disease-3 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity Stickler syndrome II autosomal dominant Tucker syndrome supposed autosomal dominant Bibliography[OMIM]: 261550 600957 233100 Scienze 264,16041608,1994 180721 autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. 600132 Nature Genet.18,177179, 1998 179605 retinal degeneration due to specific retinal protein mutation. Eye isolated anomaly. second decade onset; decreased visual 256550 acuity, cherry red spots, cataract, corneal opacity, myoclonus without somatic/bony abnormalities. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. No mental retardation. 256550 cherry red spots, myoclonus without somatic/bones anomalies. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. 602475 ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine, inducing paresis/tetraparesis due to spinal-cord compression. Heterotopic ossification occurs only in joint capsules, ligaments, etc. 106300 2nd 3rd decades onset; chronic low back pain, stiffness followed by severe dorsolumbar spine limitation of motion, severe chest expansion limitation, HLAB27 presence. Arch.Ophthal.112,765progressive macular dystrophy 772,1994 resembling Stargardt disease. Eye isolated anomaly. 600110 clinical data resembling Stickler syndrome I. adult onset; Paget-like bone disorders, insidious progressive weakness, muscular atrophy, quadriparesis, dementia, optic atrophy. 184840 167320 chromosome 6q localization albinism ocular Witkop o'Donnell type autosomal recessive nystagmus, photophobia, translucent irides. Eye isolated anomaly. 203310 argininemia autosomal recessive 207800 arthropathy progressivespondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda autosomal recessive cardiomyopathy Messina type autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia, seizures, severe mental retardation. progressive arthropathy, about 3 years age onset, joint stiffness suggesting rheumatoid arthritis, osseous distension of the terminal phalanges bone dysplasia spondyloepiphyseal type. dilated cardiomeyopathy with conduction defect and adult-onset limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 6q localization 208230 Am.J.Hum.Genet.61,9 09-917,1997 602067 32 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: chondrodysplasia punctata rhizomelic type 1 autosomal recessive rhizomelic dwarfism, microcephaly, flat face, cataract, optic atrophy, contractures, ichthyosis, alopecia. chondrodysplasia punctata rhizomelic type 2 autosomal recessive chorioretinal atrophy bifocal autosomal dominant rhizomelic dwarfism, microcephaly, flat face, cataract, optic atrophy, contractures, ichthyosis, alopecia. No some biochemical defects typical of the type 1. progressive chorioretinal atrophy. Eye isolated nomaly. deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-10 autosomal dominant late-onset progressive sensorineural hearing loss. diabetes mellitus insulindependent 15 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus insulin-dependent. diabetes mellitus insulindependent 5 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus insulin-dependent. diabetes mellitus insulindependent 8 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus, insulin dependent. diabetes neonatal permanent sporadic supposed genomic imprinting diabetes neonatal transient genomic imprinting foveal dystrophy progressive autosomal dominant permanent neonatal diabetes insulindependent in infants small-for-date; occasionally exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Occasionally paternal uniparental isodisomy of chromosome 6. Chromosome 6q localization? neonatal diabetes, intrauterin growth retardation, failure to thrive, resolving within the first months of life; often remains permanent; later in life may develop diabete II or even insulin resistant. Paternal imprinting. progressive macular dystrophy, without color vision defect. Eye isolated anomaly. Fukuyama syndrome autosomal recessive generalized weakness, hypotonia, cataract, choroidoretinal changes, optic atrophy, mental retardation, seizures, micro-lissencephaly. hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome autosomal dominant intestinal polyps, colonic adenomas, colorectal carcinomas. May be a variant of juvenile polyposis. premature coronary atherosclerosis. hyperlipoproteinemia Lp(a) autosomal dominant merosin-deficient congenital muscular dystrophy autosomal recessive mycobacterial susceptibility autosomal dominant mycobacteriosis familial autosomal recessive myoclonus-epilepsy Lafora type supposed autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 215100 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 390 222765 Prenat.Diagn.19,383385,1999 Hum.Molec.Genet.4,16 53-1656,1995 600790 Hum.Molec.Genet.5,85 3-856,1996 601316 Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,1 74-187,1997 601666 Nature 371,130136,1994 600320 Am.J.Hum.Genet.57,9 11-919,1995 600883 Eur.J.Pediatr. 154(12),944-948,1995 Arch.Dis.Child.Fetal Neonatal Ed. 76(1):F39-F42,1997 Hum.Molc.Genet.5,111 7-1121,1996 601410 J.Perinatol.16(4),288291,1996 136550 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.367 253800 156225 Hum.Genet.99,535540,1997 Am.J.Hum.Genet.58,7 70-776,1996 601228 152200 156225 Hum.Genet.99,535540,1997 disseminated, generalized familial BCG infection due to partial IFNGR1 deficiency. atypical disseminated BCG infection after newborn inoculation inducing intestinal disturbance, osteomyelitis, macrophage defect. grand mal attacksand, myoclonus, juvenile onset, severe mental deterioration, psychosis, Lafora bodies. chromosome 6q localization 209950 254780 33 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: oculo-dento-digital syndrome autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed contiguous genes ovarian tumor autosomal dominant hypoplastic alae nasi, narrow nostrils, microcornea, cataract, primary glaucoma, other ocular defects, microdontia, hypoplastic enamel, IV-V syndactyly, other skeletal defects. Occasionally reported in oculo-dentodigital, oculo-palato-cerebral, protein C deficiency. More severe ocular affection in the recessive form. familial ovarian tumors, dysgerminomas/cancer, papillary adenocarcinoma. Parkinson disease juvenile autosomal recessive plasminogen deficiency autosomal dominant retinal cone dystrophy-1 autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-25 autosomal recessive sialuria autosomal recessive Viljoen-Smart syndrome supposed autosomal dominant essential tremor, progressive akinetorigidity, shuffling gait, speech/language difficulties beginning ibefore age 40 years. recurrent thromboembolic disease, hypercoagulability. May cause severe ligneous conjunctivitis. Bibliography[OMIM]: 164200 Hum.Molec.Genet.6,12 3-127,1997 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 268 257850 167000 601404 192090 Neurology 44,437441,1994 600116 173350 Prenat.Diagn.19,483487,1999 180020 progressive loss of visual acuity, photophobia, defective color vision, cone dystrophy. Eye isolated anomaly. Am.J.Hum.Genet.62,1 autosomal recessive retinitis 452-1459,1998 pigmentosa. Eye isolated anomaly. 602772 at birth/soon thereafter onset; coarse facies, hepatosplenomegaly, diarrhea, anemia, epiphyseal punctate calcifications, vacuolated lymphocytes. Oligohydramnios, fetal ascites. microphthalmos, microcornea, mental retardation, cleft lip/palate, de novo 6;13 translocation. 269920 Clin.Dysmorph.2,274277,1993 601349 chromosome 7 localization argininosuccinic aciduria autosomal recessive hydroxyacyl-CoA autosomal recessive dehydrogenase deficiency long mitochondrial chain Meigel disease 207900 mental retardation, convulsions, episodic inconsciousness, skin lesions, liver enlargement, dry/brittle hair. recurrent hypoglycemia, 143450 cardiomyopathy, seizures, liver damage, muscular atrophy. supposed autosomal recessive clinical/radiological disorders resembling 203760 Marfan syndrome and osteogenesis imperfecta. argininosuccinic aciduria autosomal recessive blepharophimosis-ptosisepicanthus inversus 2 autosomal dominant mental retardation, convulsions, episodic inconsciousness, skin lesions, liver enlargement, dry/brittle hair. blepharophimosis, other associated anomalies, resembling BPES1. cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome autosomal dominant chromosome 7p localization Genus Clinical Database severe syndactyly, postaxial polydactyly, halluces duplication, scaphocephaly/plagiocephaly, dysmorphic face with no evidence of craniostenosis. chromosome 7p localization 207900 Hum.Molec.Genet.5,20 49-2054,1996 601649 175700 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 426 34 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: Chotzen syndrome autosomal dominant craniosynostosis, plagiocephaly, acrocephaly, facial asymmetry, low anterior hair-line, brachy-syndactyly, soft- tissue syndactyly between II and III fingers, ocular ptosis. Christodoulou syndrome autosomal dominant juvenile onset, weakness more prominent in the upper limbs, thenar muscles atrophy. craniosynostosis type 1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive cystinosis early onset autosomal recessive deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-5 autosomal dominant premature closure of sutures, leading to abnormally shaped head, including brachycephaly, oxycephaly, plagiocephaly,turricephaly/acrocephaly, cloverleaf skull. polyuria, polydipsia, recurrent fever, growth retardation, cystine crystal deposition, choroidoretinal changes, renal failure, rickets-like dysplasia, confusion, short-term memory loss. progressive hearing loss in the high frequencies. diabetes mellitus glucokinaserelated autosomal dominant maturity-onset diabetes mellitus. diabetes mellitus noninsulindependent mild juvenile autosomal dominant 125850 hand-foot-uterus syndrome autosomal dominant macular edema cystoid autosomal dominant myopathy metabolic phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency autosomal recessive juvenile onset, correction of fasting hyperglycemia without insulin, usually without ketosis, without obesity. short thumb, hypoplastic thenar eminence, clinodactyly, small feet, other mild acroskeletal anomalies, bifid uterus/septate vagina/male hypospadias. cystoid macular edema due to retinal capillary leakage, pericentral retinitis pigmentosa. Eye isolated anomaly. cramps, myoblobinuria, intolerance for exercises, gout, tophi, hyperuricemia, coronary sclerosis. Pallister-Hall syndrome supposed autosomal dominant hypothalamic hamartoblastoma, acidosis, lethargy, jaundice, ocular defects, hypogonadism, dysmorphism, multiple mouth frenula, imperforate anus, polydactyly. Occasionally increased nuchal translucency and hydrops. polydactyly postaxial autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-9 autosomal dominant isolated postaxial polydactyly, with extra digit well formed or in the form of a skin tag, i.e. pedunculated postminimi. autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Eye isolate anomaly. 146510 Prenat.Diagn.20,670672,2000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 186 174200 101400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 412 Hum.Molec.Genet.4,16 29-1632,1995 600794 123100 219800 Hum.Mol.Genet.4,215 9-2163,1995 600994 125851 140000 153880 261670 180104 chromosome 7q localization adrenoleukodystrophy neonatal autosomal recessive type aortic stenosis supravalvar Genus Clinical Database genetic heterogeneity genomic imprinting seizures, delayed neurologic development, respiratory infections, cataract, choroidoretinal defects, optic atrophy, sudden death. congenital narrowing of the ascending aorta, usually at the superior margin of the sinuses of Valsalva, above the level of the coronary arteries; frequently associated pulmonary, other peripheral arteries stenosis. Potentially paternal imprinting. chromosome 7q localization 202370 185500 35 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: cardiomyopathy hypertrophic with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome autosomal dominant hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with WolffParkinson-White syndrome. chloridorrhea congenital autosomal recessive cutis laxa cutis laxa recessive type I autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity autosomal recessive often prematurity, abdominal distension, chronic diarrhea with voluminous watery stools, containing excess of chloride, metabolic alkalosis. skin laxity, premature wrinkling, cardiac failure, hernias prolapse. cutis laxa-Marfan phenotype autosomal dominant cystic fibrosis autosomal recessive deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-4 autosomal recessive deferens vas aplasia supposed autosomal recessive diphosphoglycerate mutase deficiency autosomal recessive dysphasia familial autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked dominant delay in the development of language, without other defects Genet.Couns.5,2233,1994 600117 602081 EEC syndrome autosomal dominant midline ectrodactyly, lacrimal duct atresia, ocular changes, sparse blond/gray hair, hypodontia, cleft lip/palate, renal anomalies. Ehlers-Danlos VII autosomal dominant autosomal dominant short stature, joint laxity, skin bruisability, micrognathia. 129900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 294 130060 Ehlers-Danlos VII autosomal recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity granulomatous disease I autosomal recessive short stature, severe joint hypermobility, multiple subluxations, floppy infant aspect, bruisability, dysmorphic face. at birth/young adulthood onset; severe frequent pyogenic infections/granulomas in any organs, osteomyelitis due to 47kD neutrophil cytosol factor defect. seizures, hemorrhage, focal neurologic deficiency, ocular changes, intracranial calcifications. holoprosencephaly, hydronephrosis, other clinical findings, terminal 7q deletion. malignant hyperthermia susceptibility related to a gene located on chromosome 7q. hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, anosmia, cryptorchidism; occasionally arhinencephaly, other clinical data. hemangioma cavernous of brain autosomal dominant holoprosencephaly 3 autosomal dominant hyperthermia malignant susceptibility 3 autosomal dominant Kallmann syndrome 1 X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database multiple diverticula, pulmonary emphysema, aneurysms, herniae, other clinical findings suggesting generalized, severe elastolysis, bladder diverticula. marfanoid phenotype, congenital cutis laxa. malabsorption, failure to thrive, recurrent respiratory infections, nasal polyps, infertility, cirrhosis, pancreatic insufficiency, chronic pulmonary disease, meconium ileus at birth, high levels of the sweet electrolytes sodium/chloride. autosomal recessive hearing loss. azoospemia/severe oligozoospermia, due to vasa deferentia aplasia. mild erythrocytosis, high hemoglobin concentration. chromosome 7q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: J.Clin.Invest.96,12161220,1995 600858 214700 123700 219100 150240 219700 Hum.Mol.Genet.4,163 7-1642,1995 600791 277180 222800 225410 233700 116860 142945 154276 601707 36 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: lactic acidosis LAD deficiency autosomal recessive long QT syndrome 2 autosomal dominant first weeks of age onset; intermittent hypoglycemia, neurologic dysfunction, inspiratory stridor, increased muscle tone, optic atrophy, metabolic acidosis, lethargy. abnormal QT prolungation inducing attacks of syncope, other disturbances. Lubani syndrome autosomal recessive Marfan syndrome I autosomal dominant mucopolysaccharidosis VII autosomal recessive osteogenesis imperfecta III autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta IVA autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta IVB autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta lethal IIA autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed germinal mosaicism osteogenesis imperfecta lethal IIB autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed germinal mosaicism osteogenesis imperfecta lethal IIC autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta tarda blue sclerae osteoporosis senile Genus Clinical Database supposed autosomal dominant clinical signs of cystic fibrosis, mental retardation, megaloblastic anemia, helicobacter pylori gastritis, mild dysmorphic face. tall stature, dolichostenomelia, arachnodactyly, scoliosis, chest deformity, upward lens dislocation, primary glaucoma, other ocular changes, joint laxity, aortic/mitral involvement, tricuspid valve regurgitation, mitral annulus calcification, long slendeer limbs, arm span greater than height, little subcutaneous fat, hypotonia; arterial dissections. coarse facies, short stature, corneal clouding, hepatosplenomegaly, herniae, X-ray changes. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. short stature, progressive deformity, bluish sclerae at birth, but less blue with age, cardiorespiratory failure, clinical variability from perinatal death to little morbidity. bluish sclerae at birth, progressively less blue with age; normal teeth; deafness, other clinical data characteristic of osteogenesis imperfecta. clinical variability, bluish sclerae at birth, less blue with age; dentinogenesis imperfectas; fractures, usually in the newborn period onset, other clinical data characteristic of osteogenesis imperfecta. extreme bone fragility, intrauterine fractures, broad crupled femora, continuous rib beading, marked reduction in collagen I synthesis. extreme bone fragility, intrauterine fractures, broad crumpled femora with minimal or no rib fractures; other clinical data characteristic of osteogenesis imperfecta. extreme bone fragility, intrauterine fractures, thin femora, thin ribs. multiple bone fractures, blue sclerae, other ocular defects, opalescent teeth, deafness; arterial rupture/dissection. reduced bone mass mainly in the femoral neck and lumbar spine. chromosome 7q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 246900 152427 Prenat.Diagn.19,677680,1999 219721 154700 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 472 253220 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 470 259420 166220 166220 166210 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 490 J.Med.Genet.31(12),96 5-968,1994 Prenat.Diagn.17(6),55 9-570,1997 166210 166210 166200 166710 37 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: pancreatitis hereditary autosomal dominant Pendred syndrome autosomal recessive 167800 recurrent epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, high levels of serum/urinary amilase and lipase, steatorrhea, glucose intolerance, pancreatic calcification, other disturbances. 274600 perceptive congenital deafness, goiter. pigmentary dispersion syndrome-glaucoma autosomal dominant plasminogen activator inhibitor- autosomal dominant 1 high levels platelet thromboxane A synthase deficiency autosomal recessive pseudo-Zellweger syndrome autosomal recessive Refsum syndrome infantile type supposed autosomal recessive juvenile onset; optic nerve degeneration, open-angle glaucoma, myopia, pigment granule deposition in iris and other ocular structures. thrombophilia due to increased PLANH1, thrombosis recurrent, PLANH1 over expression. soon after birth onset; hemorrhage, bleeding diathesis, normal platelet counts with defective aggregation, due to platelet thromboxane synthase deficiency. prenatal growth failure, severe hypotonia, feeding difficulties, convulsions, hepatomegaly, cerebral depression, cataract, single umbilical artery, other oculo-visceral anomalies. retinitis pigmentosa, other ocular defects, deafness, peripheral neuropathy, hepatomegaly, facies resembling Down syndrome, steatorrhea, bleeding diathesis, simian creases. autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa.Eye isolated anomaly. prenatal growth retardation, microcephaly, dysmorphic facies, ambiguous genitalia in male, polysyndactyly, cataract, urinary and other visceral anomaly. Specificity of low maternal oestriol levels. Bibliography[OMIM]: 600510 Arch.Ophthal. 115,384-388,1997 173360 274180 261510 266510 retinitis pigmentosa-10 autosomal dominant Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome autosomal recessive split hand/foot deformity type 1 autosomal dominant lobster-claw deformity, ectrodactyly, monodactyly. teratoma presacral-sacral dysgenesis autosomal dominant tritanopia autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive autosomal recessive presacral mass, sacral dimple, anal stenosis, constipation, neurogenic bladder, other meningospinal anomalies. 190900 defect in color perception, partial or total, occasionally other ocular defects. Eye isolated anomaly. trypsinogen deficiency Williams syndrome Genus Clinical Database contiguous genes supposed autosomal dominant failure to thrive, edema, anemia, hypoproteinemia, malabsorption, duodenal peptidases activities deficiency. short stature, mild mental retardation, loquacious behaviour, elfin facies, supravalvular aortic stenosis, other cardiac defects, stellate pattern of irides, bladder diverticula. chromosome 7q localization 180105 270400 Prenat.Diagn.19,105107,1999 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 112 183600 601285 Hum.Molec.Genet.5,57 1-579,1996 176450 276000 194050 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 118 38 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: autosomal recessive prenatal growth failure, severe hypotonia, feeding difficulties, convulsions, hepatomegaly, cerebral depression, cataract, choroidoretinal changes, primary glaucoma, other oculovisceral anomalies, single umbilical artery, stippled chondral calcificationss. 214100 Prenat.Diagn.18,11951197, 1998 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 212 Prenat.Diagn.20,520521,2000 CHARGE syndrome supposed autosomal recessive choanal atresia, heart anomalies, ocular colobomas, choroidoretinal defects, mental retardation, growth deficiency, hypogenitalism, triangular shape of the concha. isoniazid inactivation autosomal recessive asymptomatic acetylator polymorphism (slow/rapid) for isoniazid, hydralazine, salicylazosulfapyridine, etc. spastic paraplegia unaccompanied by other features. 214800 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 668 243400 Zellweger syndrome 1 Bibliography[OMIM]: chromosome 8 localization paraplegia spastic hereditary-5A autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity Rothmund-Thomson syndrome autosomal recessive 270800 skin telangiectasia/atrophy/pigmentation, short stature, juvenile cataract, other ocular defects, teeth defects, sunlight sensitivity. 268400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 148 craniosynostosis, osseous and/or cutaneous syndactyly, visceral defects, strabismus. alopecia of the scalp, beard, eyebrows/eyelashes; dystrophic fingernails. Suspected autoimmunity. site-specific colonic cancer changes in bowel habit, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, anemia, weight loss, onset before 40 years. May be the same of Lynch II. Associated endometrial carcinoma/atypical hyperplasia, uterine leiomyosarcoma, renal/bladder carrcinoma, gastric/biliary carcinoma. secondary sexual development failure, small testes, vaginal atrophy, eunuchoid body proportions, sterility. coagulation defect due to combined deficiency of factors VII and VIII. 101600 chromosome 8p localization acrocephalosyndactyly Pfeiffer type autosomal dominant alopecia areata genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant colorectal familial cancer Lynch I supposed autosomal dominant undefinable eunuchoidism familial hypogonadotropic supposed autosomal recessive factor VII-VIII combined deficiency supposed autosomal dominant glutathione reductase deficiency autosomal dominant episodic hemolytic anemia, occasionally cataract. 138300 hyperfibrinolysis familial autosomal dominant thrombosis recurrent. 173370 hyperlipoproteinemia IA autosomal recessive abdominal pain, hepatosplenomegaly, ocular defects, intermittent eruptive yellowish nodules. infancy/early adulthood onset; intermittent, recurrent keratolytic erythema, peeling with redness, strikingly occurring with cold weather. 238600 keratolytic winter erythema Genus Clinical Database chromosome 8p localization 104000 114500 190020 116806 227200 134430 148370 Am.J.Hum.Genet.61,3 70-378,1997 39 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: prostate cancer hereditary autosomal dominant early-onset prostate cancer. retinitis pigmentosa-1 autosomal dominant spherocytosis type II autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity Werner syndrome autosomal recessive decreased dim light vision, and constricted visual fields, with typical retinal changes. Eye isolated anomaly. chronic hemolytic anemia, severe spherocytosis, with partial response to splenectomy, due to defect in ankyrin synthesis(binding site for spectrin on the membrane). premature aging, short stature, alopecia, diabetes, cataract, other ocular defects, hypotonia, myocardial infarction. Bibliography[OMIM]: 176807 601518 600020 180100 182900 277700 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 142 chromosome 8q localization ACTH deficiency isolated supposed autosomal recessive adrenal 18-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency autosomal recessive adrenal hyperplasia IV autosomal recessive Baldwin disease autosomal dominant Berlin breakage syndrome autosomal recessive BOR-Duane-hydrocephalus contiguous gene syndrome contiguous genes branchio-oto-renal syndrome autosomal dominant Burkitt lymphoma no genetic undefinable Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy recessive type autosomal recessive peroneal muscular atrophy, pes cavus, leg atrophy, scoliosis. 214400 cleidocranial dysplasia autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity persistently open skull sutures, bulging calvarium, clavicles hypoplasia, abnormal facility in apposing the shoulders, oligodontia, short stature, deafness, other anomalies. Cohen syndrome autosomal recessive short or tall stature, obesity, mental retardation, hypotonia, microcephaly, prominent upper central incisors, other ocular/skeletal/visceral anomalies. 119600 600211 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 408 216550 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 206 Genus Clinical Database adrenocortical insufficiency due to isolated ACTH deficiency, attacks of hypoglycemia. failure to thrive, growth retardation, abnormality in serum electrolytes, salt depletion, hyperkalemia with normal genitalia. virilization, female pseudohermaphroditism, hypertension, precocious puberty in males, signs of mineralcorticoid excess. severe degenerative osteoarthritis, calcium gout, calcium deposition in articular cartilage. 201400 203410 124080 202010 Am.J.Hum.Genet.56,6 92-697,1995 600668 Clin.Genet.33,2032,1988 600885 hydrocephalus associated with branchio- Hum.Molec.Genet. 3,1859-1866,1994 oto-renal and Duane syndrome, due to deletion of 8q12.2-q21.2. 600257 600256 113650 preauricular pits or ear tags, branchial cysts or fistulas internal/external Smith's Recognizable opening, renal hypoplasia/agenesis. Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 244 lymphoma, with chromosome 8 113970 consistently involved. 601406 microcephaly, thymus hypoplasia, dysmorphism, immunodeficiency. chromosome 8q localization 40 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: epidermolysis bullosa simplex Ogna type autosomal dominant generalized epidermal fragility, serous seasonal hands/feet blistering. 131950 exostoses multiple cartilagineous type I autosomal dominant 133700 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 436 Guibaud-Vainsel syndrome autosomal recessive juvenile absence epilepsy supposed autosomal recessive mild short stature, bone deformity due to numerous asymmetric cartilage-capped exostoses, with characteristic clubshaped appearance, usually in the tubular bones actively growing areas, such as juxtaepiphyseal areas; malignant degeneration may occur. increased bone density, mataphyses transverse banding, fractures, distal renal tubular acidosis, cerebral calcification, optic atrophy, mental retardation. childhood, juvenile onse. Absence epilepsy associated with tonic-clonic seizures, sporadic myoclonus. Kalaydjieva disease autosomal recessive first decade onset. Distal muscle wasting and atrophy, talipes, deafness. Klippel-Feil II syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes localized C2-3 and C5-6 fusion, hemivertebrae, occipitoatlantal fusion, associated findings. macular dystrophy atypical vitelliform autosomal dominant Niemi syndrome supposed autosomal recessive paraplegia spastic hereditary-8 autosomal dominant small yellow lesions in the macula and peripapillary region. Eye isolated anomaly. epidermolysis bullosa simplex and muscular dystrophy of the limb-girdle type. Weakness, progressive spastic paraplegia. Roe disease mitochondrial supposed autosomal recessive salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma sporadic Seemanova syndrome II autosomal recessive Langer-Giedion syndrome thyroid hormonogenesis defect supposed autosomal recessive V trichorhinophalangeal I autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity germinal mosaicism supposed autosomal recessive vitamin E deficiency familial supposed autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database dysmorphism, bulbous/pear-shaped nose, protruding ear, spars hair, exostoses multiple cartilaginous, joint laxity, mental retardation, cone epiphyses, ocular changes. congenital persistent hypotonia, respiratory acidosis, hyperlysinemia, other biochemical defects due to disorder in unsaturated fatty acid oxidation. tumor of the parotid gland, usually benign, with occasionally local recurrences. growth retardation with mild/without mental retardation, microcephaly, birdlike facies, hip dislocation, renal anomalies, infections from cellular/humoral immunodeficiency, with normal serum AFP levels; chromosome disorders resembling Louis-Bar disease. clinical stigmata of congenital hypothyroidism, goiter, mental/growth retardation. short stature, sparse scalp hair, pearshaped nose, long philtrum, heavy medial eyebrows, cone-shaped epiphyses, other skeletal anomalies. Bibliography[OMIM]: 259730 Prenat.Diagn.19,182,1 999 600131 Am.J.Hum.Genet.63,1 117-1129,1998 Nature Genet.14,214217,1996 601455 148900 150230 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 290 153840 226670 28799 Am.J.Hum.Genet.64,5 63-569,1999 222745 181030 251260 J.Med.Genet.34(3),196 -202,1997 274900 190350 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 292 malabsorption, steatorrhea, neurological 277460 dysfunctions, ataxia, spinocerebellar 600415 degeneration, areflexia, xanthomas, defective tocopherol-binding protein. chromosome 8q localization 41 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Zellweger syndrome 3 Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: autosomal recessive prenatal growth failure, severe hypotonia, feeding difficulties, convulsions, hepatomegaly, cerebral depression, cataract, choroidoretinal changes, other oculo-visceral anomalies, single umbilical artery, stippled chondral calcification. 170993 Prenat.Diagn.20,520521,2000 autosomal dominant acute attacks of abdominal pain, neurologic defects, paralysis, constipation, hallucinations, depression, photosensitivity. gene encoding a human leukocyte alpha(1,3)-fucosyltransferase synthesizing the sialyl Lewis x moieties. late onset benign myopathy, usually after 50 years, involving pelvic and shoulder girdles with characteristic cytoplasmic inclusions. 121300 light brown skin/hair, nystagmus, reduced retinal pigmentation, foveal hypoplasia, iridal dyschromia, choroidoretinal defects. depigmented skin with red/red-brown hair, nystagmus, reduced retinal pigmentation, iridal dyschromia, foveal hypoplasia. congenital flexion contractures, tight first hand, equinovarus/calcaneovalgus deformity, normal intelligence. Phenotype overlapping FreemanSheldon syndrome. 203290 chromosome 9 localization coproporphyria fucosyltransferase 7 myopathy inclusion body 1 autosomal dominant 602030 147420 601073 chromosome 9p localization albinism oculocutaneous IV brown type autosomal recessive albinism oculocutaneous rufous type supposed autosomal recessive arthrogryposis distal I autosomal dominant bone dysplasia-malignant fibrous histiocytoma autosomal dominant Boon syndrome autosomal dominant dicarboxylic aminoaciduria supposed autosomal recessive galactosyltransferase deficiency autosomal recessive hyperglycinemia nonketotic I autosomal recessive hyperglycinemia nonketotic II autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database 278400 108120 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 172 areas of diaphyseal necrosis in the large 112250 tubular bones changing in malignant fibrous histiocytoma/fibrosarcoma. Hum.Molec.Genet venous malformations in the tongue 3,1583-1587,1994 causing mandibular and maxillary deformation; cutaneous/mucosal 600195 venous malformations in other regions. Present at bith or puberty onset. hypoglycemia after mild fasting, ketosis. 222730 jaundice, hepatomegaly, anorexia, weight loss, vomiting, hypotonia, cataract, lethargy. early infancy onset; hypotonia, severe mental retardation, myoclonia, seizures, lethargy, hiccough; hyperglycinemia due to defect in enzyme of the glycinecleavage system different from NKH2 and NKH3. early infancy onset; mental retardation, hypotonia, seizures, lethargy; hyperglycinemia due to defect in enzyme of the glycine-cleavage system different from NKH1 and NKH3. chromosome 9p localization 230400 238300 Prenat.Diagn.19,717720,1999 238310 42 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: hyperglycinemia nonketotic III autosomal recessive interferon deficiency autosomal dominant male-determining factor defect autosomal dominant autosomal dominant 238330 early infancy onset; mental retardation, seizures, hypotonia, lethargy; hyperglycinemia due to defect in enzyme of the glycine-cleavage system different from NKH2 and NKH1. 147660 decreased resistance to viral infections/antibody sinthesis/natural killer cell activity, due to interferon decreased levels/unresponsiveness. sex reversal male 46,XX, with phenotype 154230 resembling Klinefelter syndrome. melanoma malignant supposed autosomal dominant undefinable cutaneous melanoma, developing in congenital giant nevocellular nevus. Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome autosomal dominant metaphyseal dysplasia Mckusick type autosomal recessive sudden swelling of lips/facial structures, peripheral facial nerve paralysis, fissured tongue, other clinical data. short limbed dwarfism, metaphyseal dysostosis, fine sparse light hair, anemia, malabsorption, Hirschsprung disease, chickenpox susceptibility. testis-determining factor mutation supposed autosomal recessive trichoepitheliomas autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity Genomics 22,243244,1994 600134 155600 190020 116806 123829 155900 250250 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 384 273350 sex reversal, 46,XY, female external genitalia and uterus, immature testicular tissue containing Sertoli cells but not germinal cells, due to postulated failure of a recessive gene on chromosome region 9p24. translucent papules/nodules, increasing 132700 in number and size, involving nasolabial 601606 folds, nose, forehead, upper lip, external ears; scalp, neck, upper trunk characteristic horn cysts, resembling basal cell epithelioma. May be associated with cylindromatosiss. chromosome 9q localization acrofacial dysostosis Nager type supposed autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity adenylate kinase deficiency supposed autosomal recessive ataxia Friedreich type autosomal recessive supposed genomic imprinting basal cell nevus syndrome autosomal dominant cardiomyopathy dilated-1B autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database 154400 radial ray defects, lower lid coloboma, malar hypoplasia, cleft palate, deafness. Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 258 nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. 201600 spinocerebellar degeneration before adolescence onset, incoordination, dysarthria, sensory ataxia, nystagmus, tendon reflexes diminished, pes cavus, hammer toe, cardiac dysfunction. Potentially paternal imprinting. cutaneous carcinomas, jaw cysts, skeletal anomalies, cerebral calcification, calcified falx cerebri, choroidoretinal defects, iridal changes, ocular cysts, craniofacial anomalies. dilated cardiomyopathy, heart failure, ventricular arrhythmia, sudden death. chromosome 9q localization 229300 109400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 528 Am.J.Hum.Genet.57,8 46-852,1995 600884 43 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: carnitine acetyltransferase deficiency autosomal recessive intermittent ataxia, ophthalmoplegia, hypotonia, mental disturbance. chorea-acanthocytosis syndrome autosomal recessive supposed autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity citrullinuria autosomal recessive complement component C5 deficiency autosomal dominant progressive chorea, oral-facial dyskinesia, frequent tongue-biting, acanthocytes in peripheral blood, normal betalipoproteinemia, seizures, occasionally mental retardation. 215700 severe vomiting, poor sucking, mental retardation, early onset ammonia intoxication, lethargy, hepatomegaly, hypotonia, apnea, seizures. 120900 seborrheic dermatitis, severe diarrhea, recurrent systemic infections, wasting. contracture multiple Finnish type supposed autosomal recessive corneal dystrophy lattice type II autosomal dominant sporadic marked fetal hydrops, multiple congenital contractures resembling Pena Shokeir I, facial anomalies, brain changes, joint dislocations, lung hypoplasia, generalized thinning of tubular bones. cranial neuropathy, adult onset corneal dystrophy , thickening of the skin. deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-11 autosomal recessive autosomal recessive deafness. May be the same as DFNB7. deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-7 autosomal recessive congenital neurosensory deafness. May be the same as DFNB11. dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency sporadic supposed autosomal recessive dysautonomia I autosomal recessive Ehlers-Danlos I autosomal dominant after birth cyanosis, hypotonia , vomit, hypotermia, hypoglycemic coma, facial muscle weakness, ptosis, severe orthostatic hypotension, syncope, ECG anomalies, brachydactyly. tears absence, fungiform papillae absent, insensitivity to pain, vasomotor instability, episodic fever, optic atrophy, incoordination, abnormal sweeting, other clinical data. loose jointendness, fragile/bruisable skin, 'cigarette-paper' scars, premature born, vessels/bowel rupture, bowel diverticula, hernia, retinal detachment, bladder diverticula. Ehlers-Danlos II supposed autosomal dominant epithelioma Ferguson-Smith type autosomal dominant Fanconi pancytopenia type 1 autosomal recessive Fanconi pancytopenia type 3 autosomal recessive fructose-1,6- diphosphatase deficiency autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: Genomics 23,9499,1994 600184 200150 253310 105120 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.234 Am.J.Hum.Genet.59,3 85-391,1996 Hum.Molec.Genet.4,23 91-2394,1995 600974 223360 223900 130000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 482 130010 mild joint hypermobility, velvety skin, mild propensity for bruising, parchmentlike scars over shins, joint laxity confined to the hands/feet,minimal cutaneous involvement. 132800 multiple keratoacanthomas resembling squamous epithelioma, self-healing, leaving deep pitted scars, with irregular overhanging, crenellated borders. 227650 low birth weight, anemia, WKURPERF\WRSHQLD FDIäDXODLW VSRWV Smith's Recognizable thumb defect/ supernumeray, renal Patterns of Human anomalies, chromosomal breakage. Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 320 Fanconi syndrome due to 227645 complementation group C. neonatal onset, hyperventilation, apnea, 229700 convulsions, lactic acidosis, hypoglycemia, ketosis, coma, occurring in the fasting state or febrile infections. chromosome 9q localization 44 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: fructosemia autosomal recessive Fukuyama syndrome autosomal recessive failure to thrive, vomiting, hepatomegaly, cirrhosis, ascites, jaundice, hypoglycemia, seizures. generalized weakness, hypotonia, cataract, choroidoretinal changes, optic atrophy, mental retardation, seizures, micro-lissencephaly. hypomagnesemia X-linked genetic heterogeneity hypomelanosis of Ito supposed autosomal dominant leukemia acute pre-B-cell transcription factor-3 acute leukemia. nail-patella syndrome supposed multifactorial undefinable autosomal dominant nephronophthisis infantile autosomal recessive infantile onset; polycystic kidneys, renal failure, nephronophthisis. neuropathy sensory radicular autosomal dominant platelet CO deficiency supposed autosomal dominant porphyria acute hepatic autosomal recessive porphyria acute hepatic severe infantile-onset autosomal dominant Rendu-Osler-Weber 1 autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-deafness autosomal dominant autosomal dominant juvenile onset; perforating ulcers of the feet, shooting pains, deafness. bleeding tendency due to platelet cyclooxygenase (CO) defect. acute hepatic porphyrias, mimics acute toxic porphyria from lead poisoning, but without sideroachrestic anemia. abdominal colic, constipation, hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, seizures, hemolytic anemia, other clinical data. skin/mucous membranes telangiectasias, pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas, choroidoretinal changes, recurrent nasal/gastrointestinal/bladder hemorrhage with normal coagulation factors, renal vascular malformations. retinitis pigmentosa, sensorineural deafness, subclinical myopathy. stomatocytosis I autosomal dominant torsion dystonia 1 autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant genomic imprinting tuberous sclerosis-1 Genus Clinical Database early weeks of life onset; convulsions, tetany, hypocalcemia, diarrhea, other findings. It was thought in the past Xlinked recessive. mental retardation, seizures, asymmetrical whorl-like hypopigmentation areas, ocular changes, other findings. hypoplastic nails, patella absent, elbows movements reduction, iliac horns, nephropathy, cataract, corneal clouding, iridal changes, other defects. Bibliography[OMIM]: 229600 253800 156225 Hum.Genet.99,535540,1997 Hum.Molec.Genet.6,14 91-1497,1997 602014 146150 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 504 176312 161200 Prenat.Diagn.19,287,1 999 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 438 Am.J.Hum.Genet.63,1 404-1410,1998 602088 162400 176805 125270 12527.0001 187300 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 524 Brit.J.Ophthl.81,207213,1997 601850 185000 hemolytic anemia with pale-staining bands and increased osmotic fragility. 128100 juvenile onset; involuntary movements, dystonic posturing, worsing under stress. facial adenoma sebaceum (angiofibroma), epilepsy, mental retardation, vitiligo, ocular changes. Potentially maternal imprinting. Possibility of brain tumor, includind astrocytoma. Occasionally detection cranial abnormalities, rabdomyosarcoma in prenatal eepoch. chromosome 9q localization 191100 Prenat.Diagn.19,575579, 1999 J.Med.Genet.20,303312, 1983 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 506 45 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Walker-Warburg syndrome autosomal recessive hydrocephalus, agiria, retinal dysplasia, microphthalmos, cataract, corneal clouding, ocular cysts, primary glaucoma, myopathy. xeroderma pigmentosum I autosomal recessive photosensitivity, skin tumors, poikiloderma, keratoacanthomas, freckling, photophobia, cataract, other ocular changes. xeroderma pigmentosum III autosomal recessive xeroderma pigmentosum type C, keratoacanthomas, particularly prone to malignant melanoma; occasionally cataract, corneal clouding. 278730 xeroderma pigmentosum of complementation group D, linkage with trichothiodystrophy; xeroderma pigmentosum of complementation group H, linkage with Cockayne syndrome. Occasionally ocular changes. UVinduced skin tumors. 278810 ninth complementation group of xeroderma pigmentosum. xeroderma pigmentosum IV/VIII autosomal recessive xeroderma pigmentosum IX supposed autosomal recessive Bibliography[OMIM]: 236670 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 192 278700 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 552 278720 chromosome 10 localization diabetes mellitus insulindependent10 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus insulin dependent. prostate adenocarcinoma sporadic prostate adenocarcinoma androgenundependent. sialidosis I supposed autosomal recessive second decade onset; decreased visual acuity, cherry red spots, cataract, corneal opacity, myoclonus without somatic/bony abnormalities. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. No mental retardation. Hum.Mol.Genet.6,101 1-1016,1997 601942 Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci. USA 93(6),25512556,1996 601188 256550 chromosome 10p localization anemia pernicious juvenile autosomal recessive DiGeorge 1 syndrome contiguous genes supposed autosomal dominant DiGeorge 2 syndrome autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes Genus Clinical Database pernicious anemia due to selective intestinal malabsorption of Vitamin B12 with proteinuria. neonatal hypocalcemic tetany, dysmorphic dysmorphic face, cardiac defects, hypoparathyroidism, thymic agenesis, cortical areas lymph nodes depletion, infections susceptibility, weackness, 22q11 del. Included in CATCH 22 spectrum of malformations (cardiac,, abnormal face, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcaemia, 22 chromosoma deletion). neonatal hypocalcemic tetany, dysmorphic face, cardiac defects, hypoparathyroidism, thymic agenesis, cortical area lymph nodes depletion, infections susceptibility, weakness. Chromosome 10 assignment. chromosome 10p localization 261100 188400 601362 Prenat.Diagn.18,507510,1998 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 616 188400 601362 600594 46 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Refsum disease-hyperpipecolic autosomal recessive acidemia Refsum disease intemediate between infantile and adult form. Refsum syndrome adult type autosomal recessive velocardiofacial syndrome autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes retinal degeneration, other ocular defects including cataract, peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, muscular atrophy, deafness. submucous cleft, hypernasal speech, cardiac anomalies, other ocular defects, short stature, mental retardation, microcephaly, prominent nose with squared root. Chromosome 22q11 deletion. Included in CATCH 22 spectrum of malformations (cardiac, abnormal faace, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcaemia, 22 chromosoma deletion). Bibliography[OMIM]: Hum.Mol.Genet.4,196 3-1966,1995 600964 266500 192430 601362 Prenat.Diagn.18,507510,1998 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 266 chromosome 10q localization acrocephalosyndactyly Pfeiffer type autosomal dominant adrenal hyperplasia V autosomal recessive anterior segment mesenchymal autosomal dominant dysgenesis Apert syndrome autosomal dominant Apert-Crouzon syndrome autosomal dominant Bannayan-Zonana syndrome autosomal dominant Beare-Stevenson syndrome sporadic cardiomyopathy dilated-3 autosomal dominant Cockayne II syndrome supposed autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database craniosynostosis, osseous and/or cutaneous syndactyly, visceral defects, strabismus. mild hypertension, hypokalemic alkalosis, amenorrhea, absent sexual maturation, low plasma renin, ambiguous genitalia, prominent breast in males. visual acuity reduced, corneal opacification, cataract, iridal changes. Eye isolated anomaly. craniostenosis, acrocephaly, complete/partial fusion of the digits resembling a spoon, mild mental retardation. hand-foot malformation characteristic of Apert syndrome, associated with facial features of Crouzon disease, ocular anomalies. high birth weight, normal bone age, megalencephaly, hamartomas, macrosomia, multiple lipomas. Germline mutation of PTEN. mental retardation, progeroid facies, cleft palate, dental defects, dysmorphism, skull shape changes, acanthosis nigricans, haemangiomas, pyloric stenosis. dilated cardiomyopathy, conduction defect, sudden death. Cockayne syndrome due to a second complementation group. Prenatal growth failure, microcephaly, cryptorchidism, mental retardation, other finding during the first years, including cataract, choroidoretinal changes, sunken eyes, contractures, other defectss, reduced colony-forming of amniocytes after UV irradiation. chromosome 10q localization 101600 202110 107250 101200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 418 Prenat.Diagn.20,404406,2000 101200 153480 Natur.Genet.16,333334,1997 123790 J.Clin.Invest.98,13551360,1996 601493 216410 47 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Cockayne III syndrome supposed autosomal recessive colorectal familial cancer Lynch I supposed autosomal dominant undefinable Crouzon syndrome autosomal dominant Cockayne syndrome due to a third complementation group inducing ocular/neurovisceral changes. site-specific colonic cancer changes in bowel habit, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, anemia, weight loss, onset before 40 years. May be the same of Lynch II. Associated endometrial carcinoma/atypical hyperplasia, uterine leiomyosarcoma, renal/bladder carrcinoma, gastric/biliary carcinoma. craniosynostosis, exophthalmos, divergent strabismus, other ocular defects, cleft palate, dysmorphic facies, prognatism, mental retardation, atresic auditory meatus. deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-12 autosomal recessive congenital autosomal recessive sensorineural deafness. Dubin-Johnson disease autosomal recessive epidermolysis bullosa Disentis type supposed autosomal recessive mild icterus, due to chronic benign conjugated hyperbilirubunemia. adult, atrophic form of the disease with reduced hemidesmosomes. Gaucher disease variant type autosomal recessive Gaucher disease due to mutation in the saposin gene. glioma of brain supposed autosomal dominant infancy/childhood onset; seizures, progressive weakness, speech/visual disturbances, multifocal glioblastoma involving frontal-temporal lobes, other areas. GBM arises from astrocytic cells. hamartoma multiple autosomal dominant 158350 hexokinase deficiency hypermethioninemia genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive autosomal recessive extensive facial trichilemmomas, mucosal papillomatosis, fibromatosis, verrucous lesions throughout the facial orifices/ extensor surfaces, fibrocystic breast disease, intestinal polyposis, thyroid and other visceral tumors; mental retardation, increased intracranial pressure, cerebellar tonsils erniation, megalencephaly. Germ-line mutation of PTEN. hemolytic anemia. 250850 Jackson-Weiss syndrome supposed autosomal dominant keratomalacia autosomal dominant leukodystrophy metachromatic variant type autosomal recessive lipase pancreatic deficiency autosomal recessive medulloblastoma supposed autosomal dominant asymptomatic high levels of serum methionine, with liver methionine adenosyltransferase deficiency. enlarged great toes without thumb anomalies, craniosynostosis, midfacial hypoplasia. corneal malacia, due to low levels of retinol-binding protein. Eye isolated anomaly. clinical features resembling juvenile form of MLD, with half-normal arylsulfatase A levels. early infancy steatorrhea, normal growth and developmental. cerebellar dysfunction due to neoplasm of the posterior fossa frequently associated with isochromosome17q. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 10q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 216411 114500 190020 116806 123500 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 420 Hum.Mol.Genet.5,106 1-1064,1996 601386 237500 226650 249900 176801 137800 601969 601991 165220 165230 131550 235700 123150 180250 249900 176801 246600 155255 48 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: megacolon autosomal dominant multifactorial supposed genetic heterogeneity 142623 MEN 2 syndrome autosomal dominant costipation leading to neonatal intestinal obstruction or chronic constipation/obstipation, abdominal distention, deficiency/absence of ganglion cells. Neuroblastoma tendency. bilateral pheochromocytoma, multifocal medullary thyroid carcinoma, other clinical data. MEN 3 syndrome autosomal dominant morning glory-renal failure syndrome sporadic supposed autosomal dominant myopathy metabolic phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency autosomal recessive myopathy mitochondrialexternal ophthalmoplegia 1 autosomal dominant mitochondrial myopathy, progressive external ophthalmoplegia. ornithinemia autosomal recessive orofacial cleft 1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity genomic imprinting multifactorial myopia, reduced peripheral vision, choroidoretinal changes, cataract, unconstant proximal muscle weakness, mild alopecia, sideroblastic anemia. complete or incomplete clefts of the upper lip, unilateral or bilateral, including posterior alveolar processes, and anteriorly alae nasi. Potentially paternal imprinting. 157640 Prenat.Diagn.20,426431,2000 258870 partial epilepsy autosomal dominant polyposis coli juvenile autosomal dominant porphyria congenital erithropoietic autosomal recessive schizencephaly sporadic split-hand/foot deformity type 3 autosomal dominant thyroid carcinoma medullary Bibliography[OMIM]: 171400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 526 oro-facio-intestinal neuromas, hypotonia, 162300 marfan-like habitus, medullary thyroid carcinoma. 120330 usually congenital, unilateral optic disk coloboma, occasionally cataract, optic atrophy, renal failure. cramps, myoblobinuria, intolerance for 261670 exercises, gout, tophi, hyperuricemia, coronary sclerosis. 119530 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 236 idiopathic epilepsy; juvenile age of onset. Nature Genet.10,5660,1995 600512 174900 rectal bleeding, polyp prolapse, abdominal pain, diarrhea, due to isolated 600993 or multiple intestinal/frequently colonic Science 280,1086polyps, risks for malignant degeneration. 1088,1998 263700 pink/red urine, yellow/brown teeth, photosensitivity, skin lesions leading to severe deformities, hemolysis, splenomegaly. J.Neuropathol.Exp.Neu full thickness cleft within the cerebral rol.5,169-206,1946 hemisphere. Am.J.Hum.Genet.55,2 lobster-claw deformity, ectrodactyly. 1-26,1994 600095 familial medullary thyroid carcinoma. 155240 thyroid carcinoma papillary sporadic supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal dominant papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. 188550 urofacial syndrome autosomal recessive Usher ID syndrome autosomal recessive Wolman disease autosomal recessive 236730 hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, neuropathic bladder, without neurologic problems, peculiar face characterized by inverted facial expression when laughing. 601067 congenital deafness, vestibular dysfunction, retinitis pigmentosa. J.Med.Genet.33,7779, 1996 278000 vomit, steatorrhea, calcified adrenals, hepatosplenomegaly, neuromuscular disorders, anemia, ocular changes, triglyceride storage. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 10q localization 49 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: anemia pernicious congenital autosomal recessive olivopontocerebellar V autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxia 5 autosomal dominant megaloblastic anemia, onset age 1 with normal gastric acidity and mucosal morphology, mental retardation. cerebellar signs, rigidity, mental deterioration, dementia. gait distaubance, ataxia, dysarthria, age at onset from 10 to over 60 years, with clear anticipation. Bibliography[OMIM]: chromosome 11 localization 261000 164700 Nature Genet. 8,280284,1994 600224 chromosome 11p localization acatalasemia autosomal recessive adrenocortical carcinoma autosomal recessive aniridia 2 autosomal dominant atrophia areata autosomal dominant Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome autosomal dominant genomic imprinting supposed contiguous genes bladder cancer supposed autosomal dominant cardioauditory syndrome autosomal recessive cardiomyopathy hypertrophic-4 autosomal dominant relatively benign disease or in some cases severe gangrenous gingival lesions with teeth loss due to loss of catalase activity. virilism with adrenocortical dysfunction. 115500 total or partial absence of iris. Occasionally associated cataract and mental retardation. Eye isolated anomaly. Wilms tumor tendency. peripapillary choroid atrophy with wide tongue-shaped peripheral extension. Eye isolated anomaly. macroglossia, omphalocele, visceromegaly, gigantism, hypospadias, mental retardation, occasionally mild microcephaly, other defects, hypoglycemia, hyperinsulinemia. Adrenal carcinoma, Wilms tumor, neurohepatoblastoma , pancreatoblastoma tendency. Potentiially maternal imprinting. familial malignant bladder tumor. 106210 202300 108985 130650 600856 Prenat.Diagn.21,9698,2001 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 164 109800 190020 190070 220400 prolongation of the Q-T interval, ventricular arrhythmia, loss of consciousness, deafness, sudden death. Nature Genet.4,311heart failure induced by familial 313,1993 hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 600958 115197 ceroid lipofuscinosis late infantile autosomal recessive intellectual decline, ataxia, seizures, retinal degeneration, optic atrophy. Cytosomes with curvilinear profile in the uncultured amniotic fluid. complement component C1q A chain deficiency autosomal dominant clinical findings of systemic lupus erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. complement component C1q B chain deficiency autosomal dominant 120570 clinical findings of systemic lupus erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. complement component C1s deficiency autosomal dominant 120580 clinical findings of systemic lupus erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. DEFECT 11 chromosomic contiguous genes acrocephalosyndactyly, mental retardation, multiple exostoses, parietal foramina, cutaneous syndactyly, interstitial deletion 11p11.12p12. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 11p localization 204500 Prenat.Diagn.21,99101,2001 Prenat.Diagn.20,337339,2000 120550 601224 Am.J.Hum.Genet. 58,734-742,1996 50 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: diabetes mellitus insulindependent 2 exostoses multiple cartilagineous type II Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: autosomal dominant multifactorial autosomal dominant insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. 125852 multiple exostoses, osteosarcome susceptibility 133701 B.D.Encyclopedia 2112 p.177 Prenat.Diagn.21,143145,2001 Am.J.Dis.Child.147,10 72-1075,1993 fetal maternal lupus syndrome autosomal dominant bradycardia detected in utero, heart block, skin discoid lupus, rash in the newborn. fetal maternal Sjogren-Mikulicz syndrome autosomal dominant neonatal hemochromatosis induced by maternal Sjogren-Miculicz syndrome. Freeman-Sheldon syndrome variant type autosomal dominant Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,4 26-432,1997 601680 Glaser syndrome autosomal dominant gonadotropin isolated deficiency FSH supposed autosomal recessive dysmorphic face, short stature, arthrogryposis, microstomia. Intemediate disorder compared to Freeman-Sheldon syndrome. congenital cataract, late onset corneal dystrophy, nervous system defects. primary amenorrhea, high LH, undetectable FSH. anemia, jaundice, splenomegaly, acute hemolytic episodes by exposure to oxidant drugs/infections, Heinz-bodies in the erithrocytes due to unstable hemoglobin fraction. paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria associated with vomit, splenomegaly, sickness, due to unusual erythrocytes susceptibility to lytic action of complement; hemolysis, pancytopenia, positive acidifying hemolysis test, low leukocyte alkaline phosphatase leevels, decreased RBC acetylcholinesterase. Langerhans islets neoformation, convulsions, lethargy, severe persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. neuroblastoma tendency. hyperinsulinemia, normoglycemia/hyperglycemia, normal response to exogenous insulin, presence of the one-chain insulin precursor as the major fraction of circulating insulin. autosomal recessive type of idiopathic hypoparathyroidism. 140700 hemoglobin variants Heinz-body autosomal dominant hemoglobinuria paroxysmal nocturnal genetic heterogeneity hyperinsulism familial autosomal recessive hyperproinsulinemia autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism autosomal recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism X-linked lactate dehydrogenase A deficiency Nature Genet.7,463471,1994 229070 107271 256450 600509 176730 241400 307700 convulsions, neuromuscular irritability, tetany, spasms, hyperreflexia, oro-ocular defects including cataract. myoglobinuria due to LDHA defect. 150000 childhood onset; acute lymphocytic leukemia. 151390 liver cancer-1 supposed multifactorial undefinable autosomal dominant familial primary cancer of the liver. 114550 long QT syndrome 1 autosomal dominant lupus erythematous systemic supposed autosomal dominant supposed multifactorial 192500 QT interval abnormal prolungation, attacks of syncope, ventricular fibrillation. Prenat.Diagn.19,677680,1999 152700 fever, weight loss, cutaneous lesions, erythematous butterfly rash of the face, 601690 maculopapular rash after sunlight exposure, alopecia, symmetric arthritis, myalgia, renal disease, peripheral neuropathy, immunological disorders; occasionally fetal myocardittis/heart block. leukemia acute T-cell Genus Clinical Database chromosome 11p localization 51 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: nephropathy-XY gonadal dysgenesis Frasier type sporadic Niemann-Pick A autosomal recessive Niemann-Pick B autosomal recessive O'Donnell-Pappas syndrome autosomal dominant parietal foramina permagna autosomal dominant Perlman syndrome autosomal recessive prothrombin deficiency autosomal dominant rhabdomyosarcoma-1 autosomal recessive male pseudohermaphroditism, XY gonadal dysgenesis, renal failure, occurrence of gonadoblastoma but not Wilms' tumor. hepatosplenomegaly, acute neurologic deterioration, cherry red macular changes, nodular skin. Occasionally fetal ascites/oedema. hepatosplenomegaly, cherry red macular changes, hepatic failure, nodular skin. reduced visual acuity due to mild foveal hypoplasia, presenile cataract, peripheral corneal pannus. Eye isolated anomalies. isolated, enlarged, symmetrical, oval defects in the parietal bone on sagittal suture, and separated from each other by a narrow, bone bridge. Size and location (parietal and frontal) may vary within families, without clinical significance. Common in lesss than 2% of healthy newborns. Occasionally in some syndromic associations. macrosomia at birth, enophthalmos, dysmorphic face, prominent bifid xiphisternum, cryptorchidism, hypoglicemia, distended abdomen, renal hamartomas, with/without nephroblastomatosis. bleeding manifestations, ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, other hemorrhagic disorders. childhood onset; embrional tumor involving connective-muscular tissue, with a locus suggested on chromosome 11. severe combined immunodeficiency without B-lymphocytes. severe combined immunodeficiency B-cell negative Usher IC syndrome autosomal recessive WAGR syndrome autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes Wilms tumor I autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes Wilms tumor II autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes xeroderma pigmentosumnormal DNA repair supposed autosomal recessive severe autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa-deafness syndrome. Wilms tumor, mental deficiency, hydrocephaly, ambiguous genitalia, dysmorphism, aniridia, congenital cataract/other ocular defects. fixed abdominal mass in an upper quadrant, hematuria, hypertension, fever, abdominal pain. Occasionally congenital form. nephroblastoma producing a nonmobile mass in an upper abdominal quadrant, abdominal pain hematuria, hypertension, other clinical findings. Occasionally congenital form. xeroderma pigmentosum with normal DNA repair rates and defective postreplication repair. Bibliography[OMIM]: 136680 257200 257200 136520 168500 267000 Prenat.Diagn.18,11631168, 1998 176930 268210 J.Med.Genet.20,303312, 1983 Science 274,9799,1996 601457 276904 19407.0001 194072 194070 194071 278750 chromosome 11q localization Genus Clinical Database chromosome 11q localization 52 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: acromegaly supposed autosomal dominant 102200 Albers-Schonberg recessive type autosomal recessive albinism ocular-lentiginesdeafness syndrome autosomal dominant albinism oculocutaneous I autosomal recessive alphamethyl-acetoacetic aciduria amyloid neuropathy Van Allen autosomal recessive mitochondrial autosomal dominant coarsening of facial features, feet/hands soft-tissue swelling, large hands/feet, bony proliferation, diabetes, hypermetabolism, other hormones disturbances, associated neoplasia. blindness, choroidoretinal defects, optic atrophy, deafness, macrocephaly, hepatosplenomegaly, severe anemia, osteopetrosis, cataract. ocular albinism, iridal dyschromia, reduced visual acuity, photophobia, strabismus,choroidoretinal defects, deafness, lentigines. absence of skin/hair/eyes pigmentation, nystagmus, photophobia, choroidoretinal defects, iridal dyschromia, tyrosinase negative test. severe episodic ketoacidosis, acidotic coma subsequent neurologic damage. 105100 anal canal carcinoma supposed autosomal dominant onset age 35, neuropathy followed by nephropathy, peptic ulcer, hearing loss, cataract. squamous anal canal carcinoma. angioedema hereditary autosomal dominant apolipoprotein AI/CIII deficiency autosomal dominant ataxia with lactic acidosis II syndrome autosomal recessive ataxia-telangiectasia autosomal recessive ataxia-telangiectasia complementation group D autosomal recessive atopic IgE responsiveness autosomal dominant genomic imprinting multifactorial Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 1 autosomal recessive Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 2 autosomal recessive Bartter syndrome type 2 Genus Clinical Database abdominal pain, larynx edema, other visceral involvement. prematury coronary disease, mild corneal opacifications before age 40 in homozygotes, and before age 60 in heterozygotes; renal failure weight loss, weakness, hypotonia, vomiting, seizures, ataxia, nystagmus, lactic acidosis, respiratory distress. cerebellar ataxia, telangiectases, sinopulmonary infections, oculomotor apraxia, immunodeficiency, glucose intolerance, chromosomal anomalies. cerebellar ataxia, telangiectasia, sinopulmonary infections, oculomotor apraxia, immunodeficiency, chromosomal anomalies. increased risk of allergic manifestations, asthma, hay fever, eczema, due to exuberant IgE responses to minute amounts of antigen. Potentially maternal imprinting. postaxial polydactyly, hypogonadism, obesity, mental retardation, pigmental retinopathy resembling a cone-rod retinal degeneration. postaxial polydactyly, hypogonadism, obesity, mental retardation, pigmentary retinopathy. Chromosome 16q localization. failure to thrive, renal failure, vomit, hypokalemic alkalosis, salt wasting. chromosome 11q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 259700 103470 203100 203750 105580 106100 107680 266150 208900 Prenat.Diagn.19,542545,1999 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 196 208905 147050 600807 601690 209901 209900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 590 600359 Hum.Molec.Genet.6,17 -26,1997 Prenat.Diagn.19,671673,1999 53 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Best disease Inheritance: Synthesis: autosomal dominant short time of birth or later onset.Round central yellow deposit at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium. Macular degeneration looking like "an egg with sunny-side up" or a "scrambled egg". Eye isolated anomaly. markedly restricted/absent eye movements. Eye isolated anomaly. blepharoptosis-eye movements autosomal dominant absence cerebelloparenchymal III disease autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy 4B autosomal recessive deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-11 autosomal dominant first decade onset of progressive deafness. deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-12 autosomal dominant midfrequency hearing loss. deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-8 autosomal dominant congenital severe deafness. deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-2 autosomal recessive variable age onset of neurosensory deafness. diabete mellitus insulindependent 4 autosomal dominant multifactorial diabetes mellitus insulin-dependent. diabetes mellitus insulindependent 1 genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive epidermolysis bullosa Hallopeau-Siemens type autosomal recessive fish-eye disease supposed autosomal dominant fucosyltransferase 4 autosomal dominant glycogenosis V, autosomal recessive high bone mass autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant autosomal dominant juvenile onset, polyuria, polydipsia, antibodies to pancreatic islet beta cells, ketoacidosis, vascular changes, increased in autoimmuno diseases. severe destructive skin lesions, at birth or in infancy, involving mucosal surfaces, fingers fusion, severe contractures, ocular changes. massive corneal opacity, dyslipoproteinemia. locus associated to myeloid-associated surface antigen. childhood/juvenile onset; pain/stiffness, muscle swelling with exercise, myoglobinuria. hyperlipidemia combined supposed autosomal dominant hypertriglyceridemia autosomal dominant leukemia chronic lymphatic supposed autosomal dominant undefinable leukemia mixed-lineage autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 153700 135700 congenital mental retardation, cerebellar 213200 ataxia, loss of granule cells and heterotopic Purkinje cells. Hum.Mol.Genet.5,105 peroneal muscular atrophy, pes cavus, 1-1054,1996 leg atrophy, scoliosis. 601382 Hum.Mol.Genet.5,849852,1996 601317 Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,1 168-1173,1997 601842 II Workshop Eur.Work.Genet Hear Impair Milan 1996 601543 Nature Genet.16,188190,1997 600060 276903 Nature 371,161164,1994 600319 222100 226600 136120 104230 232600 high spinal bone-mineral density. Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,1 326-1332,1997 601884 dendency to obesity, hyperinsulinemia, glucose intolerance, increased incidence of coronaropathies, no tendon xanthomas, high levels of cholesterol and/or triglycerides. phenotype resembling hyperlipoproteinemia IV, premature coronaropathies, peripheral vascular disease without xanthomas. chronic lymphocytic leukemia, familial aggregation, occasionally autoimmune disease recurrence. mixed-lineage leukemia with translocation involving chromosome 11. 144250 chromosome 11q localization 145750 151400 159555 54 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: manic-depressive psychosis 1 autosomal dominant multifactorial manic-depressive psychosis 2 X-linked dominant elated/excited/irritable mood in manic symptomatology; impaired thought processes/disturbed thought, content and perceptual processes/allucinations in schizophrenic disorders. elated/excited/irritable mood in manic symptomatology; impaired thought processes/disturbed thought, content and perceptual processes/hallucinations in schizophrenic disorders. occipital encephalocele, microcephaly, Potter-like facies, oral-oculo-neural defects, kidneys/liver cysts, polydactyly, ambiguous genitalia, single umbilical artery, spleen acessory, other anomalies; occasionally Horner syndrome. MKS2 locus on 11q13. adulthood onset; dysfunctions due to usually nonmalignant adenomatosis of more than one endocrine gland, i.e. thyroid/parathyroid/pituitary/adrenal/panc reas; occasionally, pancreatic malignancy. short trunk, blindness, retinal detachment, pseudoglioma, cataract, other ocular changes, osteoporosis, deformities, fractures, joint laxity. milk teeth/permanent teeth premature delay, palmoplantaris keratosis resembling mal de Meleda, calcification of the dura madre. nonchromaffin paraganglioma; middle ear mass, inducing hearing loss, tinnitus, bleeding, vertigo, cranial nerve palsies, other disturbances. Maternal imprinting (inacivation of the PGL gene). POssibility of genetic anticipation. severe muscular hypotonia, seizures, mental retardation, other neurological disorders. attacks of abdominal pain, constipation, tachycardia, vascular spasms, ocular changes, peripheral neuropathy, psychiatric syndromes, increased porphobilinogen excretion. acute neurovisceral porphyria, without cutaneous photosensitivity, with dual enzyme deficiency in peripheral blood cells. decreased fetal movements, breech delivery, almond-shaped eyes, full cheeks, severe hypotonia, hypogenitalism, polyphagia, obesity, short stature, hypopigmentation, iridal changes. Potentially paternal imprinting. Meckel syndrome type 2 MEN 1 syndrome autosomal dominant osteoporosis-pseudoglioma syndrome autosomal recessive Papillon-Lefevre syndrome autosomal recessive paragangliomas autosomal dominant genomic imprinting phenylketonuria III autosomal recessive porphyria acute intermittent autosomal dominant porphyria Chester type autosomal dominant Prader-Willi syndrome autosomal dominant genomic imprinting supposed contiguous genes retinitis pigmentosa digenic autosomal dominant autosoma dominant retinitis pigmentosa due to RDS and ROM1 gene. schizophrenia-2 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity multifactorial undefinable autosomal dominant young/adult age onset; psychotic symptoms, hallucinations, personality disorders. T-cell antigen receptor defect Genus Clinical Database clinical findings of immunodeficiency severe combined. chromosome 11q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 125480 309200 Am.J.Hum.Genet.63,1 095-1101,1998 603194 131100 259770 245000 168000 601650 261640 176000 176010 176270 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 202 Prenat.Diagn. 20,300306,2000 Scienze 264,16041608,1994 180721 181500 186740 55 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: tuberous sclerosis-1 autosomal dominant genomic imprinting facial adenoma sebaceum (angiofibroma), epilepsy, mental retardation, vitiligo, ocular changes. Potentially maternal imprinting. Possibility of brain tumor, includind astrocytoma. Occasionally detection cranial abnormalities, rabdomyosarcoma in prenatal eepoch. Usher IB syndrome autosomal recessive deafness, retinitis pigmentosa. vitreoretinopathy exudative 1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity vitreoretinopathy neovascular inflammatory autosomal dominant 133780 posterior vitreous detachment, in all quadrants. could be the same gene as Norrie disease in X-linked form. Occasionally retinal changes resembling pseudoglioma. Eye isolated anomaly. 193235 neovascular inflammatory vitreoretinopathy, retinal detachment, vitreal hemorrhage. Eye isolated anomalies. 191100 Prenat.Diagn.19,575579, 1999 J.Med.Genet.20,303312, 1983 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 506 Nature 374,60-61,1995 276903 chromosome 12 localization Alzheimer type 5 autosomal dominant genomic imprinting late onset dementia. Bloom syndrome autosomal recessive colitis ulcerative multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant undefinable no genetic supposed autosomal recessive undefinable low birth weight, dwarfism, cutaneous rash due to sensitivity to sunlight, hypo/hyperpigmentation spots, severe immunodeficiency, thin face with large nose, chomosome defects, propensity for leukemia. nonspecific chronic inflammatory disease involving the bowel. Crohn disease hypervalinemia autosomal recessive J.A.M.A.278,12371241,1997 602096 210900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 104 191390 601458 terminal ileum nonspecific segmental/plurisegmental inflammatory disease, with acute and chronic course, gastrointestinal tumor tendency. mental growth retardation, hyperkinesis, vomiting, weakness. 266600 601458 200990 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 226 240600 277100 chromosome 12p localization acrocallosal syndrome supposed autosomal dominant corpus callosum hypoplasia, megalencephaly, hypertelorism, strabismus, prominent forehead, depressed nasal bridge, duplicated great toes and postaxial polydactyly. aglycogenosis autosomal recessive blepharoptosis-eye movements autosomal dominant absence neonatal hypoglycemia, fasting hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia after feeding, microcephaly, mental retardation, seizures, other neurological defects. markedly restricted/absent eye movements. Eye isolated anomaly. breast cancer familial familial bilateral breast cancer. Genus Clinical Database multifactorial undefinable chromosome 12p localization 135700 114480 190020 190070 188825 56 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: complement component C1qG deficiency autosomal dominant 120575 clinical findings of systemic lupus erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. complement component C1r deficiency autosomal recessive complement component C1s deficiency autosomal dominant 216950 infections, arthralgias, lupus-like features, other signs of immunodeficiency states. clinical findings of systemic lupus 120580 erythematous and/or glomerulonephritis. hypophosphatemic rickets autosomal dominant autosomal dominant macroglobulin alpha-2 deficiency autosomal dominant myelodysplasia--myeloid leukemia factor 2 short stature, osteomalacia, rachitic deformity, laboratory data typical of rickets. chronic lung disease due to severe emphysema. 193100 no genetic sporadic myelodysplastic syndrome and/or acute myeloid leukemia with MLF2 gene mutation. myoclonus-epilepsychoreoathetosis autosomal dominant myoclonus, epilepsy, dementia, ataxia, choreoathetosis with dentatorubral and pallidoluysian system degeneration. myokymia-ataxia syndrome supposed autosomal dominant olivopontocerebellar II autosomal recessive triosephosphate isomerase deficiency autosomal recessive von Willebrand disease autosomal dominant autosomal dominant periodic ataxia with associated jerking movements, provoked by various stimulations. juvenile/adult age onset; progressive cerebellar sensory ataxia, dysarthria. chronic, nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia, weakness, hypotonia,dystonia, dysarthria, dyskinesia, other neurological changes. prolonged bleeding time, decreased Factor VIII activity. Genomics 35,392396,1996 601401 125370 Clin.Genet.50(4),199201,1996 160120 103950 258300 190450 193400 chromosome 12q localization achondrogenesis II sporadic supposed autosomal recessive lethal neonatal chondrodysplasia, short trunk, very short limbs, enlarged normally ossified skull, absent ossification of the sacrum, pubis, lumbar vertebrae. acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency short chain organic aciduria, muscle weakness, myopathy, fatty liver. Allgrove syndrome autosomal recessive mitochondrial autosomal recessive Apert-Crouzon syndrome autosomal dominant brachydactyly C autosomal dominant cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome sporadic supposed autosomal dominant cardiomyopathy hypertrophic mid-cavity 2 autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database defective tear formation, achalasia, hyperpigmentation, adrenocortical deficiency and/or neurological abnormalities, periventricular brain heterotopias, optic atrophy, choroidoretinal changes. hand-foot malformation characteristic of Apert syndrome, associated with facial features of Crouzon disease, ocular anomalies. 2nd-3rd brachymesophalangy, long 4th finger, clynodactyly, hyperphalangy, symphalangism. pulmonic stenosis, other cardiac defects, dysmorphic facies, sparse hair, hyperkeratosis/ichthyosis-like, mental retardation. variant of cardiac hypertrophy characterized by thickening of the midleft ventricular chamber; associated abnormal skeletal muscle. chromosome 12q localization 200610 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 328 201470 231550 J:Chil.Neurol. 14(5),331-334,1999 101200 113100 115150 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 126 Nature Genet.13,6369,1996 57 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: cornea plana recessive type autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity corneal dystrophy epithelial juvenile type autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity congenital corneal deformity. In the recessive form, K readings (corneal refraction) may be as low as 23 diopters. Possibility of glaucoma later in life. Eye isolated anomaly. fine, punctate opacities in the epithelium/Bowman membrane. Eye isolated anomaly. diabetes insipidus nephrogenic genetic heterogeneity autosomal recessive supposed autosomal recessive diabetes mellitus noninsulinautosomal dominant dependent 2 polyuria, polydipsia, growth retardation, without renal tubular disease. diabetes noninsulin-dependent mellitus III autosomal dominant maturity-onset diabetes mellitus. epidermolysis bullosa Cockayne-Touraine type autosomal dominant serous sanguineous traumatic blisters, involving only hands/feet, mainly in warm weather after walking/hand labor. It is the mildest and commonest form of EBS. epidermolysis bullosa resembling simplex/dystrophic/atrophic EB forms, and dermatitis herpetiformis, aggregation of tonofilaments in basal cells with normal dermo-epidermal junction. It is the severest form of EBS. generalized serous non-scarring blisters, increasing in the warm season, mainly involving soles/toes, fingers, heels; normal teeth and nails, onset at birth or first months of life. generalized epidermal fragility, serous seasonal hands/feet blistering. epidermolysis bullosa Dowling- autosomal dominant Meara type late onset diabetes with reduced insulin secretory response. Bibliography[OMIM]: 217300 122100 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998, p.218 222000 Nature Genet.14,9094,1996 601407 J.Clin.Invest.99,582591,1997 600496 131800 131760 epidermolysis bullosa simplex Koebner type autosomal dominant epidermolysis bullosa simplex Ogna type autosomal dominant erythroderma ichthyosiformis bullous autosomal dominant congenital widespread areas of blisters, followed by generalized hyperkeratosis. 113800 glycogenosis VII autosomal recessive 232800 171860 hip dysplasia Namaqualand type supposed autosomal dominant histidinemia autosomal recessive Holt-Oram syndrome autosomal dominant juvenile onset; myopathy, hemolysis induced by exercises, recurrent jaundice, mild erythrocytosis, gout, hyperuricemia. choldhood onset; hip discomfort due to femoral capital epiphyses changes, with secondary degenerative arthropathy, platispondyly, other minor findings. hyper-histidinemia, mental retardation ,corpus callosum agenesis, other defects. thumb anomaly, atrial septal defect, other cardiac/limb defects. insulinoma autosomal dominant Kallmann syndrome 1 X-linked recessive keratoderma palmoplantaris Bothnian type autosomal dominant keratosis follicularis autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database diabetes due to insulinoma amyloid polypeptide. hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, anosmia, cryptorchidism; occasionally arhinencephaly, other clinical data. diffuse nonepidermolytic variety of palmoplantar keratosis. keratotic papules in seborrheic areas; occasionally mild mental retardation, seizures. chromosome 12q localization 131900 Prenat.Diagn. 20,371377,2000 131950 12014.0006 235800 142900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 316 147940 601707 Hum.Molec.Genet.3,17 89-1793,1994 600231 124200 58 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Kniest dwarfism autosomal dominant dysproportionate metatropic-like dwarfism, flat face, cleft palate, deafness, myopia, primary glaucoma, other ocular defects, kyphoscoliosis, lordosis, contractures, X-ray anomalies. leukokeratosis mucosal autosomal dominant lipomas symmetric familial autosomal dominant mevalonic aciduria autosomal recessive monilethrix autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity autosomal recessive present at birth; asymptomatic white folded soft hyperplastic lesions, involving oral/vaginal/anal other mucosae, often mistaked for leukoplakia. 151900 adult onset; gradually increased, multiple, encapsulated, subcutaneous lipomas from a few to several hundred. 251170 psychomotor/growth retardation, diarrhea, gastroentheropahies resembling cow's milk intolerance, hypotonia, microcephaly, seizures, mental retardation, dysmorphic triangular facies, cataract, hepatosplenomegaly. 158000 friable short beaded hair, baldness, follicular hyperkeratosis, cataract, other defects. mucopolysaccharidosis IIID myopia autosomal dominant 2 clinical features of Sanfilippo syndrome, due to N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase deficiency. congenital/shortly after birth familial myopia. Retinal detachment. Eye isolated anomaly. nocturnal enuresis 2 autosomal dominant nocturnal enuresis (nightly bedwetting) without other neurologic disorders such as spina bifida occulta. Noonan syndrome autosomal dominant short stature, dysmorphism, hypertelorism, webbed neck, pectus deformity, clynodactyly , other skeletal defects, pulmonary stenosis, mild mental retardation, skin pigmentation, hypogenitalism. olivopontocerebellar atrophy II autosomal dominant osteoarthritis-mild chondrodysplasia supposed autosomal dominant every age onset; sensory ataxia, cerebellar signs, dementia, optic atrophy, ophthalmoplegia. mild chondrodysplasia with primary generalized osteoarthritis. osteoarthrosis precocious Bibliography[OMIM]: 156550 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 360 193900 252940 603221 Am.J.Hum.Genet.63,1 419-1424,1998 J.Med.Genet.34,360365,1997 600808 163950 Prenat.Diagn.19,642647,1999 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 122 183090 12014.0003 autosomal dominant multifactorial pachyonychia congenita genetic heterogeneity Jadassohn-Levwandowsky type supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive early-onset familial osteoarthrosis. 165720 nail bed hypertrophy, red/yellow horn nails, skin/oral mucous lesions, hypodontia, short stature, mental retardation, ocular defects, intestinal diverticuli. phenylketonuria I autosomal recessive Rendu-Osler-Weber 2 autosomal dominant vomiting, seizures, irritability, mental retardation, eczematoid eruptions, blue eyes, blond hair, fair skin, "mousy" smell, due to phenylacetic acid in the urine and sweat. skin/mucous membranes telangiectasias, choroidoretinal changes, recurrent nasal/gastrointestinal/bladder hemorrhage, normal coagulation factors; pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas less frequent than HHT1. 167200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 548 261600 Genus Clinical Database chromosome 12q localization Hum.Molec.Genet.4,94 5-949,1995 600376 601284 59 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: rickets vitamin D-dependent type 1 autosomal recessive rickets-alopecia syndrome autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy adult type supposed autosomal dominant spinal muscular dystrophy Frijns type autosomal dominant first year onset; hypotonia, weakness, growth failure, enamel defects, bony deformities, fractures, convulsions, tetany, diminished renal synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. first years of age onset; hypotonia, weakness, growth failure, hypocalcemic rickets/osteomalacia, alopecia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, high 1,25(OH)2 D levels. progressive scapulo-humeral hypotonia, weakness, fourth/sixth decade onset, respiratory failure. nonprogressive, congenital spinal muscular atrophy of lower limbs, pes equinovarus, contractures of knees. spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenital type autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity prenatal growth deficiency, short trunk, dwarfism with retarded ossification, flat face, cleft palate, myopia, retinal detachment, cataract, hypotonia, deafness. spondylometaepiphyseal dysplasia congenita Strudwick type supposed autosomal dominant Stickler syndrome I autosomal dominant congenital disproportionate short trunkshort limb dwarfism, pectus carinatum, severe genua valga, normal skull/facies, cleft palate. slender body, congenital myopia, occasionally cataract, primary glaucoma, other ocular defects, flat faces, joints enlargement, epiphyseal changes, joint hyperextensibility. testiculat tumor supposed autosomal recessive Thomas myopathy autosomal dominant tuberous sclerosis-1 autosomal dominant genomic imprinting facial adenoma sebaceum (angiofibroma), epilepsy, mental retardation, vitiligo, ocular changes. Potentially maternal imprinting. Possibility of brain tumor, includind astrocytoma. Occasionally detection cranial abnormalities, rabdomyosarcoma in prenatal eepoch. tuberous sclerosis-3 autosomal dominant tyrosinemia III supposed autosomal recessive ulnar-mammary syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked dominant clinical features of tuberous sclerosis due to a gene mapping on chromosome 12. mild mental deficiency, without hepatic dysfunction. upper limbs anomalies, involving ulnar ray structures, apocrine-mammary defects, characterized by axillary hair, absence small/absent mammary glands and nipples. testicular teratoma; germ cell tumor; seminoma. More than coincidental association with Klinefelter syndrome. muscular scapuloperoneal dystrophy. Bibliography[OMIM]: 264700 277440 601769 158590 Muscle Nerve 17,192197,1994 600175 183900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 358 184250 108300 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 282 273300 181430 191100 Prenat.Diagn.19,575579, 1999 J.Med.Genet.20,303312, 1983 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 506 191091 276710 181450 chromosome 13 localization breast cancer ductal-1 sporadic undefinable carboxypeptidase N deficiency autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database 211410 176705 188825 angioedema, chronic urticaria, hay fever, 212070 asthma. frequently bilateral multifocal breast cancer in premenopausal women or in males. chromosome 13 localization 60 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: chromosome 13p localization muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2A 253600 second decade onset; hip/shoulder proximal muscles weakness, difficulty climbing, stairs/holding hands above head, low back pain, occasionally cardiomyopathy/pseudohypertrophy/high serum creatine kinase levels. chromosome 13q localization adamantinoma of long bones supposed autosomal dominant bladder cancer supposed autosomal dominant cataract zonular pulverulent 3 autosomal dominant congenital caratact.Eye isolated anomaly. ceroid lipofuscinosis Finnish variant late infantile type autosomal recessive deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-3 autosomal dominant deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-1 autosomal recessive Dubin-Johnson disease autosomal recessive ectodermal dysplasia, hydrotic autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity Factor VII deficiency autosomal recessive Factor X deficiency autosomal recessive HHH syndrome autosomal recessive mitochondrial hyperglycinemia ketotic I autosomal recessive first months of age onset; microcephaly, seizures, ataxia, retinal degeneration, optic atrophy, psychomotor decline, loss of speech; pathologic inclusion body. Hum/Mol.Genet.3,221 dominant form of neurosensory 9-2222,1994 deafness; could be the same gene of DFNB1. 601544 220290 congenital autosomal recessive neurosensory deafness. Could be the same gene of NSDD1. 237500 mild icterus, due to chronic benign conjugated hyperbilirubunemia. 129500 spars hair, scanty eyelashes, cataract, brows dystrophic nails, thick pigmented Smith's Recognizable palms/soles skin, normal sweet glands Patterns of Human and teeth. Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 546 bleeding manifestation from birth, 227500 neurologic complications, protrombin time prolonged with normal partial thromboplastin time, reduced Factor VII activity. 227600 congenital bleeding, ecchymosis, epistaxis, menorrhagia, hematuria, other hemorrhagic manifestations, even after trauma or surgery. 238970 protein intollerance, seizures, vomit, tremor, paraparesis, hemihypotrophy, spastic diplegia, hemiparesis, hemiathetosis, mental retardation, lethargy, hyperammonemic coma, mitochondrial changes. 232000 early onset; vomiting, acidosis, leokopenia, thrombocytopenia, infections, transient purpura, mental retardation, variable neurological findings. Genus Clinical Database low-grade malignant tumor of unknown histogenesis, involving long bones, particularly the tibia. familial malignant bladder tumor. chromosome 13q localization 102660 109800 190020 190070 Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,1 474-1478,1997 601885 256731 61 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Letterer-Siwe disease autosomal recessive megacolon autosomal dominant multifactorial supposed genetic heterogeneity microcoria congenital supposed autosomal dominant Moebius syndrome supposed autosomal dominant infancy onset; usually acute fulminating disorder, fever, anemia, cutaneous rash, mucous bleeding, very enlarged spleen and liver, pulmonary involvement, multiple osteolytic areas, typical histiocytes disseminated proliferation. costipation leading to neonatal intestinal obstruction or chronic constipation/obstipation, abdominal distention, deficiency/absence of ganglion cells. Neuroblastoma tendency. small pupils due to hypoplasia of the iris dilator muscle. Eye isolated anomaly. mask-like facies, bilateral facial diplegia, strabismus. muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2C nocturnal enuresis 1 autosomal dominant Oguchi disease autosomal recessive osteogenic sarcoma supposed autosomal recessive pancreas congenital hypoplasia supposed autosomal recessive before 5 years of age onset; in both sexes, pelvic weakness, slow progression, calves pseudohypertrophy,ability to walk until adult age, cardiomyopathy in later age, high serum creatine kinase levels. nocturnal enuresis (nightly bedwetting) without other neurologic changes such as spina bifida occulta. stationary nightblindness, peculiar fundus discoloration, modified by dark adaptation. Eye isolated anomaly. usually secon decade of life onset; pain tender mass at the metaphyseal end of a long bone, frequent high alkaline phosphatase levels. intrauterine growth retardation, earlyonset insulin dependent diabetes, diarrhea. white pupillar "cat's eye reflex", strabismus, typical ophthalmoscopic changes. Occasionally, detected in fetus. Eye isolated anomaly. iris/cornea dysgenesis associated with other clinical changes. Primary glaucoma. retinoblastoma autosomal dominant Rieger sequence-2 autosomal dominant Stargardt disease-2 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity progressive macular dystrophy with flecks.Eye isolated anomaly. Viljoen-Smart syndrome supposed autosomal dominant microphthalmos, microcornea, mental retardation, cleft lip/palate, de novo 6;13 translocation. Wilson disease autosomal recessive xeroderma pigmentosum VII autosomal recessive hepatic dysfunction, corneal kayserfleischer ring, "sunflower cataract (chalcosis lentis), ataxia, tremor, other neurological defects. normal or mild physical/neurologic developmental delay, with mild cutaneous changes and without UVinduced tumors; keratoacanthomas, other clinical changes. Bibliography[OMIM]: 246400 142623 156600 157900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 230 253700 600119 Prenat.Diagn.18,13001303, 1998 Nature Genet.10,354356,1995 600631 258100 259500 260370 180200 601196 600697 Am.J.Hum.Genet.59,6 13-619,1996 601499 Am.J.OphThal.117,545 -546,1994 153900 Clin.Dysmorph.2,274277,1993 601349 277900 278780 chromosome 14 localization Genus Clinical Database chromosome 14 localization 62 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: achromatopsia autosomal recessive mucopolysaccharidosis IIIC autosomal recessive porphyria variegata autosomal dominant absence of cone function, normal rod function. Eye isolated anomaly. phenotype of Sanfilippo syndrome, due to alpha-glucosamide Nacetyltransferase deficiency. photosensitivity, skin lesions, vesicles, bullae, erosion, scarring, hypertrichosis, chronic or acute attacks of peripheral/abdominal pain, motor paralysis, seizures, other neurological signs. Bibliography[OMIM]: 216900 252930 176200 chromosome 14p localization paraplegia spastic hereditary-3 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity variable age of onset, progressive spastic paraplegia. 182600 chromosome 14q localization agammaglobulinemia nonBruton type autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity agammaglobulinemia due to blockage in J.Clin.Invest.98,15191526,1996 differentiation of the proB cells. 601495 Alzheimer type 1 autosomal dominant genomic imprinting multifactorial supposed mitochondrial autosomal dominant genomic imprinting multifactorial autosomal dominant dementia with onset before or after age 65. Potentially paternal imprinting. 104300 Alzheimer disease late onset dementia. Potentially paternal imprinting. 104310 early onset, presenil Alzheimer disease. 104311 antichymotrypsin alpha1 deficiency autosomal dominant 107280 antitrypsin alpha-1 deficiency autosomal recessive cardiomyopathy dilated right ventricular-1 autosomal dominant cardiomyopathy dilated right ventricular-3 autosomal dominant wide ranges of liver and lung involvement, chronic hepatitis, asthmalike disease. emphysema, breath shortness, neonatal cholestasis, cirrhosis. arrhythmias, sinoatrial/atrioventricular block, embolism, tachycardia, right ventricle dilatation, characteristic ECG, angiographic features, sudden death. arrhytmia, sinoatrial/atrioventricular block,embolism, tachycardia, right ventricular dilatation, characteristic ECG, angiographic features, sudden death. left ventricle hypertrophy, muscular subaortic stenosis, fatigability, dyspnea, angina, arrhythmia W-P-W type. cataract anterior polar. dense white opacities of the central part of the anterior lens capsule.May be associated with other congenotal malformations of the anterior segment of the eye. Eye isolated anomaly. generalized taut, shiny encasemnt at birth, including the face, defined as 'collodion membrane'. Alzheimer type 2 Alzheimer type 3 cardiomyopathy hypertrophic-1 autosomal dominant cataract anterior polar 1 autosomal dominant collodion baby autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database chromosome 14q localization 107400 107970 Brit.Heart J.71,215218,1994 602086 192600 160760 115650 242300 63 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: cystinuria I autosomal recessive deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-9 autosomal dominant radio-opaque cystine calculi, renal/ureteral colic, hematuria, disuria, urinary tract infections, unconstant short stature, mental retardation, psychiatric disturbance. Normal aminoaciduria in heterozygotes. progressive postlingual sensorineural deafness. deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-5 autosomal recessive early onset neurosensory deafness; diabetes mellitus insulindependent 11 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus, insulin-dependent. dibasicaminoaciduria II autosomal recessive erythroderma ichthyosiform nonbullous recessive autosomal recessive factor V-VIII combined deficiency autosomal recessive fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva autosomal dominant glycogenosis VI autosomal recessive goiter familial autosomal recessive failure to thrive, vomiting, hepatosplenomegaly, hypotonia, osteoporosis, stupor/lethargy, occasionally mental retardation, lens opacities. severe generalized hyperkeratotic cornification, with large dark scales, facial tautness, ectropion, spared hair, characteristic ultrastructural changes. congenital hemorrhagic disorder due to combined deficiency of factor V and factor VIII. firm, warm, tender, subcutaneous masses becoming bony hard in consistency, short hallux, hypogenitalism, deafness, severe restriction of movement, fractures, mild mental retardation, new extracartilage and bone formations; childhood onset. hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, hypotonia, growth retardation. congenital goiter; thyroglobulin low levels. goiter multinodular of adolescent autosomal dominant juvenile onset; nontoxic goiter with firm, nodular calcification without defects in thyroid hormonogenesis. holoprosencephaly 4 autosomal dominant Holt-Oram syndrome autosomal dominant semilobar holoprosencephaly, hypotelorism, ptosis, nasal septum absence, midline cleft lip-palate.other clinical data. thumb anomaly, atrial septal defect, other cardiac/limb defects. hyper-immunoglobulin G1(A1) syndrome supposed autosomal dominant chronic fatigue, autoantibodies modified levels, other clinical-laboratory data. immunoglobulin gamma 1 deficiency autosomal dominant recurrent pyogenic infections, due to gammaglobulin 1 deficiency. 147100 immunoglobulin gamma 2 deficiency autosomal dominant recurrent pyogenic infections, due to gammaglobulin 2 deficiency. 147110 immunoglobulin gamma 4 deficiency autosomal dominant recurrent pyogenic infections, due to gammaglobulin 4 deficiency. 147130 Genus Clinical Database chromosome 14q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 220100 Hum.Mol.Genet.5,104 7-1050,1996 601369 Hum.Mol.Genet.4,164 3-1648,1995 600792 Genomics 33,1-8,1996 601208 222700 Prenat.Diagn.19.771773,1999 242100 227300 135100 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 492 232700 600635 J.Biol.Chem.270,81088114,1995 601843 188450 138800 601843 188450 142946 142900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 316 144120 64 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: leukemia-lymphoma T-cell supposed multifactorial undefinable leukodystrophy globoid cell type autosomal recessive Machado-Joseph syndrome autosomal dominant microphthalmos autosomal recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity nucleoside phosphorilase deficiency autosomal dominant oculopharyngeal myopathy syndrome autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant erythroderma, skin infiltrations, neutropenia, hepatosplenomegaly without lymphadenopathy, neurological involvement. severe mental retardation, motor deterioration, hypertonicity, opistothonus, optic atrophy, deafness, decerebrated status. late onset ataxia, parkinson-like features, nystagmus, muscle atrophy, rare faciolingual fascilulations, diabetes mellitus. slight/severe reduction in size of the globes, anophthalmos, ocular cysts. Occasionally retinalk changes resembling pseudoglioma. Eye isolated anomaly. ataxia, hemolytic anemia, recurrent infections, severely depressed T-cell immunity with usually normal B-cell immunity. dysphagia, bilateral ptosis, external ophthalmoplegia, proximal muscle dystrophy; late onset. olivopontocerebellar III phenylketonuria atypical severe autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa autosomal recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity sclerosis multiple multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant situs inversus viscerum supposed autosomal recessive spherocytosis type I autosomal dominant thyrotropin unresponsiveness supposed autosomal recessive torsion dystonia Segawa type autosomal dominant transcortin asymptomatic decreasing/increasing autosomal dominant ulnar-fibular dimelia sporadic Usher IA syndrome autosomal recessive Usher IIA syndrome autosomal recessive Welander dystrophy autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 186880 245200 109150 251600 164050 164300 ataxia, dysarthria, characteristic retinal changes, infancy/adult onset. severe muscular trunk hypotonia, and limbs hypertonia, seizures, hyperthermia without infections, mental retardation. infantile, juvenile, adult onset; retinitis pigmentosa. 164500 motor/sensory problems, optic neuritis, vertigo, diplopia, bladder/bowel disturbances. in total situs inversus: complete transposition of gastrointestinal tract with normal stomach position and liver on the left side, dextrocardia. hemolytic anemia, spherocytosis. 126200 233910 268000 180072 270100 182870 275200 clinical stigmata of congenital hypothyroidism, mental/growth retardation, normal size of the thyroid gland. 128230 insidious infancy onset; postural/motor disturbance showing marked diurnal fluctuation, alleviated after sleep and aggravated toward evening; improvement by L-DOPA administration. 122500 asymptomatic, low/high cortisol plasmatic concentration. double ulna and double fibula, absence of tibia and radius, mirror hands, partial nasal cleft, peculiar facies. profound congenital deafness, with retinitis pigmentosa by age 10, occasionally cataract, sensory ataxia, mental retardation. moderate/severe congenital deafness, occasionally cataract, retinitis pigmentosa in late teens. adult life onset; weakness of hand movements, spreading proximally to the forearm; usually, muscle legs are spared or involved later. chromosome 14q localization 135750 276900 276901 160500 65 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: chromosome 15q localization adrenal hyperplasia I autosomal recessive albinism oculocutaneous II autosomal recessive Albright osteodystrophy-2 amyloidosis hemodialysis related undefinable amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 5 hypospadias, external genitalia failure, undergo masculine development, error in adrenal metabolism. decreased skin/hair/eyes pigmentation, nystagmus, photophobia, choroidoretinal defects, iridal dyschromia, tyrosinase positive test. short stature, obesity, round face, brachydactyly, fourth/fifth short matacarpals, absent 4th knuckles, ectopic calcification/ossification, mental retardation, cataract, iridal changes, hypocalcemia, parathyroid hyperplasia, high PTH levels. chronic renal failure, carpal tunnel syndrome, spondyloarthropathy, lytic bone lesions. juvenile onset with slow progression; weakness, hypotonia, muscular atrophy, spastic amyotrophy. Andermann disease autosomal recessive Angelman syndrome genomic imprinting supposed autosomal recessive supposed contiguous genes Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 2 autosomal recessive postaxial polydactyly, hypogonadism, obesity, mental retardation, pigmentary retinopathy. Chromosome 16q localization. Bartter syndrome type 1 autosomal recessive Bloom syndrome autosomal recessive corpus callosum agenesis, mental retardation, peripheral neuropathy, choroidoretinal changes, optic atrophy, dysmorphism. mental retardation, microcephaly, prognatism, happy disposition, choroidoretinal changes, optic atrophy, iridal changes, paroxysms laughter. Potentially maternal imprinting. cardiomyopathy hypertrophic-3 autosomal dominant growth/mental retardation, weakness, polyuria, hypokalemic alkalosis, hyperaldosteronism with low blood pressure, nephrocalcinosis. low birth weight, dwarfism, cutaneous rash due to sensitivity to sunlight, hypo/hyperpigmentation spots, severe immunodeficiency, thin face with large nose, chomosome defects, propensity for leukemia. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. cataract congenital-2 autosomal dominant total congenital cataract. ceroid lipofuscinosis juvenile autosomal recessive pigmentary retinopathy, motor/psychotic disturbance, seizures, myoclonia. ceroid lipofuscinosis late infantile variant autosomal recessive intellectual decline, ataxia, seizures, retinal degeneration, optic atrophy. Cytosomes with curvilinear profile in the uncultured amniotic fluid. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 15q localization 201710 600617 203200 103581 109700 602099 Am.J.Hum.Genet.61(s uppl.), A279 only,1997 218000 234400 601623 105830 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 200 Prenat.Diagn.20,300306,2000 209900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 590 241200 600839 210900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 104 115196 Hum.Genet.61,338341,1982 204200 Prenat.Diagn.20,337339,2000 Hum.Mol.Genet.6,591595,1997 601780 Prenat.Diagn.19,685688,1999 66 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: craniosynostosis type 1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive diabetes mellitus insulindependent 3 autosomal dominant premature closure of sutures, leading to abnormally shaped head, including brachycephaly, oxycephaly, plagiocephaly,turricephaly/acrocephaly, cloverleaf skull. insulin-dependent adult-onset diabetes mellitus. dyserythropoietic anemia I supposed autosomal recessive dyserythropoietic anemia III autosomal dominant dyslexia 1 autosomal dominant glutaricaciduria IIA autosomal recessive mitochondrial Griscelli syndrome autosomal recessive gynecomastia aromatase activity increased autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity sex-limited, sex influence hepatic lipase deficiency autosomal dominant Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome autosomal recessive hypomelanosis of Ito supposed autosomal dominant isovaleric acidemia autosomal recessive lens ectopia congenital autosomal dominant autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity Genus Clinical Database pallor, weakness, mild macrocytic anemia, juvenile onset, hyperbilirubinemia, normal reticulocytes, splenomegaly, hemochromatosis, occasionally brachy-syndactyly, mild short stature. refractory anemia, juvenile onset, ineffective erythropoiesis with multinucleated erythroblasts, hepatosplenomegaly, hemochromatosis. slow reading, reduced comprehension, words distortion or omission associated with behavioral and emotional dysfunctions. variable age onset; hypotonia, visceral fatty degeneration, lethargy, coma, sudden death. Mild and severe cases occurring. partial albinism, choroidoretinal changes, pyogenic infections, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, acute episodes of fever, immunological defects. progressing gynecomastia, around 10 years onset, in otherwise normal male, advanced bone age, excessive peripheral conversion of androgen to estrogen. Female limited disease. Malelimited inheritance. dyslipidemia, premature coronary atherosclerosis. albinism oculocutaneous, iridal changes, bleeding tendency, peculiar systemic pigmented reticuloendothelial cells. mental retardation, seizures, asymmetrical whorl-like hypopigmentation areas, ocular changes, other findings. Bibliography[OMIM]: 123100 Nature Genet. 8,189194,1994 600318 224120 105600 127700 231680 214450 107910 151670 203300 146150 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 504 first days of life onset; vomiting, acidosis 243500 without ketoaciduria or aminoacidemia, severe rapid neurological signs, mental retardation, characteristic "sweaty feet" odor. 129600 poor vision, monocular diplopia with bilateral lens dyslocation upward/temporally, iridodonesis, deep inferior chamber. Eye isolated anomaly. chromosome 15q localization 67 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Marfan syndrome I Inheritance: Synthesis: autosomal dominant tall stature, dolichostenomelia, arachnodactyly, scoliosis, chest deformity, upward lens dislocation, primary glaucoma, other ocular changes, joint laxity, aortic/mitral involvement, tricuspid valve regurgitation, mitral annulus calcification, long slendeer limbs, arm span greater than height, little subcutaneous fat, hypotonia; arterial dissections. second decade onset; hip/shoulder proximal muscles weakness, difficulty climbing, stairs/holding hands above head, low back pain, occasionally cardiomyopathy/pseudohypertrophy/high serum creatine kinase levels. myoclonic epilepsy, juvenile onset, isolated myoclonic, jerks, usually in the morning. progressive conductive/mixed hearing loss, young/middle-age onset. juvenile/adult onset. Weakness, progressive spastic paraplegia, occasionally sphincter incontinence muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2A myoclonus-epilepsy Janz type autosomal recessive otosclerosis autosomal dominant paraplegia spastic hereditary-6 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity Prader-Willi syndrome autosomal dominant genomic imprinting supposed contiguous genes Tay-Sachs disease autosomal recessive tyrosinemia I acute form autosomal recessive tyrosinemia I chronic form autosomal recessive Weill-Marchesani dominant form autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity Bibliography[OMIM]: 154700 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 472 253600 254770 166800 Neurology 46,835836,1996 600363 176270 decreased fetal movements, breech delivery, almond-shaped eyes, full Smith's Recognizable cheeks, severe hypotonia, Patterns of Human hypogenitalism, polyphagia, obesity, Malformation. 5th short stature, hypopigmentation, iridal Edition pag. 202 changes. Potentially paternal imprinting. Prenat.Diagn. 20,300306,2000 psychomotor delay, seizures, hypotonia, 272800 visual defect, choroidoretinal changes, apathy, exagerated responses to sound. 276700 first months age onset; failure to thrive, fever, lethargy, irritability, hepatomegaly, cirrhosis, jaundice, hemorrhage, sweet peculiar odor. 276700 renal tubular dysfunction, rickets, hepatic failure/cirrhosis, occasionally mental retardation, other neurologic abnormalities. Am.J.Med.Genet.65(1) short stature, short hand, myopia, lens ,68-75,1996 dislocation, articular stiffnes. chromosome 16 localization cylindromatosis autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked dominant cystathioninuria autosomal recessive Jabs syndrome autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database solitary/multiple, sessile or pedunculated 123850 smooth nodules on the scalp, occasionally face/neck/trunk, onset in early adulhood. May be the same as Spiegler-Brooke syndrome. 219500 mental retardation, acromegaly, diabetes insipidus nephrogenic, heart disease, urolithiasis, thrombocytopenia, convulsions, other anomalies. symmetric polysynovitis, granulomatous 186580 inflammation, cutaneous rash, cranial neuropathies, deafness, ocular involvement including uveitis and cataract. chromosome 16 localization 68 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: tuberous sclerosis-1 Inheritance: Synthesis: autosomal dominant genomic imprinting facial adenoma sebaceum (angiofibroma), epilepsy, mental retardation, vitiligo, ocular changes. Potentially maternal imprinting. Possibility of brain tumor, includind astrocytoma. Occasionally detection cranial abnormalities, rabdomyosarcoma in prenatal eepoch. Bibliography[OMIM]: 191100 Prenat.Diagn.19,575579, 1999 J.Med.Genet.20,303312, 1983 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 506 chromosome 16p localization alpha-thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome contiguous genes supposed X-linked recessive Brook-Carter syndrome contiguous genes cerebellar degeneration-related autosomal dominant autoantigen-2 mental retardation associated with alpha- 301040 thalassemia. Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 278 severe infantile polycystic kidney Nature Genet. 8,328associated with tuberous scerosis. 332,1994 600273 117340 paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration related to antigen CDR62. ceroid lipofuscinosis juvenile autosomal recessive pigmentary retinopathy, motor/psychotic disturbance, seizures, myoclonia. Crohn disease no genetic supposed autosomal recessive undefinable terminal ileum nonspecific segmental/plurisegmental inflammatory disease, with acute and chronic course, gastrointestinal tumor tendency. anemia, jaundice, splenomegaly, acute 140700 hemolytic episodes by exposure to oxidant drugs/infections, Heinz-bodies in the erithrocytes due to unstable hemoglobin fraction. 602066 paroxysmal choreoathetosis, infantile convulsion. Hum.Genet.103,608612,1998 177200 polydipsia/polyuria, hypertension, potassium loss with normal renal 600760 function. 600761 249100 childhood/juvenile onset; recurrent episodes of fever, abdominal/chest pain, peritonitis, pleuritis, associated fingings, occasionally suggesting acute polyarthritis. 141750 Hb H disease, with hypochromic microcytic anemia and mental retardation. microphthalmos, congenital cataract 156850 with/without other defects eye. Eye isolated anomalies. painless/painful muscle cramps induced 108730 by walking or exercise. 601003 hemoglobin variants Heinz-body autosomal dominant ICCA syndrome autosomal dominant Liddle syndrome supposed autosomal dominant Mediterranean fever familial autosomal recessive mental retardation-hemoglobin H autosomal dominant microphthalmos-cataract autosomal dominant myopathy Brody type autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity polycistic kidney disease 1 autosomal dominant genomic imprinting Genus Clinical Database late onset; progressive, bilateral medullary cysts enlargment in kidneys, with/without renal failure, liver cysts, occasionally cerebral cysts, ocular anomalies and other organs involvement. Potentially maternal imprinting. chromosome 16p localization 204200 Prenat.Diagn.20,337339,2000 266600 601458 173900 601313 69 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: pseudoxanthoma elasticum autosomal recessive type I and II autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity retinitis pigmentosa-22 autosomal recessive diffusa yellowish nodules xanthomas264800 like, changes in the skin of the flexural 264810 areas, ocular involvement, arterious rupture, intestinal occlusion, calcified falx cerebri. Vary rare type II without eye angioid streaks and vascular changes. autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Genomics 48,341345,1998 602594 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes supposed genetic heterogeneity thalassemia alpha autosomal recessive thalassemia beta autosomal recessive thalassemia-alpha homozygous autosomal recessive form tuberous sclerosis-2 autosomal dominant xeroderma pigmentosum VI autosomal recessive thumbs/halluces broad, deviated terminal phalanges, forehead angioma, dysmorphism with beaked/straight nose, mental/growth defects, microcephaly, sleep apnea, ocular anomalies including cataract, primary glaucoma. carriers with erythrocyte hypochromic microcytosis, mild hyperbilirubinemia; homozygous with severe anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, other disturbance, fetal hydrops, peculiar laboratory data, placental thickness. carriers with erythrocyte hypochromic microcytosis, mild hyperbilirubinemia; homozygous with Cooley anemia. nonimmune hydrops fetalis due to homozygous form of alpha-thalassemia, inducing hemoglobin Bart's. clinical features of tuberous sclerosis due to a gene mapping on chromosome 16. mild clinical symptoms of xeroderma pigmentosum, consisting of pigmented freckles, seborrheic keratosis-like papules, keratoacanthomas, mild cancer susceptibility. Bibliography[OMIM]: 180849 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 92 141800 141900 141800 191092 278760 chromosome 16q localization adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency supposed autosomal dominant aldolase A deficiency supposed autosomal recessive Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 2 autosomal recessive cataract perinuclear autosomal dominant cataract posterior polar autosomal dominant corneal dystrophy macular type autosomal recessive cortisol 11-beta ketoreductase deficiency Genus Clinical Database autosomal recessive urinary calculi mistaken for uric acid stones with/without gout or renal disease. Total (type I) or partial (type II) APRT deficiency. hemolytic anemia, mental retardation, hepatomegaly. postaxial polydactyly, hypogonadism, obesity, mental retardation, pigmentary retinopathy. Chromosome 16q localization. zonular/nuclear/anterior polar/stellate cataract. Eye isolated anomaly. congenital type of cataract. Occasionally posterior lenticonus. Eye isolated anomaly. Minute gray punctate opacities, first decade onset. Galactosidase alpha low activity in the keratocytes. Eye isolated anomaly. hypertension, growth retardation, hyperkalemia, hypoaldosteronism. chromosome 16q localization 102600 103850 209900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 590 116800 116600 217800 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.236 218030 70 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: gastric cancer familial multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant undefinable granulomatous disease cytochrome-b-negative autosomal recessive hypokalemia-hypomagnesemia supposed autosomal dominant mucopolysaccharidosis IVA autosomal recessive neuropathy giant axonal autosomal recessive Norum disease autosomal recessive spinocerebellar ataxia 4 autosomal dominant familial gastric cancer. Occasionally association with chronic atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia; presence of helicobacter pylori. recurrent pyogenic infections and/or granulomas, involving skin and any organ system including bones, due to cytochrome alpha subunit defect. chronic dermatitis, episodic of muscle weakness and tetany, precipitated by non-specific illness. short trunk, dwarfism, X-ray changes, joint laxity, hyperlordosis, corneal clouding, deafness, lower face prominent, hyperlordosis, aortic regurgitation. No mental retardation. symmetric, progressive distal weakness/atrophy, ataxia, other neurological disorders, optic atrophy, tighthy curled hair. corneal clouding, anemia, low HDL, high VLDL, renal failure. age at onset from 20 to 60 years; gait disturbance, sensory neuropathy, dysarthria, ataxia. Townes-Brocks syndrome autosomal dominant trichoepitheliomas autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity tyrosinemia II autosomal recessive Wilms tumor III autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes imperforate anus, triphalangeal thumbs, metatarsal fusion, other skeletal defects, lop ears, deafness, renal anomalies. translucent papules/nodules, increasing in number and size, involving nasolabial folds, nose, forehead, upper lip, external ears; scalp, neck, upper trunk characteristic horn cysts, resembling basal cell epithelioma. May be associated with cylindromatosiss. karatitis, hyperkeratosis palms/soles, mental retardation, hyperactivity, aberrant behaviour. Wilms tumor that does not map on chromosome 11p. Occasionally congenital form. Bibliography[OMIM]: 137215 233690 263800 600968 253000 256850 245900 Neurology 44, A361,1994 600223 107480 132700 601606 276600 194090 chromosome 17 localization deafmutism I leukodystrophy globoid cell type autosomal recessive supposed autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity autosomal recessive medulloblastoma supposed autosomal dominant pituitary dwarfism IV supposed autosomal recessive sopranuclear palsy, progressive autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database nonallelic form of deafmutism II; severe sensoryneural deafness from birth, defective speech and language. 220700 severe mental retardation, motor deterioration, hypertonicity, opistothonus, optic atrophy, deafness, decerebrated status. cerebellar dysfunction due to neoplasm of the posterior fossa frequently associated with isochromosome17q. growth retardation, delayed bone age, low somatomedin levels and anomalous growth hormone structures. sorpanuclear palsy, gait difficulty, dystonia, severe akinesia. 245200 chromosome 17 localization 155255 262650 601104 Arch.Neurol.10,333359,1964 Ann.Neurol.41,277281,1997 71 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: chromosome 17p localization amaurosis congenita Leber I autosomal recessive 204000 severe impaired visual function, optic atrophy, nystagmus; occasionally mental 600179 retardation. Eye isolated anomaly. Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.373 hemorrhagic diathesis due to PLI defect. 262850 antiplasmin deficiency autosomal recessive Bernard-Soulier syndrome autosomal recessive breast cancer familial multifactorial undefinable breast cancer-related regulator of TP53 sporadic undefinable breast-cancer associated with loss of constitutional heterozygosity (LOH) at 17p13.3 containing the TP53 gene. cataract anterior polar 2 autosomal dominant cataract anterior polar. Eye isolated anomaly. Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1A autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity choroidal sclerosis central autosomal recessive colorectal cancer-related chromosome sequence-17 autosomal dominant neonatal hypotonia; pes cavus, scoliosis, peroneal muscle weakness, legs atrophy, sensory ataxia, claw-like hands. Clinical features more severe than CMT type 1B, and caused by an over-expression of a gene found within duplication in chromosome 17p12. central areolar choroidal sclerosis. Eye isolated anomaly. colorectal carcinomas related to loss of chromosome 17p sequences. colorectal familial cancer Lynch I supposed autosomal dominant undefinable cone-rod retinal dystrophy-5 autosomal dominant cone-rod retinal dystrophy-6 autosomal dominant early onset disorder, loss of central vision followed by loss of peripheral visual field. Eye isolated anomaly. deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-3 autosomal recessive congenital deafmutism. Dejerine-Sottas disease autosomal dominant Li-Fraumeni syndrome supposed autosomal dominant childhood onset, weakness, areflexia, palpable enlargement of peripheral nerves, stocking-glove sensory loss, cranial nerve involvement, other neurological defects, ataxia, pes cavus, ocular changes. early onset familial cancer syndrome, breast cancer, brain tumor, sarcoma, other neoplasms. High level of polyclonal IgM. Genus Clinical Database congenital bleeding disorder, prolonged bleeding time, moderate thrombocytopenia, large platelets. familial bilateral breast cancer. site-specific colonic cancer changes in bowel habit, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, anemia, weight loss, onset before 40 years. May be the same of Lynch II. Associated endometrial carcinoma/atypical hyperplasia, uterine leiomyosarcoma, renal/bladder carrcinoma, gastric/biliary carcinoma. progressive loss of central vision. Eye isolated anomaly. chromosome 17p localization 231200 114480 190020 190070 188825 113721 190020 191170 Hum.Mol.Genet.5,415419,1996 601202 118220 Prenat.Diagn.19,446449,1999 601097 215500 120460 190020 116806 114500 190020 116806 Genomics 30,281286,1995 600977 Hum.Molec.Genet.6,59 7-600,1997 601777 Nature Genet.9,8691,1995 600316 145900 601097 151623 72 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Miller-Diker lissencephaly syndrome autosomal recessive supposed contiguous genes undefinable myasthenia gravis infantile autosomal recessive 247200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 194 multiple flexion contractures, intermittent 254210 myasthenic symptoms, without signs between crises, fluctuating ptosis,respiratory distress usually transient neonatal myastenia gravis, characterized by episodic feeding difficulty, easy fatigability, crises of apnea inducing anoxic brain, injury. Occasionally polyhydramnios, sudden death. 162500 neurogenic amyotrophy, inducing recurrent mono/polyneuropathy, 601097 triggered by compression, or even slightly stretching of the nerve trunks. Am.J.Ophthal.121,13progressive loss of visual acuity, cone 18,1996 degeneration. Eye isolated anomaly. 601251 neuropathy pressure palsy type autosomal dominant retinal cone dystrophy-2 autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-13 autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-4 autosomal dominant Smith-Magenis syndrome chromosomic supposed contiguous genes spongy degeneration autosomal recessive Bibliography[OMIM]: brain without convolutions or gyri, microcephaly, small mandible, bizarre facies with wrinkling of the forehead, failure to thrive, dysphagia, ocular defects, decerebrate postures. autosoma dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Am.J.Hum.Genet.57,9 62-965,1995 600059 180380 decreased dim light vision, and constricted visual fields, with typical retinal changes. Eye isolated anomaly. brachycephaly, midface hypoplasia, 182290 deafness, growth/mental retardation, other clinical findings; chromosome 17p deletion. 271900 in the first months of life apathy, sluggishness, spasticyty/ hypotonia, Prenat.Diagn.19,669blindness, optic atrophy, 670,1999 megalencephaly. chromosome 17q localization acanthocytosis band 3 red cell membrane autosomal dominant mild dyserythropoietic anemia, acanthocytosis. 109270 acetyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency autosomal recessive 200350 adrenoleukodystrophy pseudoneonatal autosomal recessive breast cancer type 1 supposed autosomal dominant hypotonic myopathy, neurological damage, other clinical findings, due to ACAC deficiency. clinical features resembling neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy with enlarged hepatic peroxisomes; choroidoretinal defects, optic atrophy. familial breast cancer, early onset. Increased risk of ovarian cancer. campomelic dysplasia dominant type cataract cerulean type-1 autosomal dominant germinal mosaicism supposed autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant cataract Coppoc-like autosomal dominant cataract zonular with sutural opacities autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database short-limb dwarfism, bones bowing, dysmorphic face, lung hypoplasia, sex reversal, other defects. peripheral bluish and white opacifications. Eye isolated anomaly. cataract embryonic nuclear type. Eye isolated anomaly. congenital autosomal dominant zonular cataract. Eye isolated anomaly. chromosome 17q localization 264470 113705 190020 188825 114290 115660 123660 Am.J.Hum.Genet.57,8 40-845,1995 600881 73 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: colorectal familial cancer Lynch I supposed autosomal dominant undefinable 114500 190020 116806 dementia Neumann type supposed autosomal recessive Ehlers-Danlos VII autosomal recessive autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity epidermolysis bullosa BullNorins type autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant site-specific colonic cancer changes in bowel habit, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, anemia, weight loss, onset before 40 years. May be the same of Lynch II. Associated endometrial carcinoma/atypical hyperplasia, uterine leiomyosarcoma, renal/bladder carrcinoma, gastric/biliary carcinoma. presenile dementia with subcortical gliosis. short stature, severe joint hypermobility, multiple subluxations, floppy infant aspect, bruisability, dysmorphic face. pyelonephrosis due to bilateral ureterovesical junction, stenosis/pyloric atresia, severe diffuse skin lesions. serous sanguineous traumatic blisters, involving only hands/feet, mainly in warm weather after walking/hand labor. It is the mildest and commonest form of EBS. epidermolysis bullosa resembling simplex/dystrophic/atrophic EB forms, and dermatitis herpetiformis, aggregation of tonofilaments in basal cells with normal dermo-epidermal junction. It is the severest form of EBS. skin blistering affecting predominantly palmar, plantar dorsal and lateral surfaces of the feet. 131800 epidermolysis bullosa Cockayne-Touraine type epidermolysis bullosa Dowling- autosomal dominant Meara type Bibliography[OMIM]: 221820 225410 226730 Prenat.Diagn.20,7075,2000 131760 epidermolysis bullosa simplex autosomal recessive autosomal recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex Koebner type autosomal dominant epidermolysis bullosa simplex Ogna type autosomal dominant erythroderma ichthyosiformis bullous autosomal dominant congenital widespread areas of blisters, followed by generalized hyperkeratosis. 113800 frontotemporal lobe dememtia supposed autosomal dominant changes in behaviour and personality reflecting frontal lobe dysfunction. galactose kinase deficiency autosomal recessive Am.J.Hum.Genet.59,1 306-1312,1996 601630 230200 Glanzmann-Naegeli syndrome glycogenosis IA autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity autosomal recessive nuclear and/or zonular cataract in early infancy, dystonia, peripheral neuropathy. 273800 bleeding diathesis, low/normal platelet number, with abnormal aggregation. glycogenosis IIa autosomal recessive hirsutism-amenorrheapolycystic ovarium autosomal recessive Howell-Evans syndrome autosomal dominant hypertension essential multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database Nature Genet.3,327331,1993 601001 generalized serous non-scarring blisters, 131900 increasing in the warm season, mainly Prenat.Diagn. 20,371involving soles/toes, fingers, heels; 377,2000 normal teeth and nails, onset at birth or first months of life. 131950 generalized epidermal fragility, serous seasonal hands/feet blistering. hypoglycemic seizures, very large liver, ketoacidosis, growth retardation, hypotonia, xanthomas, bleeding tendency. progressively severe weakness floppyinfant type, resembling WerdnigHoffmann disease, cardiomegaly, arrhythmias, macroglossia. progressive hirsutism, secondary amenorrhea, polycystic ovarium with ovarian 17-ketosteroid reductase deficiency. esophageal cancer associated with tylosis; occasionally oral leukoplakia. usually adult onset; primitive, high blood pressure values. chromosome 17q localization 232200 232300 264300 148500 145500 74 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: hyperthermia malignant autosomal dominant genomic imprinting hyperthermia malignant susceptibility 2 autosomal dominant hyperthyroidism familial autosomal dominant keratoderma palmoplantaris epidermolytic autosomal dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity keratoderma palmoplantaris nonepidermolytic autosomal dominant Potentially lethal pharmacogenetic disease. Masseter spasm, arrythmia, muscle rigidity, metabolic acidosis, rhabdomyolisis, myoglobinuria, intravascular coagulation, hyperthermia during or shortly after general anesthesia. Caffeine-hallothane contracture test ansthesia. Maternal imprinting. malignant hyperthermia susceptibility related to a gene located on chromosome 17q. hyperthyroidism, due to overstimulation by inappropriate TSH secretion. palmaris/plantaris keratosis, with histologic and kinetic findings of epidermolysis. palmoplantar keratoderma associated with oral and genital lesions. King-Denborough syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity leukokeratosis mucosal autosomal dominant Meckel syndrome type 1 autosomal recessive Mediterranean fever familial autosomal recessive mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB autosomal recessive MULIBREY syndrome supposed autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2A muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2D muscular dystrophy limb-girdle autosomal recessive type 2G myeloperoxidase deficiency Genus Clinical Database autosomal recessive myopathy, malignant hyperpyrexia, short stature, scoliosis, cryptorchidism, dysmorphic face, other clinical findings. present at birth; asymptomatic white folded soft hyperplastic lesions, involving oral/vaginal/anal other mucosae, often mistaked for leukoplakia. occipital encephalocele, microcephaly, Potter-like facies, oral-oculo-neural defects, kidneys/liver cysts, polydactyly, ambiguous genitalia, single umbilical artery, spleen acessory, other anomalies; occasionally Horner syndrome. childhood/juvenile onset; recurrent episodes of fever, abdominal/chest pain, peritonitis, pleuritis, associated fingings, occasionally suggesting acute polyarthritis. milder form of Sanfilippo syndrome due to N-acetyl-alpha -D-glucosaminidase deficiency. low birth weight-lenght, triangular face, prominent forehead, hypotonia, hepatomegaly, pericardial constriction, yellow pigmentated fundi, other defects. Bibliography[OMIM]: 145600 154275 145650 144200 Hum.Molec.Genet.4,18 75-1881,1995 600962 145600 193900 249000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 184 249100 252920 253250 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 100 253600 second decade onset; hip/shoulder proximal muscles weakness, difficulty climbing, stairs/holding hands above head, low back pain, occasionally cardiomyopathy/pseudohypertrophy/high serum creatine kinase levels. 600119 Duchenne-like muscular dystrophy. New Engl.J.Med.334,362366,1996 juvenile onset; progressive difficulty in 601954 walking and running, muscle wasting of Am.J.Hum.Genet.61,1 the upper and lower limbs. 51-159,1997 254600 recurrent infections, disseminated candidiasis, due to defect of the lysosomal enzyme myoloperoxidase in neutrophils and monocytes. chromosome 17q localization 75 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: neuritis brachial plexus autosomal dominant childhood onset; unilaterally, shouldergirdle muscle recurrent attacks of weakness, preceded by pain, followed by amyotrophy; characteristic focal thickening of myelin, occasionally other associated anomalies. 162100 neurofibromatosis 1 autosomal dominant genomic imprinting FDIäDX ODLW VSWVD[LOODU\ IUHFNOLQJ DW 162200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 508 osteogenesis imperfecta III autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta IVA autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta IVB autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta lethal IIA autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed germinal mosaicism osteogenesis imperfecta lethal IIB autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed germinal mosaicism osteogenesis imperfecta lethal IIC autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta tarda blue sclerae osteoporosis senile supposed autosomal dominant pachyonychia congenita Jackson-Lawler type genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive pachyonychia congenita genetic heterogeneity Jadassohn-Levwandowsky type supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive paralysis periodic hyperkalemic autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database birth, late neurofibromas, optic glioma, segmental hypertrophy, iris Lisch nodules, primary glaucoma, skeletal changes, other oculo-neuro-visceral involvement. Potentially maternal imprinting. short stature, progressive deformity, bluish sclerae at birth, but less blue with age, cardiorespiratory failure, clinical variability from perinatal death to little morbidity. bluish sclerae at birth, progressively less blue with age; normal teeth; deafness, other clinical data characteristic of osteogenesis imperfecta. clinical variability, bluish sclerae at birth, less blue with age; dentinogenesis imperfectas; fractures, usually in the newborn period onset, other clinical data characteristic of osteogenesis imperfecta. extreme bone fragility, intrauterine fractures, broad crupled femora, continuous rib beading, marked reduction in collagen I synthesis. extreme bone fragility, intrauterine fractures, broad crumpled femora with minimal or no rib fractures; other clinical data characteristic of osteogenesis imperfecta. extreme bone fragility, intrauterine fractures, thin femora, thin ribs. multiple bone fractures, blue sclerae, other ocular defects, opalescent teeth, deafness; arterial rupture/dissection. reduced bone mass mainly in the femoral neck and lumbar spine. milia, neonatal teeth, very thickened nails, subcutaneous infected cysts, corneal dystrophy. nail bed hypertrophy, red/yellow horn nails, skin/oral mucous lesions, hypodontia, short stature, mental retardation, ocular defects, intestinal diverticuli. childhood onset; periodic attacks of weakness, lasting 30-60 minutes, occasionally myotonic symptoms, eyelid myotonia, elevated serum potassium during attaks. chromosome 17q localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 259420 166220 166220 166210 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 490 J.Med.Genet.31(12),96 5-968,1994 Prenat.Diagn.17(6),55 9-570,1997 166210 166210 166200 166710 167210 167200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 548 170500 76 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: paramyotonia congenita autosomal dominant pituitary dwarfism I autosomal recessive placental lactogen defect autosomal dominant pseudohermaphroditism malegynecomastia autosomal recessive pseudohypoaldosteronism II recessive type autosomal recessive psoriasis vulgaris infancy onset; myotonia aggravated by cold or repeated muscle contractions, involving facial/lingual/hand; muscles attacks of flaccid weakness after exercise/cold exposure; high serum potassium levels during attacks. normal birth length, proportionate dwarfism, first year of age onset, excessive subcutaneous adipose tissue, soft wrinkled skin, round doll-like facies; high-pitched voice, hypoglycemic episodes, delayed sexual development. usually asymptomatic defect of human placental lactogen. males 46,XY, with ambiguous genitalia/sex reversal at birth, and normal masculinization at puberty, cryptorchidism, carcinoma tendency in cryptorchid testes. signs of a salt-wasting syndrome, without renal/adrenal disease, failure to thrive, anorexia, vomiting, dehydration, lethargy, collapse. Salt wasting due to target multiple organ unresponsiveness to mineral corticoids. erythematous scaling plaques, usually on elbows, kneees, scalp; arthritis, dystrophic nails. Potentially paternal imprinting. Refetoff syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity genomic imprinting multifactorial autosomal recessive renal tubular acidosis I autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-17 autosomal dominant Russell-Silver syndrome Bibliography[OMIM]: 168300 262400 150200 264300 Nature Genet.16,202205,1997 601844 177900 goiter, deafmutism, stippled epiphyses. 274300 nephrocalcinosis, acidosis, hypocalcemia, osteomalacia. autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Eye idolated anomaly. 179800 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity genomic imprinting low birth weight, skeletal asymmetry, short stature, triangular facies, Sjogren-Larsson syndrome autosomal recessive symphalangism proximal autosomal dominant Thomsen disease autosomal dominant thyroid hormone resistance autosomal dominant van Buchem syndrome autosomal recessive Wilhelmsen-Lynch disease autosomal dominant congenital ichthyosiform dermatitis, mental retardation, symmetric spastic diplegic or quadriplegic type, chorioretinal lesions, "glistening dots" in the fovea. proximal interphalangeal joints ankylosis, with carpal/tarsal bones fusion; conductive deafness. infancy onset without clinical progression, percussion myotonia in hands/legs/eyelids, cold aggravating factor; occasionally, muscular hypertrophy. goiter, without thyrotoxicosis, serum free thyroid hormone high levels, normal TSH. mandibular prominence; thichening chin, base skull, clavicle and diaphyseal cortex, occasionally ocular defects. adult onset; dementia, parkinsonism, behavioral changes, amyotrophy, frontotemporal atrophy 180860 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 96 270200 Genus Clinical Database FOLQRGDFW\O\ V\QGDFW\O\ FDIäDXODLW spots. chromosome 17q localization Hum.Mol.Genet.4,145 9-1462,1995 600852 185800 160800 188570 239100 Am.J.Hum.Genet.55,1 159-1165,1994 600274 77 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Wilms tumor IV autosomal dominant Wszolek syndrome autosomal dominant 2-12 years average age of onset. Fixed abdominal mass in an upper quadrant, hematuria, hypertension, fever, abdominal pain. progressive parkinsonism, distonia, dementia, gliosis. Bibliography[OMIM]: Nature Genet. 13,461463,1996 601363 168610 chromosome 18 localization antiplasmin deficiency autosomal recessive hemorrhagic diathesis due to PLI defect. 262850 chromosome 18p localization leiomyomatosis cutis autosomal dominant manic-depressive psychosis 1 autosomal dominant multifactorial Migeon syndrome autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity myopia autosomal dominant 1 150800 adenoides cysticum, increasing translucent papules/nodules mainly on the face consisting of horn cysts and basalioma-like cells; isolated/multiple cutaneous leiomyomata, arising from the pilar arrector muscles of the skin, in nodular/linear shape. 125480 elated/excited/irritable mood in manic symptomatology; impaired thought processes/disturbed thought, content and perceptual processes/allucinations in schizophrenic disorders. 202200 late infancy onset; skin/gums hyperpigmentation, seizures due to recurrent hypoglycemia, lethargy. congenital/shortly after birth familial myopia. Retinal detachment. Eye isolated anomaly. 160700 lower limb neuropathy, diarrhea/constipation, sexual impotence, reduced vision, corneal clouding, renal failure, orthostatic hypotension. carpal tunnel syndrome, peripheral neuropathy, cardiomyopathy, vitreous deposists, orthostatic hypotension. progressive heart failure constrictive type, right-ventricular pressure curves, orthostatic hypotension, onset about age 40. neuropathy, diarrhea, impotence, vitreous deposits, amyloid deposits in all major organs. onset age 50, lower limb neuropathy, intermittent diarrhea, renal failure. senile systemic amyloidosis involving lungs, liver, heart, kidneys, brain, other structures; orthostatic hypotension, peripheral neuropathy in late decades, progressive sensory/motor loss, corneal clouding, cutaneous/visceral involvement. 176300 chromosome 18q localization amyloid neuropathy I autosomal dominant amyloid neuropathy II autosomal dominant amyloid neuropathy III autosomal dominant amyloid neuropathy V supposed autosomal dominant amyloid neuropathy Wallace autosomal dominant amyloidosis senile systemic autosomal dominant amyloidosis Swedish type supposed autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database chromosome 18q localization 176300 176300 B.D.Encyclopedia 2880 p.100 B.D.Encyclopedia 2882 p.106 176300 105270 78 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: amyloidosis VII autosomal dominant carnosinemia autosomal recessive cholestasis intrahepatic recurrent supposed autosomal recessive cholestasis progressive familial intrahepatic 1 autosomal recessive colorectal cancer-related chromosome sequence-18 autosomal dominant episodic neurologic dysfunction resembling cortical ischemia, dementia, seizures, strokes, coma, visual impairment, vitreous opacities, ocular strucures involvement including choroidoretinal changes. occasionally mental retardation, myoclonic seizures. repeated attacks of jaundice, itching, hepatomegaly, pruritus, other complications, first years of life onset. severe form of cholestasis intrahepatic, dwarfism, foul-smelling stools, attacks of jaundice related to infections, hepatosplenomegaly, low cholesterolemia. colorectal carcinomas related to loss of chromosome 18q sequences. colorectal familial cancer Lynch II autosomal dominant cone-rod retinal dystrophy-1 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus insulindependent 6 autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus, insulin dependent. epidermolysis bullosa atrophicans Herlitz-Pearson type autosomal recessive congenital ulcerations/erosions, congenital hands/feet blisters sparing later; hemidesmosome defects. factor V-VIII combined deficiency autosomal recessive hyperbradykininism autosomal dominant congenital hemorrhagic disorder due to combined deficiency of factor V and factor VIII. orthostatic hypotension, syncope, erythema, ecchymoses. King-Denborough syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity leukemia chronic lymphatic 2 supposed multifactorial undefinable methemoglobinemiacytochrome b5 deficiency autosomal recessive Niemann-Pick C autosomal recessive Niemann-Pick D-E autosomal recessive osteolysis expansile familial autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database colonic cancer in association with other familial carcinomas, such as endometrium/ovary/pancreas. May be the same of Lynch I. childhood onset; diminished central vision, altered color vision, mental retardation, hypogenitalism. Bibliography[OMIM]: 105210 212200 243300 211600 120470 190020 116806 114400 116806 Am.J.Med.Genet.39,28 8-293,1991 600624 Hum.Molec.Genet.6,10 03-1010,1997 601941 226700 600805 Prenat.Diagn.17,343354,1997 227300 143850 Lancet II,10481053,1972 myopathy, malignant hyperpyrexia, short 145600 stature, scoliosis, cryptorchidism, dysmorphic face, other clinical findings. 151430 chronic lymphocytic leukemia, with relatively immature B-cells in the bone, peripheral lymphocytosis, lymphoadenopathy, splenomegaly, marrow/lymph nodes/spleen involvement. 250790 cyanosis, congenital methemoglobinemia due to cytochrome b5 deficiency. hepatosplenomegaly, chronic neurologic 257220 deterioration, cherry red macular changes. 257250 adult type of N.P., with hepatosplenomegaly, neurologic deterioration, cherry red macular changes. juvenile onset; peripheral distribution of 174810 focal skeletal changes characterized by resorption, medullary expansion, painful, deformity, fractures; frequent deafness, loss of dentition. chromosome 18q localization 79 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: polyposis coli juvenile autosomal dominant protoporphyria erythropoietic autosomal dominant sclerosis multiple multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant Tourette disease genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked recessive 174900 rectal bleeding, polyp prolapse, abdominal pain, diarrhea, due to isolated 600993 or multiple intestinal/frequently colonic Science 280,1086polyps, risks for malignant degeneration. 1088,1998 177000 usually infancy onset; photosensitivity, skin lesions on exposure to sunlight, liver disease, jaundice, hepatic failure. 126200 motor/sensory problems, optic neuritis, vertigo, diplopia, bladder/bowel disturbances. disorder affecting speech, learning, 137580 behaviour; multiple motor and vocal tics, throat, clearing, sniffing, sucking, inappropriate words /phrases, including coprolalia. chromosome 19 localization glutaricaciduria IIA autosomal recessive mitochondrial mannosidosis autosomal recessive variable age onset; hypotonia, visceral fatty degeneration, lethargy, coma, sudden death. Mild and severe cases occurring. coarse facies, mental retardation, hepatosplenomegaly, infections, deafness, cataract, skeletal dysplasia. 231680 diabetes insulin-resistance type, choroidoretinal defects, acanthosis nigricans, severe muscle cramps, large hands, enlarged kidneys. diabetes insulin-resistance type, choroidoretinal defects, acanthosis nigricans. episodic attacks of vertigo, diplopia, ataxia, early adulthood onset. 200170 248500 chromosome 19p localization acanthosis nigricans Flier type supposed autosomal recessive acanthosis nigricans-diabetes autosomal dominant ataxia periodic vestibulocerebellar autosomal dominant atherosclerosis susceptibility autosomal dominant Bare lymphocyte syndrome autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia Cayman type autosomal recessive complement component C3 autosomal dominant exostoses multiple cartilagineous type I autosomal dominant exostoses multiple type III autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database 147670 108500 high risk for myocadial infarctions; high LDL and low HDL. Defective expression of class I-II MHC molecules. Severe persistent bacterial infections, diarrhoea/malabsorption, mucocutaneous candidiasis, panhypogammaglobulinemia with normal number of T and B lymphocytes, defective expression of HLA class I/II moleccules. ataxia, nystagmus, dysarthria, mental retardation. 108725 glomerulonephritis, recurrent infectionspyogenic, lupus systemic. mild short stature, bone deformity due to numerous asymmetric cartilage-capped exostoses, with characteristic clubshaped appearance, usually in the tubular bones actively growing areas, such as juxtaepiphyseal areas; malignant degeneration may occur. asymmetric cartilage-capped exostoses; malignant degeneration may occur. 120700 chromosome 19p localization 209920 601863 Hum.Mol.Genet.5,525531,1996 601238 133700 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 436 Hum.Molec.Genet.3,71 7-722,1994 600209 80 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: fucosyltransferase 3 autosomal dominant fucosyltransferase 5 autosomal dominant fucosyltransferase 6 autosomal dominant glutaricacidemia I autosomal recessive hypercalcemia benign type II autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia type B supposed autosomal dominant leprechaunism syndrome autosomal recessive leukemia lymphoid 1 sporadic undefinable Peutz-Jeghers syndrome autosomal dominant pseudoachondroplasia III autosomal dominant pseudohermaphroditism male internal autosomal recessive Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome autosomal recessive spinocerebellar ataxia 6 autosomal dominant locus linkage to blood group-Lewis system. plasma type of alpha-3fucosyltransferase. gene encoding alpha(1,3)fucosyltransferase activity. first months of age onset; opisthotonus, dystonic cerebral palsy, athetosis. easy fatiguability, mild muscle weakness, unconstant other disturbances such as chondrocalcinosis, lipomas, pancratitis, nophrolithiasis, peptic ulcer. tuberous/tendon xanthomas, xanthelasmas, premature coronary disease. tuberous/tendon xanthomas, xanthelasmas, premature coronary disease. severe dystrophy, low birth weight, elfin face, mental retardation, failure to thrive, prominence clitoris/penis/ears/hands and feet, hypoglycemia, severe insulin resistance, visceral anoamlies; occasionally Horner syndrome. acute lymphoblastic leukemia with typical nucleotide sequence analysis in a t(7;19) chromosomal translocation. infancy onset; abnormal mucocutaneous pigmentation, pigmented spots on the lips and buccal mucosa, multiple gastrointestinal hamartomatous, polyps intestinal, obstruction, gastrointestinal cancer. spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia with clinical-radiological features of pseudoachondroplasia, cytoplasmic metachromasia, characteristic changes in chondrocytes. normal external genitalia and testes in males 46, XY, with uterus and falloppian tubes, prolapsing into inguinal hernia; cancer tendency in cryptorchid testes. onset at birth or shortly thereafter; hyperpigmentation, hirsutism, followed by acanthosis nigricans; premature, supernumerary dentition; coarse/senile appearing facies, enlarged genitalia, thick nails, diabetes, pineal hyperplasia, other anomalies. juvenile onset of progressive cerebellar ataxia; occasionally dementia. Stein-Leventhal syndrome sex-limited, sex influence supposed autosomal dominant thyroid hormonogenesis defect autosomal recessive I Wegener granulomatosis autoantigen sporadic obesity, irsutism, amenorrhea, bilateral enlarged ovaries, normal urinary ketosteroids. congenital hypothyroidism, mental/growth/skeletal retardation, dry skin, cretinoid facies. vasculitis, capillaritis, severe renal dysfunction, pulmonary hemorrhage. Bibliography[OMIM]: 111100 136835 136836 231670 145981 143890 144010 246200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 600 151440 175200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 520 177170 261550 600957 262190 183086 601011 184700 274400 177020 chromosome 19q localization Genus Clinical Database chromosome 19q localization 81 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Alzheimer disease late onset dementia. Potentially paternal imprinting. 104310 Bannayan-Zonana syndrome autosomal dominant genomic imprinting multifactorial autosomal dominant 153480 Natur.Genet.16,333334,1997 brain-bone-fat disease autosomal recessive bundle branch block autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive autosomal dominant high birth weight, normal bone age, megalencephaly, hamartomas, macrosomia, multiple lipomas. Germline mutation of PTEN. third decade of life onset, wrist/ankle pain and swelling, fractures, epiphyseal cystic rarefactions conteining jelly-like material, progressive dementia resembling Alzheimer disease. arrythmias, extrasystoles, StokesAdams attacks, ECG similar to WPW syndrome. early onset bilateral cataract associated with asymptomatic hyperferritinemia. Eye isolated anomaly. Nature Genet.11,444446,1995 600886 258840 Alzheimer type 2 cataract-hyperferritinemia Clayton Smith-Donnai syndrome autosomal recessive cone-rod retinal dystrophy-2 autosomal dominant convulsion benign infantile autosomal dominant cystinuria III autosomal recessive deafness neurosensory autosomal dominant-4 autosomal dominant dementia multi-infarcts type supposed autosomal dominant Diamond-Blackfan disease recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive epiphyseal dysplasia multiple 1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity fucosyltransferase 1 deficiency autosomal recessive fucosyltransferase 2 autosomal dominant glucosephosphate isomerase deficiency autosomal dominant hyperlipoproteinemia IB autosomal recessive hyperlipoproteinemia III supposed autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database low birth weight, dysmorphic face, prominent ear crus, digits/toes in fixed flexion deformity, ichthyosis. diminished central vision, altered color vision. Eye isolated anomaly. infantile onset of benign convulsion. clinical data similar to cystinuria I; cystine urinary tract stones. Moderate hyperexcretion of cysteine and bibasic amino acidis in heterozygotes. second decade of onset; sensorineural deafness. Bibliography[OMIM]: 221770 113900 120970 Europ:J:Pediat.151,60 8-612,1992 601764 Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,6 11-616,1997 600918 Hum.Molec.Genet.4,10 73-1076,1995 600652 occlusive cerebrovascular infarcts in the white matter and dementia. hypoplastic macrocytic anemia/ aplastic anemia, without associated propensity for leukemia. 125310 severe hip osteoarthritis, distal tibial ossification defects, short stature, brachydactyly. red cell surface lacking H-antigen ; presence of anti-H, anti-A, anti-B in the serum. locus linkage to Lutheran blood group and myotonic dystrophy. neonatal/early childhood onset; chronic nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia, mental retardation, sensory ataxia. periodic attacks of abdominal pain/colic/vomiting, hepatosplenomegaly, eruptive xanthomas, without premature vascular disease. high cholesterol/triglyceride levels, xanthoma striata palmaris, coronary/vascular disturbance, ocular defects, tuberous xanthomata. 132400 chromosome 19q localization 205900 211100 182100 172400 207750 107741 82 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: hyperthermia malignant autosomal dominant genomic imprinting King-Denborough syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity leukocyte adhesion deficiency type II supposed autosomal recessive maple syrup urine disease 1 autosomal recessive methylglutaconicaciduria III supposed autosomal recessive migraine-hemiplegia supposed autosomal dominant myopathy central core type autosomal dominant myotonic dystrophy neonatal form autosomal dominant nephrosis congenita Finnish type autosomal recessive Potentially lethal pharmacogenetic disease. Masseter spasm, arrythmia, muscle rigidity, metabolic acidosis, rhabdomyolisis, myoglobinuria, intravascular coagulation, hyperthermia during or shortly after general anesthesia. Caffeine-hallothane contracture test ansthesia. Maternal imprinting. myopathy, malignant hyperpyrexia, short stature, scoliosis, cryptorchidism, dysmorphic face, other clinical findings. mental retardation, short stature, coarse facial appearance, recurrent infections, leukocyte adhesion defect, Bombay phenotype, leukemoid reactions. vomiting, lethargy, convulsions, acidosis, hypoglycemia, typical maple syrup-like odor in urine and other secretions, acidosis, hypoglycemia, due to E-1 alpha subunit deficiency. infantile optic atrophy, early onset choreic movements, mild ataxia, occasionally spastic paraparesis. attacks of hemicranial pain, hemiparesis, occasionally retinal degeneration, nystagmus, deafness, other clinical findings. onset at birth/shortly after birth; weakness, hypotonia, slow motor milestones, hip dislocations, kyphoscoliosis, features of "floppy infant". severe, congenital muscular hypotonia, facial diplegia, ptosis; severe respiratory insufficiency. Transmitted by mildly affected mothers. Potentially maternal imprinting. congenital edema, hypoproteinemia, proteinuria, abdominal distension, respiratory distress, renal failure, infections, electrolyte imbalance, cystic dilatation of proximal tubules. orofacial cleft 3 genomic imprinting multifactorial ovarian tumor autosomal dominant poliovirus susceptibility no genetic supposed multifactorial prolidase deficiency supposed autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 145600 145600 266265 248600 258501 141500 117000 Wiedemann H.R.Kunze J.: Clinical syndromes 1997 pag.588 256300 Prenat.Diagn.19,489,1 999 Prenat.Diagn. 21,8184,2001 complete or incomplete clefts of the Am.J.Hum.Genet. upper lip, unilateral or bilateral, including 57,257-272,1995 posterior alveolar processes, and 600757 anteriorly alae nasi. Potentially paternal imprinting. 167000 familial ovarian tumors, dysgerminomas/cancer, papillary 601404 adenocarcinoma. 192090 173850 susceptibility to poliovirus infections, symptoms of aseptic miningitis, followed by paralysis due to spinal/bulbar poliomyelitis. juvenile onset; lower extremities multiple 264130 recurrent ulcers, telangiectasias, other 170100 dermatologic lesions, photosensitivity, mild mental retardation, recurrent infections, other associated findings. chromosome 19q localization 83 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: pseudoachondroplasia I autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity pseudohermaphroditism male LH molecule defect autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-11 autosomal dominant normal-appearing at birth, two years of age onset; normal skull and face, disproportionate short stature, shortbowed limbs, lumbar lordosis, knockknees, short hand/foot, characteristic Xrays features. ambiguous external genitalia resembling a female type with 46,XY karyotype, due to secretion of an abnormal LH molecule. autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa.Eye isolated anomaly. sclerosis multiple multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant Steinert disease autosomal dominant genomic imprinting warfarin resistance autosomal dominant xeroderma pigmentosum IV/VIII autosomal recessive motor/sensory problems, optic neuritis, vertigo, diplopia, bladder/bowel disturbances. weakness, facial/oropharyngeal/distal muscles, expressionless facies, myotonia, cataract, ptosis, other ocular defects, testicular atrophy, mild mental retardation. Potentially maternal imprinting. Linkege to FUT2 gene. congenital resistance to hypoptothrombinemic effects of coumarin drugs. xeroderma pigmentosum of complementation group D, linkage with trichothiodystrophy; xeroderma pigmentosum of complementation group H, linkage with Cockayne syndrome. Occasionally ocular changes. UVinduced skin tumors. Bibliography[OMIM]: 177150 152780 180104 600138 126200 160900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 216 122700 278730 chromosome 20 localization corneal dystrophy polymorfous autosomal dominant posterior corneal endothelial dystrophy 1 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity Holt-Oram syndrome autosomal dominant Very early onset, may be present at birth. Irregular, broken sheetlike opacities and vacuoles in the posterior parts of the cornea. Eye isolated anomaly. endothelial type of congenital corneal dystrophy. Eye isolated anomaly. 122000 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.242 thumb anomaly, atrial septal defect, other cardiac/limb defects. 142900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 316 118450 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 586 105150 176640 121700 chromosome 20p localization Alagille syndrome autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes cholestasis intrahepatic, peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis, triangular shaped facies, anomalies of the anterior chamber of the eye, choroidoretinal defects, ocular cyst, nephronophthisis. amyloid neuropathy VIa autosomal dominant Creutzfeldt-Jacob syndrome autosomal dominant recurring cerebral hemorrhage, sometimes preceded by migrainous headaches or mental changes, thickening of the cerebral arteries. middle age insidious onset, with various physical and behavioral symptoms, followed by progressive dementia, myoclonus, pyramidal/extrapyramidal signs, heightened startle reaction, cerebral atrophy, cortical blindness. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 20p localization 123400 176640 84 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: diabetes insipidus neurohypophyseal type genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant X-linked recessive Gerstmann-StrausslerScheinker syndrome supposed autosomal dominant Huntington-like neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant Kaufman-McKusick syndrome autosomal recessive 125700 polydipsia, polyuria, low urine osmolarity, growth retardation, mental 304900 retardation due to dehydration, responsivity to vasopressin. 137440 middle age onset, cerebellar ataxia, dysarthria, incoordination, bradykinesia, 176640 nystagmus, progressive dementia, characteristic CNS amyloid plaques. progressive choreic movements, usually Am.J.hum.Genet.63,1 30-40 years onset, dementia, appearing 431-1438,1998 indipendently of the movements disorders, first manifestations may be paranoia, emotional instability. No mutation in 4p16.3 chromosome. 236700 hydrometrocolpos, due to transverse vaginal membrane inducing accumulation of secretions caused by vaginal obstruction, postaxial polydactyly, congenital heart disease. chromosome 20q localization adenosine deaminase deficiency autosomal recessive severe recurrent infections, failure to thrive, intestinal malabsorption. 102700 Albright osteodystrophy-1 autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity genomic imprinting sex-limited, sex influence supposed X-linked dominant 103580 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 446 Albright osteodystrophy-1 supposed autosomal dominant supposed early somatic mutation/gametic half-chromatid mutation short stature, obesity, round face, brachydactyly, fourth/fifth short matacarpals, absent 4th knuckles, ectopic calcification/ossification, mental retardation, cataract, iridal changes, hypocalcemia, parathyroid hyperplasia, high PTH levels.Potentially maaternal imprinting. pseudocystic skeletal lesions, sclerotic convulsions benign neonatal diabetes mellitus II noninsulindependent autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive autosomal dominant diabetes mellitus noninsulindependent mild juvenile autosomal dominant dyserythropoietic anemia II supposed autosomal recessive Fanconi pancytopenia type 1 autosomal recessive VNXOO IUDFWXUHV FDIäDXODLW VSRWV precocious puberty with advanced skeletal maturation, ocular defects. neonatal convulsions that cleared spontaneously after a few weeks, in healthy, neurologically normal infant. late onset diabetes. Polyuria, polydipsia, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, obesity, microvascular complications, including neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, myocardiopathy, alterations in insulin behaviour. juvenile onset, correction of fasting hyperglycemia without insulin, usually without ketosis, without obesity. mild to severe anemia, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, peripheral hemolysis, inffective erythropoiesis, hemochromatosis. low birth weight, anemia, WKURPERF\WRSHQLD FDIäDXODLW VSRWV thumb defect/ supernumeray, renal anomalies, chromosomal breakage. Fanconi pancytopenia type 2 autosomal recessive galactosialidosis infantile late type autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database Fanconi syndrome due to a separate locus different from type 1. dwarfism, gargoyle face, mental retardation, seizures, corneal clouding, macular cherry red spot, dysostosis multiplex, deafness. chromosome 20q localization 174800 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 510 121200 125853 601283 125850 224100 227650 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 320 227660 256540 85 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: galactosialidosis juvenile type autosomal recessive Grebe syndrome autosomal recessive skeletal dysplasia, joint stiffness, coarse dysmorphic facies, corneal clouding, cherry red spots, mental retardation, deafness. marked deformed hypomelia, progressive shortness from proximal to distal segments, extremely small digits/toes, postaxial polydactyly, obesity. phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 deficiency autosomal recessive visceral massive fatty deposition, liver impairment, hypoglycemia, lethargy. pyroglutamicaciduria autosomal recessive Waardenburg I syndrome autosomal dominant mental retardation, ataxia, other neurological dysfunctions, chronic metabolic acidosis, jaundice at birth, hemolytic anemia, vomiting, thrombosis tendency. deafness, dystopia canthorum, broad nasal bridge, synophrys, heterochromia irides, other ocular defects, white forelock, skin depigmentation. Bibliography[OMIM]: 256540 200700 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 300 261680 266130 601002 193500 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 248 chromosome 21q localization acute myeloid leukemia 1 Alzheimer type 1 amyloidosis VIb acute myeloid leukemia; frequent t(8;21)(q22q22). autosomal dominant genomic imprinting multifactorial supposed mitochondrial autosomal dominant amyotrophic lateral sclerosis adult type autosomal dominant breast cancer estrogeninducible sequence autosomal dominant carboxylase multiple deficiency autosomal recessive neonatal form cardioauditory syndrome autosomal recessive complement component C3 autosomal dominant deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-10 autosomal recessive deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive-8 autosomal recessive Genus Clinical Database dementia with onset before or after age 65. Potentially paternal imprinting. peculiar cerebral amyloid protein similar to those described in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. adult onset; progressive weakness, wasting, fasciculations,spinal/cranial/bulbar involvement, sleep apnea. breast cancer with BCEI gene located at 21q22.3 which codes for a small secreted protein. neonatal onset; severe lactic acidosis, alopecia, keratoconjunctivitis, perioral erosions, seizures, reversed by biotin. 602439 151385 Genomics 14,506507,0992 Blood 87,52185224,1996 104300 104760 105400 113710 253270 Prenat.Diagn.19,108112,1999 220400 prolongation of the Q-T interval, ventricular arrhythmia, loss of consciousness, deafness, sudden death. glomerulonephritis, recurrent infections- 120700 pyogenic, lupus systemic. Am.J.Hum.Genet.58,1 autosomal recessive hearing loss. 254-1259,1996 601072 childhood onset neurosensory deafness. Am.J.Hum.Genet.58,1 254-1259,1996 601072 chromosome 21q localization 86 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Dowton disease autosomal dominant enteropeptidase deficiency autosomal recessive holoprosencephaly 1 genetic heterogeneity undefinable bleeding tendency due to thrombocytopenia, defect in platelet aggregation, different from any known thrombopenic/thrombopathic disease; tendency to tumors, acute myelogenous leukemia. diarrhea, failure to thrive, early infancy onset, hypoproteinemia, edema. mid cranial-face defects, single ventricle, hypotelorism, median cleft, single nostril-nose, occasionally other associated anomalies. homocystinuria autosomal recessive downward lens dyslocation, marfanoid habitus, thromboembolic events, cataract, other ocular defects, moderate mental retardation. Knobloch-Layer syndrome supposed autosomal recessive leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 1 autosomal dominant muscular dystrophy benign congenital supposed autosomal dominant myeloproliferative syndrome transient chromosomic supposed autosomal dominant myoclonus-epilepsy Baltic type autosomal recessive high myopia, vitreoretinal degeneration, retinal detachment, occipital encephalocele. Defective cell-cell interaction. Recurrent severe bacterial/viral/fungal infections with little pus formation, delayed umbilical cord separation, leukocytosis, characteristic leukocyte dysfunction. early childhood onset; slow progression, involving proximal limb muscles, sternocleidomastoid and anterior tibial muscles, without cardiomyopathy; high creatine kinase levels. leukemoid reaction, usually in infants with Down syndrome due to disomic homozygosity. childhood onset; progressive invalidity from myoclonic features, mild mental deterioration, emotional lability. polyglandular autoimmune syndrome I autosomal recessive thrombocytemia essential supposed autosomal dominant Usher IE syndrome autosomal recessive Bibliography[OMIM]: 173420 601399 226200 236100 601475 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 605 Prenat.Diagn.20,400403,2000 236200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 478 267750 116920 600065 158810 159595 254800 601145 602103 240300 childhood onset; chronic candidal granulomatous infections of mucous membrane, skin, nails; parathyroid/adrenal/other hormones deficiency, hepatitis, thymic dysplasia, pernicious anemia, other anomalies. thrombohemorrhagic manifestation, high 187950 levels of platelets, increased megakaryocytes, sideroblastic anemia. 602097 congenital deafness, vestibular dysfunction, retinitis pigmentosa. Hum.Molec.Genet.6,27 -31, 1997 chromosome 22q localization autism purine type autosomal recessive cataract cerulean type-2 autosomal dominant Genus Clinical Database autism, growth/psychomotor retardation, 103050 seizures, muscular wasting. Prenat.Diagn.20,3336,2000 115660 peripheral bluish and white opacificatons. Eye isolated anomaly. 601547 chromosome 22q localization 87 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: cat-eye syndrome chromosomic supposed autosomal dominant eye colobomas, anal atresia, preauricular appendages or fistulae, mental retardation, heart defects, other visceral/skeletal anomalies. colorectal familial cancer Lynch I supposed autosomal dominant undefinable site-specific colonic cancer changes in bowel habit, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, anemia, weight loss, onset before 40 years. May be the same of Lynch II. Associated endometrial carcinoma/atypical hyperplasia, uterine leiomyosarcoma, renal/bladder carrcinoma, gastric/biliary carcinoma. conotruncal malformations including truncus arteriosus communis, great arteries transposition, other associated cardiac anomalies. 22q11 del. Included in CATCH 22 spectrum of malformations (cardiac, abnormal face, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalccaemia, 22 chromosoma deletion). neonatal hypocalcemic tetany, dysmorphic dysmorphic face, cardiac defects, hypoparathyroidism, thymic agenesis, cortical areas lymph nodes depletion, infections susceptibility, weackness, 22q11 del. Included in CATCH 22 spectrum of malformations (cardiac,, abnormal face, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcaemia, 22 chromosoma deletion). dysphagia, stridorous cry, hoarse voice, typical dysmorphism, hypertelorism, prominent occiput, hypospadias, other anomalies. conotruncal heart malformation genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive DiGeorge 1 syndrome contiguous genes supposed autosomal dominant G syndrome autosomal dominant glucose-galactose malabsorption autosomal recessive glutathionuria autosomal recessive heart transposition great vessels multifactorial neonatal onset; severe diarrhea, dehydration, failure to thrive, glucose/galactose in feces. mental retardation, urinary/plasma high glutathione concentration, normal erithrocyte glutathione concentration. congenital cyanosis, congestive heart failure, right ventricular hypertrophy. Occasionally 22q del. thrombosis recurrent. Bibliography[OMIM]: 115470 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag.68 114500 190020 116806 217095 Prenat.Diagn.18,507510,1998 188400 601362 Prenat.Diagn.18,507510,1998 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 616 145410 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 132 Am.J.Med.Genet.59(1) ,103-113,1995 182380 231950 B.D.Encyclopedia 0962 p.847 heparin cofactor II deficiency autosomal dominant Hirschprung-pigmentary anomaly supposed autosomal recessive white eyebrows/forelock, isochromia irides with mosaic pattern, intestinal obstruction, microcolon, no deafness, no dystopia canthorum. hyperprolinemia I autosomal recessive leukemia chronic myeloid undefinable leukodystrophy metachromatic late infantile type autosomal recessive asymptomatic, occasionally nephropathy, photogenic epilepsy. granulocytic leukocytosis in all stages of 151410 differentiation, bone marrow hyperplasia, high platelet count, Philadelphia chromosome, BCR/ABL hybrid gene, splenomegaly, other clinical findings. 250100 central/peripheral nervous system involvement, inability to walk, spasticity, hypotony, no ataxia, ocular changes. Genus Clinical Database chromosome 22q localization 142360 277580 Nat.Genet.12(4),445447,1996 Nat.Genet.18(2),171173,1998 239500 88 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: megacolon autosomal dominant multifactorial supposed genetic heterogeneity meningioma autosomal dominant methemoglobinemia I supposed autosomal recessive methemoglobinemia II supposed autosomal recessive costipation leading to neonatal intestinal obstruction or chronic constipation/obstipation, abdominal distention, deficiency/absence of ganglion cells. Neuroblastoma tendency. neurologic dysfunctions, due to relatively benign tumor, involving meninges. cyanosis without cardiac pulmonary disease, enzymatic deficiency confined to the erythrocytes. congenital cyanosis, without cardiac/pulmonary disease, severe progressive encephalopathy, microcephaly, mental retardation, diaphorase deficiency involving several tissues in addition to erythrocytes/leukocytes/platelets. severe hypotonia, myoclonic epilepsy, arrest of development, gait disturbance, ocular defects, dementia, decerebration, diabetes insipidus. bilateral acoustic neuromas, neuroaxonal dystrophy infantile autosomal recessive neurofibromatosis 2 syndrome autosomal dominant genomic imprinting rhabdoid tumor sarcoma Ewing undefinable Schindler syndrome autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity schizophrenia-4 autosomal dominant multifactorial undefinable Sorsby-Mason-Gardner syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity autosomal dominant thrombophilia due to heparin cofactor II deficiency transcobalamin II deficiency autosomal recessive velocardiofacial syndrome autosomal dominant supposed contiguous genes Bibliography[OMIM]: 142623 156100 250800 250800 256600 101000 VSLQDOSDUDVSLQDO VLJQV FDIäDXODLW spots, occasionally ocular anomalies. Potentially maternal imprinting. highly malignant group of tumors, childhood onset, involving mainly the kidney or the CNS. childhood/adults onset; painful, swelling, usually extremity bone destruction, with a soft tissue mass; high frequency of metastasis, characteristic chromosome rearrangement. progressive psychomotor deterioration, myoclonic seizures, decorticate posture, optic atrophy, blindness, coarse facies, skeletal dysplasia. juvenile/adult onset; psychotic syndromes in previously normal subject, schizophrenic disorders, paranoid hebephrenic disturbance, hallucinations, delusions. macular edema, hemorrhage, exudates. Eye isolated anomaly. 601607 133450 104170 600850 136900 recurrent thrombosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation. 142360 failure to thrive, irritability, weakness, pallor, infections, megaloblastic anemia, immunodeficiency. submucous cleft, hypernasal speech, cardiac anomalies, other ocular defects, short stature, mental retardation, microcephaly, prominent nose with squared root. Chromosome 22q11 deletion. Included in CATCH 22 spectrum of malformations (cardiac, abnormal faace, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcaemia, 22 chromosoma deletion). 275350 192430 601362 Prenat.Diagn.18,507510,1998 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 266 chromosome X localization Genus Clinical Database chromosome X localization 89 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: adrenomyodystrophy supposed X-linked recessive Akesson syndrome supposed X-linked recessive amelia X-linked supposed X-linked recessive amelo-cerebro-hypohydrotic syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity X-linked dominant X-linked recessive myopathy, psychomotor retardation, liver fatty degeneration, megalocornea, bladder ectasia, chronic constipation. mental retardation, spasticity, microcephaly, thyroid aplasia, folds/furrows scalp, cutis verticis gyrata, cataract. tetra-amelia, facial clefts, ears absence, nose absence, atresia ani. early infancy onset, seizures, spasticity, mental deterioration, muscular spasticity, demineralized enamel. amelogenesis imperfecta hypoplastic smooth androgen insensitivity minimal Bibliography[OMIM]: 300270 304200 301090 226750 hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta smooth type. 104530 small penis without hypospadias, minimal scrotal bifidity, delayed puberty, gynecomastia, 46,XY karyotype with normal testosterone levels. kindred showing affected males having either anencephaly or spina bifida. B.D.Encyclopedia 2954 p.116 anencephaly-spina bifida syndrome X-linked recessive anonychia thenar genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked recessive genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive X-linked recessive absence of nails, limited to thumbs. 188200 isolated deficiencies in the sense of smell. 301700 isolated form of imperforate anus. Hypospadias and hearing loss in Xlinked recessive inheritance. 207500 301800 Prenat.Diagn.18,11951197, 1998 arthrogryposis, cholestatic jaundice resembling Dubin-Johnson syndrome, renal dysfunction, nephrocalcinosis. 301820 arthrogryposis X-linked lethal X-linked recessive 301830 arthrogryposis X-linked moderately severe X-linked recessive severe contractures, scoliosis, chest deformity, hypotonia, respiratory insufficiency. contractures, scoliosis, ptosis, cryptorchidism, inguinal hernias. arthrogryposis X-linked resolving X-linked recessive resolving arthrogriposis, with mild to moderate contractures, normal intelligence and no other anomalies. juvenole onset. Deafness, peroneal muscular atrophy, sensory ataxia, cardiomyopathy, other clinical signs. 301830 anosmia congenital isolated anus imperforate arthrogryposis multiplex congenita-renal and hepatic abnormality ataxia Friedreich type-Charcot supposed contiguous genes Marie Tooth-peroneal muscular supposed X-linked recessive atrophy ataxia Shokeir type X-linked recessive ataxia-deafness X-linked supposed X-linked recessive athrombia essential Bergia syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked dominant supposed X-linked recessive branchial arch defects X-linked supposed X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database 301410 301830 302900 302500 ataxia, nystagmus, without kyphoscoliosis and pes cavus, late teens onset. infancy onset; hypotonia, ataxia, 301790 developmental delay, esotropia, optic atrophy, deafness. prolonged bleeding time with normal clot 209050 retraction, decreased platelet adhesion and aggregation with normal count. lethal hypertrophic cardiomyopaty, mental retardation childhood onset, muscle weakness with humeroperoneal distribution, severe myopia. microcephaly, deafness, short stature, dysmorphic face, cryptorchidism. chromosome X localization 309660 301950 90 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: bullous dystrophy macular type X-linked recessive calvarial hyperostosis supposed X-linked recessive Cantalamessa syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive supposed X-linked recessive Cantu-Hernandez syndrome carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type I autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive cardiomyopathy dilated X-linked supposed X-linked recessive Casamassimo syndrome X-linked recessive cataract zonular-nystagmus supposed X-linked recessive cataract-microcorneamicrophthalmia autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive supposed X-linked recessive cataract-spasticity-mental retardation syndrome bullae, alopecia, hyper-depigmentation, acrocyanosis, short stature, mental retardation. calvarium irregularity, frontoparietal exophytic prominences, without craniostenosis or intracranial pressure. short stature, mild mental retardation, primary gonadal failure, gynecomastia, mitral valve prolapse. Bibliography[OMIM]: 302000 302030 Am.J.Med.Genet.33,11 7-120,1989 308830 growth retardation, cerebral atrophy, very short stature, microcephaly, eyebrows/eyelashes absent, generalized keratosis follicularis. 212065 severe psychomotor retardation, hypotonia, ataxia, other neurological 601785 disorders. juvenile onset; idiopathic cardiomyopathy, progressive congestive heart failure; sudden death. microdontia, taurodontia, dens invaginatus. hereditary cataract zonular type associated with nystagmus, limited to male. Eye isolated anomalies. cataract, microcornea, microphthalmia. Eye isolated anomalies. 302045 313490 315000 302300 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 cataract, hypotonia, ataxia, spasticity, mental retardation. Ophthal.Paed.Genet.5, 201-203,1985 Am.J.Dis.Child.119,17 6,1970 cava left superior vena Gorlin syndrome X-linked recessive cleft palate, left superior vena cava anomalies, club foot. chondrodysplasia punctata Maroteaux type X-linked recessive choroideremia-deafnessobesity syndrome supposed X-linked recessive choroideremia-hypopituitarism syndrome contiguous genes supposed X-linked dominant choroidoretinal degeneration Falls Cotterman type supposed X-linked recessive 302940 moderate growth disturbance without asymmetry, distal phalanges hypoplasia, epiphyseal stippling persisting third years of life, facial dysmorphism resembling Binder dysostosis. visual fields constriction, choroidoretinal 303110 changes, obesity, congenital deafness. Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.399 choroideremia, short stature, Am.J.Med.Genet.34,51 hypopituitarism, neurological 1-513,1989 abnormalities. visual reduction in man, tapetal-like 303200 reflex in woman. Eye isolated anomaly. choroidoretinal dystrophy supposed X-linked recessive Christian II syndrome X-linked dominant Chudley-Lowry-Hoar syndrome X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database visual reduction beginning in middle age in man, resembling retinitis pigmentosa, absence of annular scotoma, early involvement of central vision. Eye isolated anomaly. craniosynostosis involving metopic suture, hemivertebrae/ cervical vertebrae fusion, imperforate anus. severe mental retardation, short stature, mild obesity, hypogonadism, dysmorphic facies, macrostomia, low total finger ridge count. chromosome X localization 303300 Stewart Prescott:Oral Facial Genetics C.V.Mosby Ed.p.751 1976 309490 91 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Collins-Partington syndrome colon atresia Inheritance: Synthesis: genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked dominant undefinable supposed X-linked recessive severe short stature, disproportionately short limb, small hands, heart disease, ptosis, high-arched palate, crowded dentition. 126190 later in infancy onset, intestinal obstruction, abdominal distention, vomiting, congenital colonic atresia with massive dilatation of the small intestine and colon, proximal to the atretic colonic segment. peculiar greenish-golden tapetal-like sheen in man, late onset. Eye isolated anomaly. severe mental retardation, seizures, septum pellucidum absent, communicating variety of hydrocephalus. early in infancy onset; slow progressive spastic quadriparesis, mental retardation. 303650 cone dystrophy X linked-tapetal supposed X-linked recessive like sheen type corpus callosum partial agenesis X-linked recessive Davis mental retardation syndrome supposed X-linked recessive deafness-dystonia-retardation syndrome supposed X-linked recessive deafness-hypogonadism syndrome supposed X-linked recessive deafness-hypogonadismalopecia syndrome supposed X-linked recessive undefinable deafness-spastic paraparesis syndrome X-linked recessive d'Ercole syndrome X-linked recessive Deshaies-Rott-Wissmuller syndrome supposed X-linked recessive dextrocardia-other cardiac malformations X-linked supposed X-linked recessive diabetes neonatal-diarrhea X-linked recessive diaphragm eventration X-linked supposed X-linked recessive Dinno syndrome X-linked recessive Dyggve-Melchior-Clausen syndrome X-linked Egeberg disease Genus Clinical Database supposed X-linked recessive progressive deafness, dysarthria, hyperactivity, bizarre dystonic posture of head and neck, other motor disorders, mental retardation. congenital deafness, primary hypogonadism, thickened calvarium, heterochromia hiridis. hypogenitalism, sensorineural deafness, alopecia. spastic paraparesis, 10 years onset, tremors, deafness, short stature, lens opacities, corneal clouding, choroidoretinal changes, hypogonadism. prenatal growth deficiency, microcephaly, mental retardation, dysmorphic face, hypogenitalism, cardiopathy, other clinical findings. mental retardation, microcephaly, short stature, obesity, hernias, other clinical data. dextrocardia associated with other malformation, such as pulmonic stenosis, transposition of great arteries, asplenia or polysplenia. severe diarrhea, insulin dependent diabetes, high level of IgE. anterior diaphragmatic hernia. bilateral microcornea, iridochoroidal coloboma, short stature, sloping shoulders, underdeveloped clavicles, kyphosis. short trunk dwarfism, platyspondyly, mild coarse face resembling Hurler syndrome, iliac crest irregularities, mucopolysacchariduria, without mental retardation. prolonged bleeding time and capillary fragility due to combining features of hemophilia A and Willebrand disease. chromosome X localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 304030 304100 309640 305050 304350 Genetic and Metabolic deafness. London W.B.Saunders 258259,1976 312910 Synd.Ident.4(2),58,1976 J.Genet.Hum.27,221236,1979 304750 300063 306950 B.D.OAS XII(6),109114,1976 304950 306800 92 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Ehlers-Danlos IX supposed X-linked recessive Ehlers-Danlos V X-linked recessive epidermodysplasia verruciformis genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive skin laxity, digits hyperextensibility, occiput protuberance characterized by symmetrical bony horns on each side of the foramen magnum, pointing caudad; bladder diverticula, frequent loose stool, copper and ceruloplasmin high levels. moderate joint hypermobility, with marked skin hyperextensibility, bruising tendency, mild skin fragility. lesions resembling verruca plana, with peculiar vacuolization in the epidermal cells, not involving nails, mucous membranes, hair, frequent squamous carcinomatous degeneration. polyhydramnios, short stature, skeletal dysplasia, hip dislocation, talipes, polydactyly, cryptorchidism, dysmorphic face, cleft palate, glossoptosis, microstomia, micrognathia, contractures. megaloblastic anemia, few months of life onset, low serum folate levels. prominent supraorbital ridges, joint contractures, micro-retrognathia, dental abnormalities, short trunk, straight thoracic spine, scoliosis, hyperostosis. facio-palato-osseous syndrome X-linked recessive folic acid transport defect X-linked dominant frontometaphyseal dysplasia X-linked recessive gangliosidosis GM3 supposed X-linked recessive Gibson syndrome X-linked recessive Gilbert-Dreyfus syndrome autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity sex-limited, sex influence X-linked recessive glomerulonephritis X-linked supposed X-linked recessive glutamyl ribose-5-phosphate storage disease X-linked recessive Grix syndrome X-linked recessive Gutenberger syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Haar-Dyken syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Harris syndrome X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database coarse face, macroglossia, gingival hypertrophy, stubby hands/feet, hernias, hepatosplenomegaly, normal fundi, mental retardation. bilateral radial agenesis, hydrocephalus, hypospadias, imperforate anus. infertile 46,XY male, hypospadias, hypogonadism, gynecomastia, testicular histological changes resembling Klinifelter syndrome. May be the same of Rosewater, Lubs, Reifenstein syndromes, reported as pseudohermaphroditism male incomplete type I, or allelicc forms of the same disorder. X-linked recessive, also autosomal dominant male-limited, autosomal recessive male-limited. mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis characterized by peculiar appearance of the capillary walls with/without mesangial cell interposition (type I-type II). coarse facies, mental retardation, seizures, hypotonia, weakness, proteinuria, renal failure, optic atrophy. hirsutism, other cutaneous changes, cleft palate, dysmorphic face, cleft tongue, cardiopathy, microcephaly, convulsions, other clinical findings. thrombocytopenia, hematuria, glomerulonephritis, high serum IgA levels. hemilateral congenital paresis, followed by ipsilateral hemihypotrophy and involuntary movements. neonatal teeth, congenital cardiopathy, intestinal anomalies/dysfunction. chromosome X localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 304150 305200 305350 J.Pediatr.98,747752,1981 229050 305620 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 396 305650 312190 307300 312100 305800 305920 B.D.OAS 11(5),107114,1975 314000 306960 Clin.Genet.9,479482,1976 93 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Holmes-Gang syndrome X-linked recessive B.D.Encyclopedia 3200 p.1796 hydrocephalus-cerebellar agenesis supposed X-linked recessive mental retardation, microcephaly, large anterior fontanel, short nose, club foot deformity, hypotonia. hydrocephalus, cerebellar agenesis, absence of the foramina of Luschka and Magendie. mental retardation, dysmorphic face, hypospadias, other clinical data. low levels of uricemia due to tubular hypersecretion. atrichia, baldness, ichthyosis follicularis, photophobia. 307830 hypospadias-mental retardation genetic heterogeneity syndrome supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive undefinable hypouricemia familial supposed X-linked recessive ichthyosis follicularis-atrichiaphotophobia supposed contiguous genes supposed X-linked recessive ichthyosis-male hypogonadism contiguous genes syndrome X-linked recessive immunodeficiency-6 X-linked recessive infantile spasm X-linked supposed X-linked recessive infertile male due to defective meiosis sex-limited, sex influence supposed X-linked recessive infertile male syndrome X-linked recessive Jonas syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Kallmann syndrome-spastic paraplegia supposed X-linked recessive Kapur syndrome X-linked dominant Kozlowski-Pietron syndrome supposed X-linked recessive lactic acidemia-E2 lipoyl transacetylase defect lenticonus posterior familial genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive undefinable supposed X-linked recessive Lesch-Nyhan mild X-linked recessive Lesch-Nyhan phenotypenormal HGPRT X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database male hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, with congenital ichthyosis, ocular defects. infancy/adult onset; recurrent infections, severe varicella, paucity of lymphoid tissue with normal serum immunoglobulin levels, normal B and NK cells, decreased T lymphocytes responses to immunogens. peculiar, infantile type of seizure similar to the one observed in West syndrome, EEG hypsarrhythmic type. male infertility due to spermatogenic arrest. X-linked recessive, also autosomal dominant male-limited, autosomal recessive male-limited. 46,XY male, cryptorchisidm without genital ambiguity, azoospermia, infertility due to androgen resistance. congenital insulin-dependent diabetes, intractable secretory diarrhea, dysplastic changes of intestinal mucosa, absence of islets of Langerhans. anosmia, infertility, other clinical findings of Kallmann syndrome with spastic paraplegia. rheumatic-like fever, arthritic conditions, widow's peak, ptosis, high ileal wings, inability to touch the ipsilateral shoulder, recurrent subluxations, other skeletal defects. stationary, unilateral, dysplastic carpal changes. hyperammonemia, profound lactic acidosis due to deficiency in the E2 segment of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. familial posterior lenticonus, less severe in the female. gouty arthritis, spasticity, involuntary movements, nephrolitiasis, occasionally mental retardation/dementia, without self-mutilation. phenotype typical for Lesch-Nyhan disease with self-mutilation, mental retardation, spasticity, hyperuricemia, normal HGPRT. chromosome X localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 307010 241760 308205 308200 312863 308350 309120 308370 415000 304790 308750 314570 Pediatr.Radiol.19,261262,1989 245348 Eye 9,119-123,1995 J.Inherit.Metab.Dis.5,1 83-186,1982 308950 94 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Lockhart syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive undefinable macular dystrophy X-linked X-linked recessive Malamud-Cohen syndrome X-linked recessive plurimalformation syndrome less marked in females, characterized by abdominal muscle hypoplasia, urinary tract malformations resembling prune belly syndrome, mental retardation, deafness, pulmonic stenosis. dystrophy of the fundus oculi macular area. Eye isolated anomaly. males affected cerebellar ataxia, followed by extrapiramidal signs. male pseudohermaphroditism, deafness, ocular changes, mental retardation. male pseudohermaphroditismmental retardation syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive Melnick-Needles osteodysplasty genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked dominant mental retardation X-linked and supposed X-linked recessive psoriasis long bones cortical irregularity, other skeletal dysplasia, dysmorphism, micrognathia, full cheeks, urinary/cardiac defects. severe mental retardation, seizures, dysmorphic face, strabismus, psoriasis, other clinical findings, normal chromosomes without fragile X. obesity, mental retardation, megalencephaly, dysmorphic facies, macroorchidism. tall thin Marfanoid habitus, long thin face, joint hyperextensibility, large head, moderate mental retardation without macroorchidism, fra-X test negative. mental retardation, distonic movements of the hands, dysarthria. Bibliography[OMIM]: 264140 309100 302600 Genet.Counsel.1,219225,1990 600122 309350 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 588 309480 mental retardation X-linked Clark-Baraitser X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked Lujan-Fryns type X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked Partington type X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked Tranebjaerg type X-linked recessive mental retardation, macrostomia, hypotonic mouth-breathing, psoriasis. mental retardation X-linkedprecocious puberty supposed X-linked recessive mental retardation-male hypogonadism-skeletal anomalies syndrome X-linked recessive Am.J.Med.Genet.23,12 males with tall stature, mental 7-137,1986 retardation, precocious puberty, macrocephaly; mother affected by acanthosis nigricans, keratosis, prominent jaw. moderate short stature, mental 307500 retardation, infertility, hypogonadism, cervical ribs/cervical vertebral anomalies. mental retardation-Xq duplication chromosomic X-linked recessive metacarpal 4-5 fusion genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive supposed X-linked recessive metaphyseal anadysplasia microcephaly-white matter calcification Mikati-Barakat syndrome Morse syndrome Genus Clinical Database genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive undefinable genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive undefinable genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive B.D.Encyclopedia 2640 p.1789 309520 Am.J.Med.Genet.30,25 1-262,1988 Am.J.Med.Genet 30,263-273,1988 males severe mental retardation, dysmorphic facies, short stature, ptosis, hernia, small testes. fourth and fifth metacarpal fusion. B.D.Encyclopedia 3250 p.1801 irregular distal metaphyses, hypoplastic femoral neck, recognized in the first months of age and disappearing after two years. microcephaly, severe mental retardation, calcification of the cerebral white matter, corneal clouding. 309645 prenatal growth deficiency; growth retardation, hypotonia, proximal renal tubular failure, distal tubule calcification, cholestatic jaundice, recurrent infections, dysmorphic facies, skeletal anomalies. decreased fetal activity, congenital contractures, microcephaly, severe oloprosencephaly. chromosome X localization 309630 251290 210550 306990 95 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: muscular dystrophy cardiac type supposed X-linked recessive muscular dystrophy limited to females supposed X-linked dominant cardiomyopathy, globular hypokinetic heart, ECG changes, similar to Duchenne disease, high serum creatine kinase levels. slowly progressive limb-girdle form of muscular dystrophy; limited to female, lethality in hemizygous males. puberty onset; slow progression of muscular dystrophy, resembling Becker type; high creatine kinase levels. shoulder/girdle/back muscular dystrophy, sparing face, calves; high serum CK levels; no myocardial involvement. progressive seizures, myoclonus, mental retardation, psychosis; mild symptoms in females. progressive muscle weakness,involving the legs without cardiac or neural disturbance, high serum creatine kinaselevels, characteristic autophagic vacuoles. congenital mild weakness, myopathy with characteristic fingerprint bodies at the muscle fibers periphery. adulthood onset; males affected by hypertrophy/patches of hypotrophy inducing quadriceps unusual appearance; later involvement of girdle and hand muscles. nephrolithiasis, renal tubular dysfunction, nephrocalcinosis. juvenile onset in males; motor-sensory neuropathy restricted to the feet inducing deformities and ulcerations. neutrophils with partial Pelger-Huet anomaly, neutropenia, lymphatic system involvement, severe viral/bacterial infection susceptibility. hereditary, X-linked recessive or dominant nystagmus. Eye isolated anomaly. myoclonia with nustagmus. muscular dystrophy Mabry type supposed X-linked recessive muscular dystrophy pectorodorsal supposed X-linked recessive myoclonus-epilepsy X-linked supposed X-linked recessive myopathy excessive autophagy X-linked recessive myopathy fingerprint body type supposed X-linked recessive myopathy quadriceps supposed X-linked recessive nephrolithiasis X-linked supposed X-linked recessive neuropathy sensory X-linked supposed X-linked recessive neutropenia Pelger-like anomaly X-linked recessive nystagmus X-linked X-linked dominant X-linked recessive nystagmus-myoclonic syndrome supposed X-linked dominant O'Brien-Nyhan-Shear syndrome supposed X-linked recessive obsessive-compulsive disorder- supposed autosomal dominant 1 short stature, joint contractures, dysostosis multiplex, mucopolysacchariduria. obsessive compulsion. Bibliography[OMIM]: 309930 309950 310000 310095 310370 310440 305550 310450 310468 310470 310350 310700 310800 Clin.Genet.9,399411,1976 164230 occipital hair-white lock supposed X-linked recessive patches of white hair on occipital area. 310900 olivopontocerebellar X-linked X-linked recessive 302500 ophthalmoplegia externalmyopia X-linked recessive optic atrophy-spastic paraplegia syndrome supposed X-linked recessive infantile onset; cerebellar ataxia, slow progression, normal strength/reflex/sensation. bilateral blepharoptosis, external ophthalmoplegia, eccentric pupil, other ocular changes, severe myopia, cardiac/skeletal defects. optic atrophy, spastic paraplegia, neurodegenerative disorders. orofaciodigital syndrome Xlinked recessive supposed X-linked recessive clinical features resembling OFD I syndrome, involving males, with preand postaxial polydactyly, median cleft, other clinical changes. Clin.Genet.34,325332,1988 Genus Clinical Database chromosome X localization 311000 311100 96 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: osteopathia striata WhyteMurphy type supposed X-linked dominant 311280 otopalatodigital II syndrome supposed X-linked dominant long bones longitudinal striations, increased bone density, macular hyperpigmented dermopathy, white forelock. dysmorphic face, large anterior fontanelle, microstomia, cleft palate, overlapping/flexed fingers, curved long bones, other skeletal defects, respiratory distress, deafness. palatodigital syndrome supposed X-linked recessive first decade of life onset; mental retardation, lower limb spasticity, cerebellar ataxia, tremor, bilateral posterior periventricular white matter lesions. spastic paraparesis, tremors, lens opacity, other ocular changes, short stature, hypogonadism, deafness. severe viral, protozoan, bacterial infections due to immune abnormalities; deficiency of a lymphocyte surface glycoprotein. low birth weight, small face resembling Silver-Russell, short stature, patches of widespread skin pigmentation, large head. juvenile onset; idiopathic destruction of alveolar bone, leading to premature loss of teeth. Am.J.Med.Genet.36,25 1-257,1990 pancreas adenocarcinoma familial genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive X-linked recessive paraplegia spastic Gutman type supposed X-linked recessive paraplegia spastic Wells syndrome X-linked recessive Parkman disease supposed X-linked recessive Partington syndrome supposed X-linked dominant periodontosis juvenile Plott syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked recessive undefinable supposed X-linked recessive poliosis occipital type X-linked recessive Porteous-Burn syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Powell syndrome supposed X-linked recessive proteinuria asymptomatic supposed X-linked recessive pseudohermaphroditism male 17,20-desmolase deficiency supposed X-linked recessive pterygium syndrome X-linked supposed X-linked dominant supposed X-linked recessive pigmented paravenous chorioretinal atrophy Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 304120 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 272 micrognathia, cleft palate resembling 302380 Robin sequence, index finger deviation Smith's Recognizable due to accessory phalangeal ossification Patterns of Human center, other anomalies. Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 288 abdominal pain, jaundice, anorexia, 260350 weight loss, diabetes due to pancreatic 190070 adenocarcinoma. 312910 308220 312780 260950 characteristic fundus appearance due to corpuscle pigmentation in a paravenous distribution, usually asymptomatic. Eye isolated anomaly. 172870 congenital laryngeal abductor paralysis, laryngeal stridor, mental retardation, occasionally ocular changes. small area of occipital white lock, with normal colour of the skin beneath the hair. microcephaly, developmental delay, dysmorphic facies resembling CoffinLowry, hypogenitalism, hypotonia. resistent profuse diarrhea, eczema, hemolytic anemia, cogenital diabetes, severe viral infections, normal immunologica/chemotaxis data. tubular proteinuria low-molecular-weight, without renal failure. females with normal genitalia, infertility, failure of pubertal development; males 46,XY with ambiguous genitalia/sex reversal, rudimentary uterus/falloppian tubes; no adrenogenital syndrome. multiple flexion contractures, skin webbing, cystic hygroma, fetal hydrops, intrauterine growth retardation. 308850 chromosome X localization Heredity in Ophthalmology: p.519 C.V.Mosby Ed. 1961 J.Med.Genet.27,339340,1990 304930 308990 309150 312150 97 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: pulmonary hypertension of the newborn X-linked dominant X-linked recessive R-binder deficiency X-linked recessive Reifenstein syndrome autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity sex-limited, sex influence X-linked recessive renal tubular acidosis II supposed genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive Renier syndrome X-linked recessive reticuloendotheliosis X-linked supposed X-linked recessive retinal detachment congenital autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive persistent, congenital pulmonary hypertension inducing right-to-left shunt through the foramen ovale or ductus arteriosus. unstable gait, paresthesia, other neurologic disability diagnosed as multiple sclerosis, congenital absence of R-type binders of cobalamin (vitamin B12). infertile 46,XY male, hypospadias, hypogonadism, gynecomastia, testicular histologic features resembling Klinefelter syndrome. May be the same of Lubs, Gilbert-Dreyfus, Rosewater syndromes, reported as pseudohermaphroditism male incomplete type I, or alleelic forms of the same disorder. X-linked recessive, also autosomal dominant male-limited, autosomal recessive malelimited. male infants with failure to thrive, dehydration, metabolic acidosis, without nephrocalcinosis and bone disease; occasionally neuro-ocular clinical findings including cataract. adrenal hypoplasia, muscular dystrophy, mental retardation, glycerol-kinase deficiency. malignant reticuloendotheliosis characterized by fever, anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, lymphadenopathy. congenital retinal nonattachment; occasionally changes resembling pseudoglioma. Eye isolated anomaly. retinal dysplasia Robin sequence-facial digital anomalies supposed X-linked recessive Robin sequence-heart malformation-clubfoot X-linked recessive Rosenberg-Chutorian syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive Rosewater syndrome X-linked recessive Rubinstein-like syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked dominant Genus Clinical Database visual function defect one/both eyes, other ocular dysfuncions, characteristic ophthalmological changes. Eye isolated anomalies. cleft palate, severe micrognathia, glossoptosis, tapering fingers, brachytelephalangy, hyperconvex nails. cleft palate, micrognathia, glossoptosis, resembling Pierre-Robin sequence, clubfoot, congenital cardiopathy. n.s.deafness, loss visual acuity, optic atrophy, dysarthria, muscular neurogenic atrophy, polyneuropathy suggesting Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. infertile 46,XY male, hypospadias, hypogonadism, gynecomastia, testicular histological changes resembling Klinefelter. Mai be the same of Reifenstein, Lubs, Gilbert-Dryfus syndromes, reported as pseudohermaphroditism male incomplete type I, or allelic forrms of the same disorder. Male-limited inheritance. clinical appearance of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, without mental retadation. chromosome X localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 265380 193090 312300 312100 312400 Clin.Genet.24,243251,1983 312500 312530 312550 311895 311900 311070 306500 312100 180850 98 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: sacral meningocele X-linked supposed X-linked dominant 312800 Saul-Stevenson syndrome supposed X-linked dominant undefinable Say syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked recessive Say-Meyer syndrome supposed X-linked recessive scapulo-peroneal dystrophy X-linked recessive SCARF syndrome supposed genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive Schimke-Horton syndrome supposed X-linked recessive schneckenbecken skeletal dysplasia X-linked recessive scleroderma familial progressive autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive sclerosis cerebral Scholtz type supposed X-linked recessive Scott syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Seemanova syndrome I supposed X-linked recessive Sengers syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Setchell disease Shear-Nyhan syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive undefinable supposed X-linked dominant preponderance of female sex; anterior sacral meningocele, partial absence of sacrum/coccyx, urinary incontinence, constipation, other clinical findings due to neurological involvement. Marfanoid habitus, ectopic pupils, mental retardation, tall stature, arachnodactyly. cleft palate, microcephaly, mental retardation, micrognathia, short stature, tapered fingers with hypoplastic distal phalanges, low-set thumb, renal dysplasia. trigonocephaly, short stature, mental retardation, developmental delay. first decade onset; slowly progressive humeroperoneal muscle weakness, contractures, neck flexion limitation, without pseudohypertrophy. May be the same of Emery-Dreifuss syndrome. lax skin, joint hyperextensibility, herniae, craniosynostosis, pectus carinatum, vertebral anomalies, teeth hypoplasia, dysmorphic face, ambiguous genitalia, liver nodules, psychomotor retardation. choreoathetosis, hypotonia, mental/growth retardation, postnatal microcephaly, strabismus, deafness. polyhydramnios, short-limb, large skull, flat face, skeletal dysplasia, snail-like iliac wings. generalized/limited dermis thickening or atrophy, due to collagen accumulation; visceral involvement, calcinosis, Raynaud disease, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, vasculitic, ulcers. deafness, blindness, weakness, spasticity, dementia, chyldhood onset. brachycephaly, dysmorphic facies, hirsutism, syndactyly , growth/mental retardation, spina bifida occulta, dermatoglyphics anomalies. microcephaly, spastic diplegia, mental retardation, epilepsy. congenital hydrocephalus, mental retardation , short stature, obesity, hypogenitalism. severe intrahepatic cholestasis due to inborn error in bile acid synthesis. 308050 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 308 Siber syndrome X-linked recessive unilateral ichthyosiform erythroderma, involving trunk/limbs, sparing the face; ipsilateral limb anomalies, with/without ipsilateral visceral anomalies, transitory punctate cartilage calcification, other associated findings. microcephaly, microphthalmia, corneal opacity, hypospadias, cryptorchidism, spastic quadriplegia. smell cyanade inability supposed X-linked recessive inability to smell cyanide. Smith-Fineman-Myers syndrome supposed X-linked recessive undefinable microcephaly, mental retardation, short stature, hypotonia, dysmorphic face. Genus Clinical Database chromosome X localization Bibliography[OMIM]: Proc.Gr.Genet.Center 1,14-15,1982 181180 314320 B.D.Encyclopedia 2491 p.613 312830 312840 269250 181750 302700 312860 311400 Tijd.Kindergen.53,3134,1985 235555 Clin.Genet.26,453456,1984 Am.J.Ophthalmol. 99,51-55,1985 304300 309580 99 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: spastic paraplegia-athetosis X-linked recessive 312890 Spiegler-Brooke syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant X-linked dominant spondylometaphyseal dysplasia Richmond type X-linked recessive teeth buried X-linked recessive athetosis, spastic paraplegia, occasionally seizures and myoclonus. cylindroma and epithelioma, adenoides cysticum, increasing translucent papules/nodules, mainly on the face, consisting of horn cysts and basaliomalike cells; cancer tendency. May be the same as cylindromatosis. coarse face, flat wide nasal bridge, hypertelorism, strabismus, nystagmus, contractures, severe kyphosis, speech impairment, flar vertebral bodies. metaphyseal dysplasia teeth buried by mucopolysaccharide. teeth impacted supposed X-linked recessive 308280 teeth oligodontia X-linked X-linked dominant testicular feminization incomplete X-linked recessive thumbs clasped genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive Tourette disease genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked recessive ulnar-mammary syndrome autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked dominant Usher IV syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Van den Berghe syndrome sex-limited, sex influence supposed X-linked recessive supposed contiguous genes X-linked recessive unerupted tooth, positioned against another tooth, or against bone/soft tissue, leading difficult its further eruption. oligodontia, hypodontia in both dentitions. detectability age at birth or at puberty; phallic enlargement, reported as clitoromegaly, partial labioscrotal fusion, without pubertal virilization, abdominal/inguinal testes; 46,XY, normal plasma testosterone. adducted/flexed thumbs, due to extension defect; extending during Moro reflex, usually persisting until 3-4 months of age. disorder affecting speech, learning, behaviour; multiple motor and vocal tics, throat, clearing, sniffing, sucking, inappropriate words /phrases, including coprolalia. upper limbs anomalies, involving ulnar ray structures, apocrine-mammary defects, characterized by axillary hair, absence small/absent mammary glands and nipples. male with retinitis pigmentosa and congenital deafness; occasionally cataract. ulnar hypoplasia/agenesis and lobsterclaw of feet. van den Bosch syndrome varicose veins W syndrome genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked dominant supposed genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive Waters-West syndrome X-linked recessive Winkelman syndrome genetic heterogeneity multifactorial supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 313100 313420 313550 313500 B.D.Encyclopedia 0050 p.119 314100 137580 181450 312650 314360 anhidrosis, mental retardation, choroideremia, acrokeratosis verruciformis, winged scapulae. varicose veins of the lower extremities. 314500 mild mental retardation, seizures, dysmorfism, median cleft palate/ lip, upper limbs anomalies. male affected; lethal congenital hemolytic anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, external genital anormalies. 311450 early-onset retinitis pigmentosa, dysarthria, extrapyramidal rigidity, other clinical findings due to progressive pallidal degeneration. chromosome X localization 192200 Am.J.Med.Genet.55,31 9-324,1995 600461 260200 100 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: X-linked recessive polyhydramnios, fetal movements decreased, intestinal atresia, atelia, urogenital anomalies, hydrocephalus, other neurological defects, ectromelia, amelia, other clinical findings including ocular defects. Eur.J.Pediatr.144,412414,1985 Aarskog syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked dominant X-linked dominant ptosis, other ocular abnormalities, widow's peak, short nose, short stature, brachydactyly, mild syndactyly, scrotal fold, hemochromatosis, other clinical data. adrenal hypoplasia congenital X-linked X-linked recessive agammaglobulinemia X-linked type 2 X-linked recessive Aicardi syndrome X-dominant lethal in male vomiting, cyanosis, apneic spells, hypoglycemia, seizures, collapse, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, signs of Addison disease. clinical data of agammaglobulinemia Bruton type but due to a gene not located at Xq21.3. corpus callosum agenesis, psychomotor retardation, infantile flexion spasms, myoclonic seizures, corneal clouding, lacunar chorioretinopathy. 305400 100050 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 128 300200 albinism ocular ForsiusEriksson type X-linked recessive albinism ocular X-linked type 1 X-linked recessive albinism ocular-deafness syndrome Winship type supposed X-linked recessive amelogenesis imperfecta hypomaturation X-linked X-linked recessive amelogenesis imperfecta hypoplastic rough X-linked dominant amyloidosis cutaneous familial X-linked dominant ataxia-myoclonic encephalopathy-macular degeneration X-linked recessive Brunner syndrome X-linked recessive cataract Walsh-Wegman type X-linked recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy X-linked 2 X-linked recessive Zimmer syndrome Bibliography[OMIM]: chromosome Xp localization Genus Clinical Database ocular albinism, fovea hypoplasia, nystagmus, myopia, protanomalous colorblindness. Eye isolated anomalies. nystagmus, head nodding, depigmented fundus, iridal dyschromia. Eye isolated anomaly. ocular albinism, iridal dyscromia, choroidoretinal defects, late onset sensorineural deafness. opaque soft easily abraded enamel with normal thickness resembling fluorosis. 300310 304050 Prenat.Diagn.20,344346,2000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 534 300600 300500 300650 301100 hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta with rough surface and very hard but abnormally thin enamel. in man diarrhea, respiratory infections, photophobia, skin hypopigmentation, ocular changes; in female:skin hyperpigmentation (linear streaks). congenital ataxia, myoclonic encephalopathy, macular degeneration. 301200 mild mental retardation, behavior change, aggressivity. cataract total congenital, slight vision reduction in heterozygous femals. Eye isolated anomaly. ambulation disability due to slowly progressive peroneal muscle weakness and wasting, pes cavus, scoliosis, difficulty in walking,foot drop and steppage gait, atrophy of the small muscle hands, occasionally upper extremity tremor. Am.J.Hum.Genet.52,1 032-1039,1992 302200 chromosome Xp localization 301220 Am.J.Med.Genet.64(1) ,69-72,1996 302801 101 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: chondrodysplasia punctata Xlinked recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive Coffin-Lowry syndrome X-linked dominant cone dystrophy X-linked,1 supposed X-linked recessive craniofrontonasal dysostosis genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked dominant supposed X-linked recessive symmetric distribution of the punctate calcifications, distal phalanges hypoplasia, mental retardation in affected males. short stature, mental retardation, pleasant attitude, dysmorphic coarse facies, thick lower lip, pugilistic nose, kyphoscoliosis, short puffy tapering fingers, drumstick terminal phalanges by X-ray. diminished visual acuity, normal color vision, myopia in man. Eye isolated anomaly. hypertelorism, broad bifid nasal tip, midface hypoplasia, craniosynostosis, cleft lip/palate, skeletal anomalies. deafness neurosensory Xlinked 6 X-linked dominant dermoids corneal X-linked recessive exudative vitreoretinopathy 2 genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive focal dermal hypoplasia genetic heterogeneity X-linked dominant glycogenosis IXA X-linked recessive glycogenosis VIII X-linked recessive Golabi-Ito-Hall syndrome X-linked recessive gonadotropin deficiency Xlinked supposed X-linked recessive granulomatous disease X-linked genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive hemoglobinuria paroxysmal nocturnal Genus Clinical Database genetic heterogeneity Bibliography[OMIM]: 302950 303600 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 274 304020 304110 122920 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 422 deafness, neurosensorial with 300066 incomplete penetrance and variable Hum.Mol.Genet.5,138 manifestation in carrier females. Infantile 3-1387,1996 onset. 304730 abnormal mesoblastic tissue, covered by epithelium. Eye isolated anomaly. 305390 posterior vitreous detachment, in all quadrants; more severe form than autosomal dominant. Could be the same gene of Norrie disease. Occasionally retinal changes resembling pseudoglioma. Eye isolated anomalies. 305600 dermal hypoplasia with fat herniations, red streaking skin, Smith's Recognizable microphthalmos/anophthalmos, other Patterns of Human ocular/ cutaneous/orodental/skeletal Malformation. 5th defects. Edition pag. 532 in males protuberant abdomen, 306000 hepatomegaly, growth retardation, delayed puberty, hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia without muscles involvement and mild symptoms in females. 306000 growth retardation, hepatomegaly, muscle cramps, stiffness, fatigability after exercise, myoglobinuria, sexual delay. Am.J.Med.Genet.17,36 postnatal growth deficiency, mental 7-374,1984 retardation, triangular face, dysmorphism, microcephaly, heart defects, other anomalies. hypogonadism hypogonadotropic. 306190 infant onset; severe pyogenic infections/granulomas in any organs, immunodeficiency, susceptibility to infections by any catalase-positive organisms. paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria associated with vomit, splenomegaly, sickness, due to unusual erythrocytes susceptibility to lytic action of complement; hemolysis, pancytopenia, positive acidifying hemolysis test, low leukocyte alkaline phosphatase leevels, decreased RBC acetylcholinesterase. chromosome Xp localization 306400 107271 102 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: hyperglycerolemia infantile form X-linked recessive ichthyosis X-linked X-linked recessive incontinentia pigmenti I X-dominant lethal in male Kallmann syndrome 1 X-linked recessive keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans cum ophiasi X-linked recessive Lenz syndrome X-linked recessive Leri-Weill syndrome X-linked dominant McLeod syndrome X-linked recessive mental retardation Wilson type X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked 49 mental retardation X-linked 50 acanthocytosis, chronic granulomatous disease. severe mental retardation, mutism, seizures, dysmorphic face. Xp11 localization. males affected by isolated mental retardation. males affected by isolated mental retardation. mental retardation X-linked Atkin-Flaitz type X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked Renpenning type X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked Sutherland type X-linked recessive mesomelic dwarfism Langer type genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive supposed X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database gluco-mineralocorticoid defect, osteoporosis, cryptorchidism, dystrophic myopathy, developmental delay. ichthyosis in male, especially calves/cubital fossae/neck, dirty appearance sparing palms, corneal opacity. females with congenital/neonatal linear skin bullae/vesicles, band-like hyperpigmentation, blisters, alopecia, oro-neuro-ocular defects including cataract. Four stages of development: inflammatory- verrucous-pigmentedhypopigmented. Occasionally developmment of retinoblastoma, paratesticular rabdomyosarcoma, acute leukemia, Wilms tumor, rabdoid renal tumors. hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, anosmia, cryptorchidism; occasionally arhinencephaly, other clinical data. thickening of the skin, loss of hair, loss of eyebrows/eyelashes, absent beard, blepharitis, ectropion, corneal degeneration, ophiasis, i.e. baldness in winding streaks about the head. microphthalmos/anophthalmos, ptosis, other ocular changes, microcephaly, mental retardation, large protruding ears, skeletal anomalies, camptosyndactyly, urogenital/other visceral anomalies. mesomelic dwarfism, with Madelung wrist deformity, forearm bowing, short thickened radius, elbow/wrist motion limitation. Pseudoautosomal gene. short stature, macrocephaly, coarse face, broad nasal tip, thick lips, macroorchidism. May be the same as Warkany syndrome. short stature, microcephaly, mental retardation, unremarkable face; without fragile X. mental retardation, short stature, microcephaly, spastic diplegia, small testes, intra-uterine growth retardation. severe mesomelic dysplasia, curved/short radius and tibia, hypoplastic ulna and fibula, restricted elbows movements, hands/feet displaced laterally, mandible hypoplasia. chromosome Xp localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 307030 308100 308300 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 502 601707 308800 309800 127300 312865 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 440 314850 309545 300114 Am.J.Med.Genet.73,47 4-479,1997 300115 Am.J.Med.Genet.73,47 4-479,1997 309530 308400 309500 309470 249700 312865 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 442 103 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: microphthalmos-linear skin defects Inheritance: Synthesis: supposed contiguous genes supposed X-dominant lethal in male X-linked dominant irregular linear skin defects involving head/neck; ocular defects, occasionally other clinical findings. Deletion Xp22.3. muscular dystrophy Becker type X-linked recessive muscular dystrophy Duchenne type genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive myopathy dystrophin defect X-linked recessive N syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Nance-Horan syndrome X-linked recessive nephrolithiasis X-linked 2 X-linked recessive night blindness congenital stationary type 1 genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive night blindness congenital stationary type 2 X-linked recessive Norrie disease X-linked recessive Opitz syndrome type I X-linked recessive optic atrophy Leber type mitochondrial optic atrophy non-Leber type X-linked recessive ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency X-linked dominant orofaciodigital syndrome I X-dominant lethal in male X-linked dominant Genus Clinical Database late childhood onset; pelvic muscle weakness, calf muscles pseudohypertrophy, high serum creatine kinase level. 3-5 years of age onset; pelvic weakness/atrophy, difficulty in squatting/climbing, stairs waddling gait, hyperlordosis, calves pseudohypertrophy, cardiomyopathy, high serum creatine kinase levels. Dystrophin gene defect. myopathy non progressive, cramps, myalgia. mental retardation, visual impairment, deafness, eyelids laterally overlapping, large corneas, abnormal auricles, cryptorchidism, hypospadias, spasticity. male cataract, other ocular defects, dental anomalies, supernumerary incisors, peculiar ear malformation, short fourth metacarpals. nephrocalcinosis, renal stones, progressive renal failure, microglobinuria. congenital non-progressive night blindness, subnormal vision, myopia, nystagmus, without progressive retinal degeneration. Eye isolated anomaly. decreased visual acuity and congenital loss of night vision, without progressive retinal degeneration. Eye isolated anomaly. bilateral leukocoria at birth, microphthalmos, other ocular defects, mental retardation, late-onset deafness, hypogonadism. Occasionally retinal changes resembling pseudoglioma. Could be the same gene as vitreoretinopathy exudative. dysphagia, stridorous cry, hoarse voice, typical dysmorphism, hypertelorism, prominent occiput, hypospadias, other anomalies. sudden progressive central vision loss due to optic atrophy, second/third decades onset; heart conduction defects. Exclusively (non-mendelian) maternally inheritance. early onset/congenital optic atrophy; occasionally mental retardation, other neurological findings. The gene may be between markers DXS993 and DXS991. ataxia, headaches, vomiting, respiratory distress, hypotonia, lethargy, coma, hyperammonemia, arginine/citrulline low levels. jaw/tongue, cleft lobulated tongue with hamartomas, irregular cleft palate, multiple milia, hyperplastic oral frenula, synbrachydactyly-polydactyly, mental retardation. chromosome Xp localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 309801 J.Med.Genet. 27,5963,1990 J.Med.Genet. 28,143144,1991 310200 310200 600119 310200 310465 302350 300009 310500 300071 310600 300000 535000 311050 Am.J.Hum.Genet.61,9 34-939,1997 311250 311200 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 262 104 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate X-linked recessive synthetase II phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate supposed X-linked dominant synthetase overexpression 1 X-linked recessive Prieto mental retardation syndrome X-linked recessive properdin deficiency X-linked recessive Proud-Levine-Carpenter syndrome X-linked recessive pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive X-linked recessive renal cell carcinoma papillary type autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa-15 X-linked dominant retinitis pigmentosa-2 X-linked recessive retinitis pigmentosa-3 X-linked recessive retinitis pigmentosa-6 X-linked recessive retinitis pigmentosa-mental retardation syndrome retinoschisis X-linked supposed contiguous genes X-linked recessive genetic heterogeneity rickets vitamin D-resistant I X-linked dominant rickets vitamin D-resistant II X-linked dominant Rud syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked recessive sarcoma synovial sporadic sideroblastic anemia X-linked X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: ataxia, mental retardation, other neurological disorders, cardiomyopathy, renal failure, arthritis, diabetes, dysmorphic face. severe phenotype in early onset; no neurologic expressions in late onset. Gout, due to PRPS overexpression, deafness, neurologic involvement. mental retardation, subcortical atrophy, dysmorphism, supernumerary teeth, sacral dimple, patella luxation, ocularskeletal changes. fulminant meningococcal infections due to properdin deficiency. male with severe acquired micrencephaly, contrattures, scoliosis, optic atrophy, other clinical data. Variable expression in females. growth retardation, lactic acidosis, weakness, ataxia, respiratory infections, optic atrophy, mental retardation, other neurological defects. hereditary multiple papillary renal cell carcinoma. 311860 X-linked dominant retinitis pigmentosa. May be the same of RP6. Eye isolated anomaly. decreased dim light vision, and constricted visual fields, with typical retinal changes. Eye isolated anomaly. decreased dim light vision, and constricted visual fields, with typical retinal changes; choroidoretinal degeneration with retinal reflex in heterozygous women. Eye isolated anomaly. decreased dim light vision, and constricted visual fields, with typical retinal changes.May be the same of RP15. Eye isolated anomaly. mental handicap and retinitis pigmentosa. 300029 visual defect with typical ophthalmological data, juvenile/middle life onset. Occaionally retinal changes resembling pseudoglioma. Eye isolated anomaly. rachitic deformity, short stature, osteomalacia, high alkaline phosphatase levels, hypophosphatemia. Misdiagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis in adult males. rachitic deformity, short stature, osteomalacia, high alkaline phosphatase levels, hypophosphatemia, deafness. congenital ichthyosis, seizures, mentalgrowth retardation, hypogonadism, retinitis pigmentosa, other anomalies. soft tissue sarcoma of synovial, juvenile onset, more common in males, frequent t(X;18)(p11.2;q11.2). 311850 309610 312060 300004 208800 312170 179755 312600 312610 Genomics 8,3540,1990 312612 Am.J.Hum.Genet.55,9 16-922,1994 312700 307800 307810 312770 312820 600192 300192 hypochromic anemia, hemochromatosis, 301300 somewhat enlarged spleeen. chromosome Xp localization 105 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Bibliography[OMIM]: Snyder-Robinson syndrome X-linked recessive spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive X-linked recessive Swyer syndrome supposed X-linked recessive undefinable thrombocytopenia X-linked supposed contiguous genes X-linked recessive Wilson mental retardation syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome autosomal dominant supposed autosomal recessive supposed genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive 309583 Clin.Pediat. 8,669674,1969 Am.J.Hum.Genet. 51 (suppl.9: A181 only,1992 male affected, childhood/juvenile onset; 313400 short trunk, platyspondyly, premature Smith's Recognizable osteoarthrosis, restricted mobility, Patterns of Human characteristic vertebral changes, arthritic Malformation. 5th complaints in female carriers. Edition pag. 378 sex reversal 46,XY female, without 306100 secondary sexual characteristics at puberty, amenorrhea, streak gonads, gonadal calcification, presence of small uterus and falloppian tubes; gonadoblastoma tendency, no Turner appearance. 313900 only affected male, with hemorrhagic diathesis, due to essential thrombocytopenia, occasionally tendency to infections and eczema. 309585 mental retardation, obesity, gynecomastia, speech difficulties, other clinical findings. 301000 defective T-lymphocyte activation. Eczema, megakaryocytic 600903 thrombocytopenia, recurrent infections, Am.J.Hum.Genet.57,A diarrhea, dysgammaglobulinemia. 98 only,1995 277970 marfanoid habitus, scoliosis, arachnodactyly, mild mental retardation, other clinical data. Carrier females clinically normal. chromosome Xq localization achromatopsia incomplete X-linked recessive adrenoleukodystrophy X-linked X-linked recessive adrenomyeloneuropathy X-linked recessive agammaglobulinemia Bruton type X-linked recessive agammaglobulinemia Swiss type autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive X-linked recessive albinism deafness X-linked syndrome alpha-thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome Genus Clinical Database contiguous genes supposed X-linked recessive color confusions of shades of red, grey, bluish, blue-green. Eye isolated anomaly. spastic paraplegia, hyperactivity, seizures, impaired vision, optic atrophy, dementia, psychosis, ataxia, impotence, pigmentation, thin/sparse hair, hypoglycemia, high levels of very-longchain fatty acids (doubt on the reliability of cultured CVS cell), impaired auditory discrimination. milder form of adrenoleukodystrophy with later onset and slow progression. early recurrent severe infections in males, tonsillar/adenoid tissues defect, periodic neutropenia, low levels of immunoglobulins, absence of Blymphocytes. lymphocytopenia, thymus atrophy, lack of delayed hypersensitivity, severe viral/fungal/bacterial infections. 303700 profound deafness, piebald trait without ocular albinism. 300700 300100 300100 300300 300400 mental retardation associated with alpha- 301040 thalassemia. Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 278 chromosome Xq localization 106 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Alport syndrome autosomal dominant autosomal dominant autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive Alport-leiomyomatosis syndrome supposed autosomal dominant sexlimited, sex influence supposed contiguous genes X-linked dominant hematuria, proteinuria with uncostant renal failure, ocular defects including anterior lenticonus, high-tone sensorineural deafness, other clinical findings. sensorineural deafness, hematuria, proteinuria, ocular changes including anterior lenticonus, diffuse leiomyomatosis involving esophagus, genital and thoracal structures. amelogenesis imperfecta-3 X-linked dominant anophthalmos X-linked X-linked recessive Arts syndrome X-linked recessive ataxia spinocerebellar-anemia sideroblastic supposed contiguous genes supposed X-linked recessive supposed X-linked recessive ataxia-dementia enamel hypomaturation inducing amelogenesis imperfecta resembling AIH1 type. anophthalmos, ankyloblepharon, mental retardation, preauricular tags, cleft palate. ataxia, optic atrophy, deafness, recurrent respiratory infections, early childhood death. first year onset; hypochromic microcytic anemia, ataxia. delayed walking, ataxia, tremor, nystagmus, adult onset dementia. early infancy onset; multiple ice-pick marks, follicular atrophoderma, hypotrichosis, followed by basal cell carcinoma. severe mental retardation, epilepsy, hypogonadism, obesity, microcephaly, coarse facial features, ocular-skeletal anomalies. Bibliography[OMIM]: 104200 308940 303631 Am.J.Kidney Dis.22(5),641648,1993 301201 301590 301835 301310 301840 Bazex syndrome genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked recessive Borjeson syndrome X-linked recessive cardiomyopathy dilated-3A X-linked recessive severe infantile dilated cardiomyopathy. Charcot Marie Tooth neuropathy X-linked 1 and 3 X-linked dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy deafness-mental retardation syndrome supposed contiguous genes X-linked recessive 302800 ambulation disability due to slowly progressive peroneal muscle weakness and wasting, pes cavus, scoliosis, difficulties in walking,foot drop and steppage gait, atrophy of the small muscle hands, occasionally upper extremity tremor. infancy onset; males with severe muscle 310490 weakness,deafness, mental retardation. Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy X-linked 1 X-linked dominant peroneal muscle weakness/atrophy, pes 302800 cavus, scoliosis. chondrodysplasia punctata Xlinked dominant X-dominant lethal in male X-linked dominant choroideremia X-linked recessive possible lethality in hemizygous male; female with asymmetric shortening, saddle nose, ichthyosis, cataract, kyphoscoliosis, contractures, asymmetric punctate calcifications disappearing in infancy; occasionally polydactyly. choroidal sclerosis, central vision reduction, night blindness. Eye isolated anomalies. Christian-DeMyer-Franken syndrome supposed X-linked recessive cleft palate X-linked X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database short stature, prominent metopic suture, cervical vertebral fusion, other skeletal dysplasia, mental retardation, strabismus, glucose intolerance. cleft palate usually incomplete/submucous; occasionally bifid uvula in carrier females. chromosome Xq localization 301845 301900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 584 300069 302960 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 388 303100 Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Ed. Elias I. Traboulsi 1998 p.397 309620 303400 107 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: deafness perceptive type X-linked recessive deafness stapes fixation anomaly X-linked recessive deuteranopia X-linked recessive congenital deafness perceptive type, mental retardation. conductive hearing loss, vestibular disturbance, fixed stapes footplate, abnormal patency of the cochlear aqueduct. normal visual acuity, with chromatic discrimination loss. Eye isolated anomaly. polyuria, polydipsia, low urine osmolarity, dehydration, secondary mental retardation, growth defect, ineffective vasopressin administration. fatal infectious, mononucleosis following infection with Epstein-Barr virus, inducing lymphoproliferative syndrome, lymphadenomegaly, hepatosplenomegaly, acquired hypogammaglobulinemia, B-cell lymphoma. nail dystrophy, skin depigmentation, hyperkeratosis, oral leukoplakia pancytopenia, mental retardation, other clinical data. diabetes insipidus nephrogenic genetic heterogeneity I X-linked recessive Duncan disease genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive dyskeratosis congenita genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive X-linked recessive ectodermal dysplasia, anhidrotic autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive hypo-anhidrosis, hypodontia, corneal clouding, hypotrichosis, frontal bossing, protruding lips, dry periorbital skin. Ehlers-Danlos IX supposed X-linked recessive Fabry disease X-linked recessive favism supposed autosomal dominant FG syndrome X-linked recessive fibroelastosis endocardial left ventricle supposed X-linked recessive Fleisher syndrome contiguous genes X-linked recessive glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency X-linked recessive skin laxity, digits hyperextensibility, occiput protuberance characterized by symmetrical bony horns on each side of the foramen magnum, pointing caudad; bladder diverticula, frequent loose stool, copper and ceruloplasmin high levels. male with dark, nodular angiectases in clusters, acroparesthesias, fever rheumatic-like, corneal opacities, optic atrophy, neuro-cardio-renal failure, orthostatic hypotension. hemolytic anemia following ingestion of the bean of Vicia fava or exposure to its pollen, due to erythrocyte G6PD deficiency. postnatal growth failure, macrocephaly, typical dysmorphism, tall/broad forehead, upsweep frontal hair, contractures, seizures, severe constipation, imperforate anus, hypotonia, corpus callosum partial agenesis. diffuse thickening of the left ventricular endocardium inducing myocardial contractility reduction, mitral regurgitation, pulmonic hypertension without cardiomegaly. short stature, retarded bone age, delayed puberty, recurrent infections, immunoglobulin/B cells deficiency. episodic/nonremitting hemolytic anemia, hemoglobinuria, jaundice, following ingestion or exposure to hemolytic agents, such as oxidant drugs, chemicals infections, favism. Genus Clinical Database chromosome Xq localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 304500 304400 303800 304800 308240 305000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 538 305100 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 540 304150 301500 134700 305450 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 280 305300 307200 305900 108 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: glycogenosis muscle X-linked X-linked recessive Golabi-Rosen syndrome X-linked recessive Gustavson syndrome X-linked recessive hemophilia A genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant X-linked recessive hemophilia B X-linked recessive hydrocephalus X-linked autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive late onset; distal weakness, cramps on exertion, high serum CK, low muscle PHK activity, normal enzyme activity in the liver. males infant pre-postnatal overgrowth, microcephaly usually without mental retardation, hypertelorism, macrostomia, large lower lip, tongue, midline groove, inguinal hernia, cryptorchidism, other defects. severe mental retardation, oprtic atrophy, seizures, hearing defect. hemorrhages into joints/muscles, inducing arthropathy/muscular fibrosis, frequent oral hemorrhages, occasionally central nervous system hemorrhages, due to Factor VIII deficiency. hemorrhages into joints/muscles, inducing arthropathy/muscular fibrosis, frequent oral hemorrhages, occasionally central nervous system hemorrhages, due to Factor IX deficiency. hydrocephalus, mental retardation, spasticity, adducted thumb, other neural defects, optic atrophy. Can be present, within the same family, syndromes including upon the acronym CRASH. Rare autosomal recessive form of this abnormality has been described. hypertrichosis generalized Xlinked X-linked dominant hypoparathyroidism X-linked autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive X-linked recessive immunodeficiency with increased IgM incontinentia pigmenti II X-dominant lethal in male Juberg-Marsidi syndrome X-linked recessive Kelley-Seegmiller syndrome X-linked recessive Lesch-Nyhan syndrome X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 311870 312870 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 168 309555 306700 306900 307000 308840 Prenat.Diagn.19,10671069 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 188 307150 congenital excessive hair, covering severely the body, especially face/trunk/upper limbs, and sparing palms/soles/mucous membranes. 307700 convulsions, neuromuscular irritability, tetany, spasms, hyperreflexia, oro-ocular defects including cataract. infancy onset; recurrent severe bacterial/monilial infections, enlarged tonsils/spleen/lymphnodes, arthritis, nephritis, other clinical findings, lymphoma tendency, absent IgG and IgA with elevated IgM levels. typical signs of incontinentia pigmenti due to gene located in the Xq28 band, inducing ocular/neurovisceral defects. Occasionally development of retinoblastoma, paratesticular rabdomyosarcoma, acute leukemia, Wilms tumor, rabdoid renal tumors. prenatal growth deficiency, growth/bone age/mental retardation, deafness, dysmorphism, saddle nose, hyperfolded ears, hypogenitalism, ocular defects. uric acid overproduction, gout, urolithiasis, occasionally mild neurologic disorders; partial deficiency of HPRT. clinically normal at birth; progressive choreoathetosis, spastic cerebral palsy, mental retardation, bizarre aggressive behaviour, self-mutilations, usually by biting, hyperuricemia, gout, urinary tract stones. chromosome Xq localization 308230 308310 309590 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 57,1735,1967 308000 109 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: lissencephaly X-linked X-linked dominant Lowe syndrome X-linked recessive Lubs syndrome X-linked recessive manic-depressive psychosis 2 X-linked dominant MASA syndrome supposed X-linked recessive undefinable megalocornea genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive X-linked recessive Menkes syndrome mitochondrial X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked FRAXE genomic imprinting X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked Martin-Bell type X-linked recessive severe mental retardation, seizures, corpus callosum agenesis, pachygiriaagyria. male with growth failure, mental retardation, ocular anomalies including cataract, primary glaucoma, hypotonia, acidosis, renal failure, rickets, osteomalacia, cryptorchidism. infertile 46,XY male, hypospadias, hypogonadism, gynecomastia, testicular histological changes resembling Klinefelter syndrome. May be the same of Rosewater, Gilbert-Dreyfus, Reifenstein syndromes, or allelic forms of the same disorder. Male-limited inherritance. elated/excited/irritable mood in manic symptomatology; impaired thought processes/disturbed thought, content and perceptual processes/hallucinations in schizophrenic disorders. hyposomia, hyperlordosis, mental retardation, shuffling gait, spasticity, adducted thumbs due to hypoplasia extensor pollicis muscles. Can be present, within the same family, syndromes including upon the acronym CRASH. symmetric, bilateral corneal diameter increase, with normal endothelial cells, occasionally presenile cataract. Eye isolated anomaly. male sex growth retardation, seizures, coarse/colorless/sparse/friable hair, pili torti, trichopoliodystrophy, cherubic expressionless face, microcephaly, spasticity, lethargy, nystagmus, bladder diverticula, other neuro-visceral-skeletal defects, low serrum copper/ceruloplasmin. mental retardation, macroorchidism, other clinical features of X-linked mental retardation syndromes. macrocephaly, long face, large prominent ears, macro-orchidia, mental retardation, fingers hyperestention. Potentially maternal imprinting. mental retardation X-linked muscular atrophy syndrome X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked nonspecific type 3 X-linked recessive methylglutaconicaciduria II mitochondrial X-linked recessive Miles-Carpenter mental retardation syndrome supposed X-linked recessive mitral valve dysplasia X-linked X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 300067 300121 309000 Prenat.Diagn.18,11171121, 1998 313700 300068 312100 309200 303350 308840 309300 309400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 198 309548 309550 Prenat.Diagn.20,611614,2000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 150 severe mental retardation, awkward gait, 309600 speech disability, unabitity to walk, muscular atrophy. mental retardation resembling Martin309541 Bell syndrome. dilated cardiomyopathy, neutropenia, skeletal myopathy, weakness, abnormal mitochondria. mental retardation, microcephaly, exotropia, muscular hypotonia, contractures, dermatoglyphic changes. male affected by congenital heart disease due to myxomatous valvular dystrophy; aortic-tricuspid regurgitation; secondary valvular calcifications. chromosome Xq localization 302060 309605 314400 110 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: Mohr-Tranebjaerg syndrome supposed X-linked recessive 3-5 year onset; progressive hearing loss in males, myopia, decreased visual acuity, mental retardation. mucopolysaccharidosis II X-linked recessive muscular dystrophy DreifussEmery type X-linked recessive myopathy centronuclear Xlinked type X-linked recessive myopia X-linked X-linked recessive coarse facies, respiratory distress, herniae, joint stiffness, hepatosplenomegaly, skin nodules/thickening, mental retardation, ocular defects including atypical retinitis pigmentosa. first decade onset; progressive humeroperoneal weakness, without pseudohypertrophy; cardiomyopathy, elbows/neck contractures. severe respiratory distress, facial diplegia, cataract, other ocular defects, severe myopathy, weakness, hydramnios. myopia. Eye isolated anomaly. otopalatodigital I syndrome X-linked recessive deafness, cleft palate, borad nasal root with pugilistic appearance, wide toes spacing resembling tree frog, generalized bone dysplasia. ovarian failure premature genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant supposed X-linked dominant ovarian failure premature 1 paraplegia spastic X-linked 1 supposed genetic heterogeneity supposed X-linked dominant supposed contiguous genes X-linked recessive X-linked recessive menstrual irregolarities, followed by premature ovarial failure, estrogen deficiency, and high levels of gonadotropin, with/without Xq deletion. premature ovarian failure. paraplegia spastic X-linked 2 X-linked recessive parkinsonism Laxova-Brown syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Pelizaeus-Merzbacher syndrome 1 X-linked recessive Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like X-linked recessive Pettigrew-Jackson-Ledbetter syndrome X-linked recessive phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive X-linked recessive panhypopituitarism X-linked Genus Clinical Database Bibliography[OMIM]: 304700 Acta Ophthalmol.Scand.74( 6),632-635,1996 309900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 456 310300 310400 310460 311300 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 270 176440 311360 non dysmorphism, short stature due to growth hormone deficiency. 312000 early onset slow progression of spastic paraplegia, ocular/cerebellar involvement, mild mental retardation. Can be present, within the same family, syndromes including upon the acronym CRASH. spastic gait, hyperreflexia, without mental retardation/spinocerebellar signs. early onset parkinsonism, seizures, tremors, postural changes, megalencephaly, no basal ganglia calcification, shuffling gait, mental retardation, no macroorchidism. nystagmoid eye movements, head jerking and rolling, ataxia, spasticity, choreic movements, optic atrophy, microcephaly, laryngeal stridor. Commomnly, duplication in DNA which contains the PLP gene. nystagmoid eye movements, head jerking and rolling, ataxia, spasticity, choreic movements, optic atrophy, laringeal stridor, microcephaly, no proteolipid- protein defect. severe mental retardation, choreoathetosis, seizures, other signs of basal ganglia involvement, iron accumulation in the basal ganglia, Dandy-Walker malformation. in males chronic, nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia, myopathy, neurological disorders. 312900 308840 chromosome Xq localization 312920 311510 312080 Prenat.Diagn.19,266268,1999 311601 304340 311800 111 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate supposed X-linked dominant synthetase overexpression 1 X-linked recessive protanopia X-linked recessive situs inversus-heart defectssplenic defects genetic heterogeneity spinal muscular atrophy Kennedy type X-linked recessive testicular feminization complete X-linked recessive thoracoabdominal syndrome X-linked dominant thyroxine-binding globulin defects torsion dystonia X-linked supposed X-linked dominant X-linked recessive X-linked recessive torticollis Goeminne type X-linked dominant Wieacker syndrome supposed X-linked recessive Wood-Black-Norbury syndrome X-linked dominant Synthesis: severe phenotype in early onset; no neurologic expressions in late onset. Gout, due to PRPS overexpression, deafness, neurologic involvement. defect in screening red-green color. Eye isolated anomaly. primary defect in lateralization, leading situs inversus, congenital heart defects, polysplenia/asplenia, other clinical findings. juvenile onset; facial, bulbar, spinal, lateonset; proximal muscle atrophy with fasiculations, cramps, tremor; sexual dysfunction, impotence, decreased fertility, gynecomastia. sex reversal syndrome, inguinal herniae, containing testes, in infant female 46,XY; absent/rudimentary uterus, blind vagina, breast development/female fat deposition, occurring before pubarche; no menses, absent/scanty pubic and axillary hair, peculiar laaboratory data; breast cancer susceptibility. anterior diaphragmatic and abdominal wall hernia, diaphragmatic pericardium defect, hypoplastic lung, cardiac anomalies. high/low levels of TBG or thyroxine, without clinical disease. Bibliography[OMIM]: 311850 303900 306955 313200 313700 300068 313850 314200 affected males, age onset third decade; spasmodic eye blinking, parkinsonian symptoms, accompanied or preceded by dystonia. torticollis, facial asymmetry, plagiocephaly, periocular pigmentation, keloids/nevi, pyelonephritis, duodenal ulcer, infertility, cryptorchidism. multiple contractures, motor speech retardation, dysarthria, ptosis, other ocular anomalies. severe hypotonia in males resembling "floppy baby", spastic paraplegia in females, low birth weight, nightblindness. 314250 hematuria, proteinuria, renal failure, ocular defects including anterior lenticonus, high-tone sensorineural deafness, other clinical findings. 301050 303630 abnormal behavior from early infancy, lack of effective human contact. bullae, alopecia, hyper-depigmentation, acrocyanosis, short stature, mental retardation. diminished visual acuity. Eye isolated anomaly. 209850 314300 314580 300076 600486 chromosome Xq22 localization Alport syndrome X-linked supposed contiguous genes supposed X-linked recessive chromosome Xq27 localization autism infantile autosomal recessive bullous dystrophy macular type X-linked recessive cone dystrophy X-linked, 2 Genus Clinical Database X-linked recessive chromosome Xq27 localization 302000 300085 Am.J.Hum.Genet.60,1 468-1473,1997 112 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: hemophilia B X-linked recessive hypoparathyroidism X-linked Lesch-Nyhan syndrome autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive X-linked recessive 306900 hemorrhages into joints/muscles, inducing arthropathy/muscular fibrosis, frequent oral hemorrhages, occasionally central nervous system hemorrhages, due to Factor IX deficiency. 307700 convulsions, neuromuscular irritability, tetany, spasms, hyperreflexia, oro-ocular defects including cataract. prostate cancer hereditary autosomal dominant schizophrenia-2 autosomal dominant genetic heterogeneity multifactorial undefinable clinically normal at birth; progressive choreoathetosis, spastic cerebral palsy, mental retardation, bizarre aggressive behaviour, self-mutilations, usually by biting, hyperuricemia, gout, urinary tract stones. early-onset prostate cancer. young/adult age onset; psychotic symptoms, hallucinations, personality disorders. Bibliography[OMIM]: 308000 176807 601518 600020 181500 chromosome Xq28 localization achromatopsia incomplete X-linked recessive adrenoleukodystrophy X-linked X-linked recessive adrenomyeloneuropathy X-linked recessive anophthalmos X-linked X-linked recessive cardiomyopathy dilated-3A X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata Xlinked dominant X-dominant lethal in male X-linked dominant Christian-DeMyer-Franken syndrome supposed X-linked recessive deuteranopia X-linked recessive diabetes insipidus nephrogenic genetic heterogeneity I X-linked recessive dyskeratosis congenita Genus Clinical Database genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive X-linked recessive color confusions of shades of red, grey, bluish, blue-green. Eye isolated anomaly. spastic paraplegia, hyperactivity, seizures, impaired vision, optic atrophy, dementia, psychosis, ataxia, impotence, pigmentation, thin/sparse hair, hypoglycemia, high levels of very-longchain fatty acids (doubt on the reliability of cultured CVS cell), impaired auditory discrimination. milder form of adrenoleukodystrophy with later onset and slow progression. anophthalmos, ankyloblepharon, mental retardation, preauricular tags, cleft palate. severe infantile dilated cardiomyopathy. 303700 possible lethality in hemizygous male; female with asymmetric shortening, saddle nose, ichthyosis, cataract, kyphoscoliosis, contractures, asymmetric punctate calcifications disappearing in infancy; occasionally polydactyly. short stature, prominent metopic suture, cervical vertebral fusion, other skeletal dysplasia, mental retardation, strabismus, glucose intolerance. normal visual acuity, with chromatic discrimination loss. Eye isolated anomaly. polyuria, polydipsia, low urine osmolarity, dehydration, secondary mental retardation, growth defect, ineffective vasopressin administration. nail dystrophy, skin depigmentation, hyperkeratosis, oral leukoplakia pancytopenia, mental retardation, other clinical data. 302960 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 388 chromosome Xq28 localization 300100 300100 301590 300069 309620 303800 304800 305000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 538 113 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency X-linked recessive hemophilia A genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal dominant X-linked recessive hydrocephalus X-linked autosomal recessive genetic heterogeneity X-linked recessive episodic/nonremitting hemolytic anemia, hemoglobinuria, jaundice, following ingestion or exposure to hemolytic agents, such as oxidant drugs, chemicals infections, favism. hemorrhages into joints/muscles, inducing arthropathy/muscular fibrosis, frequent oral hemorrhages, occasionally central nervous system hemorrhages, due to Factor VIII deficiency. hydrocephalus, mental retardation, spasticity, adducted thumb, other neural defects, optic atrophy. Can be present, within the same family, syndromes including upon the acronym CRASH. Rare autosomal recessive form of this abnormality has been described. incontinentia pigmenti II X-dominant lethal in male Juberg-Marsidi syndrome X-linked recessive manic-depressive psychosis 2 X-linked dominant MASA syndrome supposed X-linked recessive undefinable mental retardation X-linked FRAXE genomic imprinting X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked FRAXF X-linked recessive mental retardation X-linked Martin-Bell type X-linked recessive macrocephaly, long face, large prominent ears, macro-orchidia, mental retardation, fingers hyperestention. Potentially maternal imprinting. mental retardation X-linked nonspecific type 3 X-linked recessive mental retardation resembling MartinBell syndrome. mental retardation X-linked type 41 X-linked recessive nonspecific mental retardation methylglutaconicaciduria II mitochondrial X-linked recessive dilated cardiomyopathy, neutropenia, skeletal myopathy, weakness, abnormal mitochondria. Genus Clinical Database typical signs of incontinentia pigmenti due to gene located in the Xq28 band, inducing ocular/neurovisceral defects. Occasionally development of retinoblastoma, paratesticular rabdomyosarcoma, acute leukemia, Wilms tumor, rabdoid renal tumors. prenatal growth deficiency, growth/bone age/mental retardation, deafness, dysmorphism, saddle nose, hyperfolded ears, hypogenitalism, ocular defects. elated/excited/irritable mood in manic symptomatology; impaired thought processes/disturbed thought, content and perceptual processes/hallucinations in schizophrenic disorders. hyposomia, hyperlordosis, mental retardation, shuffling gait, spasticity, adducted thumbs due to hypoplasia extensor pollicis muscles. Can be present, within the same family, syndromes including upon the acronym CRASH. mental retardation, macroorchidism, other clinical features of X-linked mental retardation syndromes. mental retardation, macroorchidism, other clinical features of X-linked mental retardation syndromes. chromosome Xq28 localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 305900 306700 307000 308840 Prenat.Diagn.19,10671069 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 188 308310 309590 309200 303350 308840 309548 300031 Hum.Molec.Genet.2,19 7-200,1993 309550 Prenat.Diagn.20,611614,2000 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 150 309541 300104 Nature Genet. 19,134139,1998 309541 302060 114 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: mitral valve dysplasia X-linked X-linked recessive 314400 mucopolysaccharidosis II X-linked recessive muscular dystrophy DreifussEmery type X-linked recessive myopathy centronuclear Xlinked type X-linked recessive male affected by congenital heart disease due to myxomatous valvular dystrophy; aortic-tricuspid regurgitation; secondary valvular calcifications. coarse facies, respiratory distress, herniae, joint stiffness, hepatosplenomegaly, skin nodules/thickening, mental retardation, ocular defects including atypical retinitis pigmentosa. first decade onset; progressive humeroperoneal weakness, without pseudohypertrophy; cardiomyopathy, elbows/neck contractures. severe respiratory distress, facial diplegia, cataract, other ocular defects, severe myopathy, weakness, hydramnios. progressive muscle weakness,involving the legs without cardiac or neural disturbance, high serum creatine kinaselevels, characteristic autophagic vacuoles. myopia. Eye isolated anomaly. 311300 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 270 312900 308840 myopathy excessive autophagy X-linked recessive myopia X-linked X-linked recessive otopalatodigital I syndrome X-linked recessive deafness, cleft palate, borad nasal root with pugilistic appearance, wide toes spacing resembling tree frog, generalized bone dysplasia. paraplegia spastic X-linked 1 X-linked recessive paraplegia spastic X-linked 2 X-linked recessive parkinsonism Laxova-Brown syndrome supposed X-linked recessive early onset slow progression of spastic paraplegia, ocular/cerebellar involvement, mild mental retardation. Can be present, within the same family, syndromes including upon the acronym CRASH. spastic gait, hyperreflexia, without mental retardation/spinocerebellar signs. early onset parkinsonism, seizures, tremors, postural changes, megalencephaly, no basal ganglia calcification, shuffling gait, mental retardation, no macroorchidism. epileptic seizures, multiple bilateral subependymal nodules diagnosed on MRI. Most patients are female. Males with BPNH are rare and may present mental retardation and other anomalies. severe mental retardation, choreoathetosis, seizures, other signs of basal ganglia involvement, iron accumulation in the basal ganglia, Dandy-Walker malformation. defect in screening red-green color. Eye isolated anomaly. only females, 1-2 years of age onset; progressive dementia, autistic features, acquired microcephaly, spasticity, loss of purposeful hand use, ataxia, tachypnea. Possible urea cycle defect. Occasionally sudden death due to cardiac dysfunction. male affected, childhood/juvenile onset; short trunk, platyspondyly, premature osteoarthrosis, restricted mobility, characteristic vertebral changes, arthritic complaints in female carriers. periventricular bilateral nodular X-dominant lethal in male heterotopia Pettigrew-Jackson-Ledbetter syndrome X-linked recessive protanopia X-linked recessive Rett syndrome sporadic supposed X-linked dominant spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda genetic heterogeneity supposed autosomal recessive X-linked recessive Genus Clinical Database chromosome Xq28 localization Bibliography[OMIM]: 309900 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 456 310300 310400 310440 310460 312920 311510 300049 304340 303900 312750 Neuropediatrics 30(3),146-148,1999 313400 Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation. 5th Edition pag. 378 115 of 116 12.2 Elenco delle malattie per distribuzione cromosomica da Genus: Clinical Database for over 5,000 Genetic Disorders Disorder: Inheritance: Synthesis: X-linked dominant torticollis, facial asymmetry, plagiocephaly, periocular pigmentation, keloids/nevi, pyelonephritis, duodenal ulcer, infertility, cryptorchidism. deafness neurosensory Xlinked 4 X-linked recessive deafness, congenital neurosensorial with 300030 mild manifestation in carrier females. male-determining factor defect autosomal recessive autosomal recessive Swyer syndrome supposed X-linked recessive undefinable sex reversal male 46,XX, resembling Klinefelter syndrome. 46,XY karyotype or Y-X translocation or Y-autosome translocation. sex reversal 46,XY female, without secondary sexual characteristics at puberty, amenorrhea, streak gonads, gonadal calcification, presence of small uterus and falloppian tubes; gonadoblastoma tendency, no Turner appearance. torticollis Goeminne type Bibliography[OMIM]: 314300 chromosome Yp localization 278850 306100 chromosome Yq localization lissencephaly X-linked X-linked dominant Sertoli cell only defect genetic heterogeneity germinal mosaicism sex-limited, sex influence supposed X-linked recessive supposed Y-limited Genus Clinical Database severe mental retardation, seizures, corpus callosum agenesis, pachygiriaagyria. infertile 46,XY male, with seminiferous tubules lacking in spermatogonia, normal secondary sexual development, uncommon transitory pubertal gynecomastia. Yq deletion. Male-limited disease. chromosome Yq localization 300067 300121 305700 400003 116 of 116