Unit 3 Self-Quiz, pages 404–405
advertisement

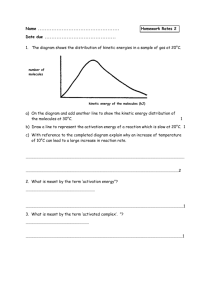
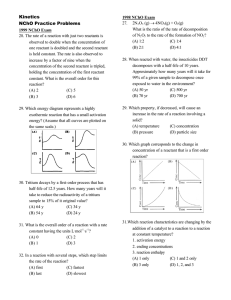
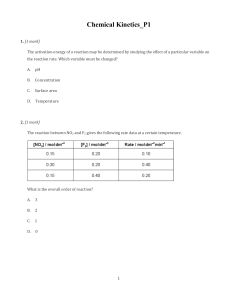
Unit 3 Self-Quiz, pages 404–405 1. (d) 2. (c) 3. (b) 4. (b) 5. (a) 6. (b) 7. (a) 8. (a) 9. (c) 10. (c) 11. (c) 12. (d) 13. (c) 14. (a) 15. (a) 2.6 × 10−2 mol/(L·s) 16. (c) 17. True 18. False. When a reaction is reversed in enthalpy calculations, the sign of ΔH changes but its magnitude remains the same. 19. True 20. True 21. False. Combining 2 light nuclei to form a heavier, more stable nucleus is called fusion. 22. False. One of the most abundant energy sources is the energy that binds the atomic nucleus together. 23. False. A modern wind turbine can generate enough electricity to supply several homes. 24. True 25. False. The effect of changing reactant concentrations on the rate of a reaction cannot be predicted by looking at a balanced chemical equation. 26. False. A catalyst is a substance that increases reaction rate by providing an alternative reaction mechanism with a lower activation energy and is not consumed in the reaction. 27. True 28. False. Biocatalysts are thought to increase reaction rate by providing an alternative reaction mechanism with a lower activation energy. 29. True 30. False. The rate constant, k, varies depending on the chemical reaction and conditions. 31. True 32. False. The global warming potential of “super” greenhouse gases is much greater than that of carbon dioxide. Copyright © 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Unit 3: Energy Changes and Rates of Reaction U3-3