The of Thermodynamics “Zeroth Law”
advertisement

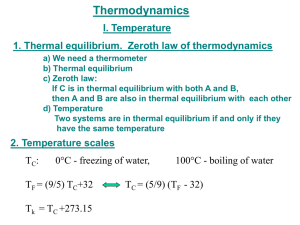
The “Zeroth Law” of Thermodynamics Definition of Thermal Equilibrium: • 2 systems are in thermal equilibrium: If & only if there is no net flow of heat between them when they are brought into thermal contact. • A system’s Temperature is an indicator of Thermal Equilibrium because, if 2 systems at the same temperature are in thermal contact, There is no net flow of heat between them. The “Zeroth Law” of Thermodynamics A TA B TB C TC • Consider 3 Objects, A, B C: “If A is in thermal equilibrium with B & if B is in thermal equilibrium with C, then A is in thermal equilibrium with C”. • In terms of system Temperatures: If TA = TB & TB = TC, then TA = TB. The ZEROTH Law is 1. The main reason that thermometers work! & also 2. The main reason that they are useful!! A More General Discussion! • As we know, if warm & cold objects are placed in thermal contact, Heat Energy Q flows from the Warm Object to the Cold Object until Thermal Equilibrium is established. th “0 ” Law of Thermodynamics: “If 2 systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a 3rd system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other” th “0 ” Law of Thermodynamics “If 2 systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a 3rd system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other” • The property which the 3 systems have in common is known as a Thermometric Parameter, X. • So, generally, The “0th” Law of Thermodynamics is If X1 = X2 & X1 = X3, then X2 = X3. The “Zeroth” Law of Thermodynamics Example The “Zeroth” Law of Thermodynamics Example Another Example of the “Zeroth” Law a) b) B C A VA, PA VC, PC C VB, PB VC, PC “If two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are in equilibrium with each other.” c) A B VA, PA VB, PB The “0th Law” of Thermodynamics “If two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are in thermak equilibrium with each other.” • For gases, this leads to an Equation of State: q = f(P,V ) where the parameter q (= temperature) characterizes the equilibrium. • Even more useful is the fact that this same value of q also characterizes any other system which is in thermal equilibrium with the first system, regardless of its state. The 3rd Law of Thermodynamics •The 3rd Law of Thermodynamics is a Quantum Mechanical Law that fixes the absolute value of the entropy: S → 0 as T → 0 •Reif’s statement of the 3rd Law is S → S0 as T → 0+ with 0+ < ~ 0.01 K Corollary to the 3rd Law: The attainment of a temperature of T = 0 K (“Absolute Zero”) is not possible. • The 3rd Law says that the entropy-temperature curves for a fixed external parameter, such as magnetic field, meet at T → 0. • So, it is impossible to reach T = 0 in a finite number of steps. Adiabatic Processes Isothermal Processes Another Statement of rd The 3 Law of Thermodynamics “As T 0, the entropy of a pure substance S 0.” • In general, we know that S = kBln(Ω) • So, as the system energy approaches its ground quantum mechanical state of energy E E0, the temperature T 0 & Ω 1 so S 0 The rd 3 Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S = kBln(Ω) As T 0 , E E0, & Ω 1 so S 0 Ordered System Disordered System The 3rd Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of a pure substance at T = 0 is S = 0.