Document 14312568
advertisement

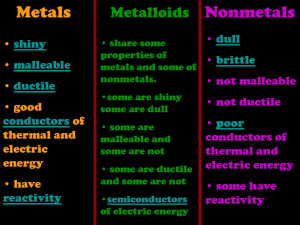
Station 1 4.neutron 1.nucleus 3. proton 2. electron Fill in the table below about the parts of the atom. Particle Charge Location Mass Proton + nucleus 1 amu Neutron 0 nucleus 1 amu Electron - Orbits around nucleus 0 Describe the structure of the nucleus. (What particles are inside? Where in the atom is it?) The nucleus is in the center of the atom. It holds the protons and neutrons. Therefore, the mass of the atom is in the nucleus. Station 2 1. What does the atomic number tell us about the atoms of an element? It tells us the number of protons and can be used to identify (the name) of the element. What two things are included in the atomic mass number of an element? The protons and neutrons 1. Give the following information for each element: A B C Name: Lead Name: Neon Name: Arsenic Atomic Number: 82 Atomic Number: 10 Atomic Number: 33 Protons: 82 Protons: 10 Protons: 33 Electrons: 82 Electrons: 10 Electrons: 33 Atomic Mass Number: 207 Atomic Mass Number: 20 Atomic Mass Number: 75 Station 3 • Give the properties of: – Metals: shiny, ductile, malleable, good conductors, high melting point, high density – Metalloids: shiny, not malleable, not ductile, semiconductors – Nonmetals: poor conductors, brittle solids or gases, low melting point – Noble gases: gases at room temperature, poor conductors, not reactive Station 4 • Give the properties of: – Rhodium: It is a metal, therefore it is shiny, a good conductor, malleable, ductile, high melting point, high density. – Tellurium: It is a metalloid, therefore it is a semiconductor, shiny, not malleable, not ductile. – Xenon: It is a Noble Gas, therefore it is a gas at room temperature, not reactive, and is a poor conductor. – Iodine: It is a nonmetal, therefore it is a brittle solid, a poor conductor, has a low melting point. Station 5 • Give the definitions of the following: 1. Solubility: ability of a substance to dissolve 1. Flammability: ability of a substance to burn 1. Ductile: ability of a metal to be stretched into a wire 1. Conductivity: ability to allow heat and electricity to flow 2. Malleable: ability of a metal to be bent or hammered into thin sheets 1. Corrosive: ability to eat away at something, such as a metal by acid Station 6 • Classify the following properties as physical or chemical: 1. Boiling point= P 6. Flammable= C 2. Corrosive= C 7. Ductile= P 3. Conductivity= P 8. Ability to mold= C 4. Ability to rust= C 9. Solubility= P 5. Malleable= P 10. Reactive= C Station 7 1. Which type of change produces a new substance? A chemical change produces a new substnace. 2. Classify the following changes as physical or chemical: a) Dissolving= P h) Baking= C b) Burning= C i) Frying= C a) Melting= P j) Decaying= C b) Digesting= C k) Molding= C a) Mixing= P b) Rusting= C a) Melting= P l) Corroding= C m) Boiling= P