Maxwell’s Equations 1 Fall 2008 ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics

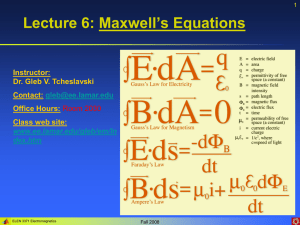
Maxwell’s Equations
1
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
Maxwell’s Equations
The behavior of electric & magnetic waves can be fully described by a set of four equations
(which we learned already).
Faraday’s Law of Induction:
B
t
Ampere’s Law:
H J
D
t
Gauss’s Law for
Electricity:
D
v
Gauss’s Law for
Magnetism:
0
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
2
Maxwell’s equations
And the constitutive relations :
D
E
B
H
(6.3.1)
(6.3.2)
J
E
(6.3.3)
They relate the electromagnetic field to the properties of the material, in which the field exists. Together with the Maxwell’s equations, the constitutive relations completely describe the electromagnetic field. Even the EM fields in a nonlinear media can be described through a nonlinearity existing in the constitutive relations.
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
3
Maxwell’s equations
Integral form
Faraday’s Law of induction
Ampere’s Law
L
E dl
s
B
t ds
L
H dl
s
D
t
J ds
Gauss’s Law for electricity
Gauss’s Law for magnetism
S
D ds
v
v dv
S
B ds
0
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
(6.4.1)
(6.4.2)
(6.4.3)
(6.4.4)
4
Maxwell’s equations
Example 6.1
: In a conductive material we may assume that the conductive current density is much greater than the displacement current density. Show
that the Maxwell’s equations can be put in a form of a Diffusion equation in this
material.
B
We can write:
t
(6.5.1) and, neglecting the displacement current:
H J
E
(6.5.2)
Taking curl of (6.5.2) :
E
(6.5.3)
Expanding the LHS:
B
0
2
B
0
B
t
The first term is zero and
2
B
0
B
t
Is the diffusion equation with a diffusion coefficient D = 1/(
0
)
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
(6.5.4)
(6.5.5)
5
Maxwell’s equations
Example 6.2
: Solve the diffusion equation for the case of the magnetic flux density B x
(z,t) near a planar vacuum-copper interface, assuming for copper:
=
0 and
= 5.8 x 10 7 S/m. Assume that a 60-Hz time-harmonic EM signal is applied.
Assuming e j
t time-variation, the diffusion equation is transformed to the ordinary differential equation: x
( ) dz
2
j
0 x
(6.6.1)
Where z is the normal coordinate to the boundary. Assuming a variation in the z -direction to be B x
(z) = B
0 e -
z , we write:
2 j
0
j
j
0
(6.6.2)
6
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
Maxwell’s equations
The magnitude of the magnetic flux density decays exponentially in the z direction from the surface into the conductor x
( )
B e
0
z where
0
10
7 7
117.2
m
1
(6.7.1)
(6.7.2)
The quantity
= 1/
is called a “skin depth” - the distance over which the current (or field) falls to
1/e
of its original value.
For copper,
= 8.5 mm.
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
7
Maxwell’s equations
Example 6.3
: Derive the equation of continuity starting from the Maxwell’s equations
The Gauss’s law:
Taking time derivatives:
From the Ampere’s law
Therefore:
The equation of continuity:
D
v
t v
t
D
D
t
v
t
D
t
H J
J
v
t
J
(6.8.1)
(6.8.2)
(6.8.3)
(6.8.4)
(6.8.5)
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
8
Poynting’s Theorem
It is frequently needed to determine the direction the power is flowing. The
Poynting’s Theorem is the tool for such tasks.
We consider an arbitrary shaped volume:
Recall:
H J
B
t
D
t
(6.9.1)
(6.9.2)
We take the scalar product of E and subtract it from the scalar product of H .
H E E H
H
B
t
E J
D
t
(6.9.3)
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
9
Poynting’s Theorem
Using the vector identity
( A B ) B A A B
(6.10.1)
Therefore:
( E H )
H
B
t
E
D
t
E J
(6.10.2)
Applying the constitutive relations to the terms involving time derivatives, we get:
H
B
t
E
D
t
1
2
t
H H
E E
t
1
2
H
2
E
2
(6.10.3)
Combining (6.9.2) and (6.9.3) and integrating both sides over the same
v …
10
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
Poynting’s Theorem
v
(
t
v
1
2
H 2
E 2
dv
v
E Jdv
Application of divergence theorem and the Ohm’s law lead to the PT:
s
(
t
v
1
2
H
2
E
2
dv
v
2
E dv
Here S E H is the Poynting vector – the power density and the direction of the radiated EM fields in W/m 2 .
(6.11.3)
(6.11.1)
(6.11.2)
11
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
Poynting’s Theorem
The Poynting’s Theorem states that the power that leaves a region is equal to the temporal decay in the energy that is stored within the volume minus the power that is dissipated as heat within it – energy conservation.
EM energy density is w
1
2
H
2
E
2
(6.12.1)
Power loss density is p
L
E
2
(6.12.2)
The differential form of the Poynting’s Theorem:
S
w t
p
L
(6.12.3)
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
12
Poynting’s Theorem
Example 6.4
: Using the Poynting’s Theorem, calculate the power that is dissipated in the resistor as heat. Neglect the magnetic field that is confined within the resistor and calculate its value only at the surface. Assume that the conducting surfaces at the top and the bottom of the resistor are equipotential and the resistor’s radius is much less than its length.
The magnitude of the electric field is
E
V L
0 and it is in the direction of the current.
(6.13.1)
The magnitude of the magnetic field intensity at the outer surface of the resistor:
H
I
2
a
(6.13.2)
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
13
Poynting’s Theorem
The Poynting’s vector S E H (6.14.1) is into the resistor. There is NO energy stored in the resistor. The magnitude of the current density is in the direction of a current and, therefore, the electric field.
J
I
a 2
(6.14.2)
The PT:
V
0
I
L 2
a
2
aL
d dt
v dv
V I
V I
I V
0
2 a L
2 a L
The electromagnetic energy of a battery is completely absorbed with the resistor in form of heat.
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
(6.14.3)
(6.14.4)
14
Poynting’s Theorem
Example 6.5
: Using Poynting’s Theorem, calculate the power that is flowing through the surface area at the radial edge of a capacitor. Neglect the ohmic losses in the wires, assume that the radius of the plates is much greater than the separation between them: a >> b.
Assuming the electric field E is uniform and confined between the plates, the total electric energy stored in the capacitor is:
W
E
2
2 a b
2
(6.15.1)
The total magnetic energy stored in the capacitor is zero.
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
15
Poynting’s Theorem
The time derivative of the electric energy is
dW
dt
2 a bE dE dt
(6.16.1)
This is the only nonzero term on the RHS of PT since an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy.
We express next the time-varying magnetic field intensity in terms of the displacement current. Since no conduction current exists in an ideal capacitor:
H dl
s
E
t ds (6.16.2)
Therefore:
2
aH
dE
dt a
2
a dE
2 dt
(6.16.3)
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
16
Poynting’s Theorem
The power flow would be:
In our situation: and
Therefore:
We observe that
P
S
s
ds
2
r
S u
r
1
P
S
2
abEH
P
S
2 a bE dE dt
dW dt
The energy is conserved in the circuit.
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
17
(6.17.1)
(6.17.2)
(6.17.3)
(6.17.4)
(6.17.5)
Time-harmonic EM fields
Frequently, a temporal variation of EM fields is harmonic; therefore, we may use a phasor representation:
( , , , )
Re E x y z e
( , , , )
Re H x y z e
(6.18.1)
(6.18.2)
It may be a phase angle between the electric and the magnetic fields incorporated into E(x,y,z) and H(x,y,z) .
Maxwell’s Eqn in phasor form:
j
( )
( )
j
( )
( )
E r
v r
( )
0
(6.18.3)
(6.18.4)
(6.18.5)
(6.18.6)
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
18
Time-harmonic EM fields
Power is a real quantity and, keeping in mind that:
Since
Re ( )
Re ( )
Re
Re ( )
( ) complex conjugate
A
A
*
2
Therefore:
Re
( )
Re
H r
( )
2
* ( ) ( )
( )
2
E r
*
H r
*
E r
H r
E r
H r
*
E r
*
( )
4
Taking the time average, we obtain the average power as:
S av r
1
2
Re E r
H r
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
(6.19.1)
(6.19.2)
(6.19.3)
(6.19.4)
19
Time-harmonic EM fields
Therefore, the Poynting’s theorem in phasors is:
s
E r
*
H r
ds
j
v
H
2
E
2
dv
v
2
E dv (6.20.1)
20
Total power radiated from the volume
The energy stored within the volume
Indicates that the power (energy) is reactive
The power dissipated within the volume
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
Time-harmonic EM fields
Example 6.6
: Compute the frequency at which the conduction current equals the displacement current in copper.
Using the Ampere’s law in the phasor form, we write:
Since and
( )
( )
j
( )
J
E
J r
J r
( )
j
( )
(6.21.1)
(6.21.2)
(6.21.3)
Therefore:
Finally: f
2
2
0
2
7
1
36
10
9
18
Hz
At much higher frequencies, cooper (a good conductor) acts like a dielectric.
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
(6.21.4)
(6.21.5)
21
Time-harmonic EM fields
Example 6.7
: The fields in a free space are:
E
10 cos
t
4
z
3 u x
; H u z
E
120
Determine the Poynting vector if the frequency is 500 MHz.
In a phasor notation:
e j
4
3 z u x
( )
10
120
4
z j e 3 u y
And the Poynting vector is:
S av r
1
2
Re
E r
*
( )
10
2
u z
0.133
u z
HW 5 is ready
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
(6.22.1)
(6.22.2)
(6.22.3)
22
What is diffusion equation?
The diffusion equation is a partial differential equation which describes density fluctuations in a material undergoing diffusion.
Diffusion is the movement of particles of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, resulting in the uniform distribution of the substance.
Similarly, a flow of free charges in a material, where a charge difference between two locations exists, can be described by the diffusion equation.
ELEN 3371 Electromagnetics Fall 2008
23