CHAPTER 1/2 Cumulative REVIEW Name: __________________________ Date: ___________ Color __________
advertisement
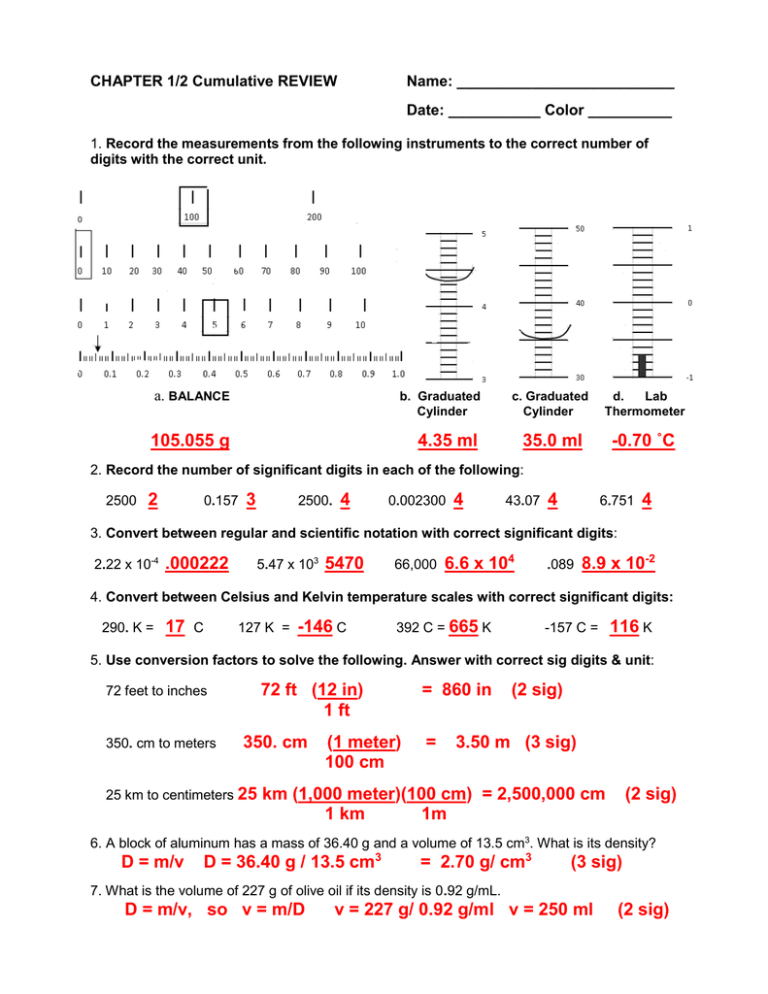
CHAPTER 1/2 Cumulative REVIEW Name: __________________________ Date: ___________ Color __________ 1. Record the measurements from the following instruments to the correct number of digits with the correct unit. a. BALANCE b. Graduated Cylinder 105.055 g 4.35 ml c. Graduated Cylinder d. Lab Thermometer 35.0 ml -0.70 ˚C 2. Record the number of significant digits in each of the following: 2500 2 0.157 3 2500. 4 0.002300 4 43.07 4 6.751 4 3. Convert between regular and scientific notation with correct significant digits: 2.22 x 10-4 .000222 5.47 x 103 5470 66,000 6.6 x 104 .089 8.9 x 10-2 4. Convert between Celsius and Kelvin temperature scales with correct significant digits: 290. K = 17 C 127 K = -146 C 392 C = 665 K -157 C = 116 K 5. Use conversion factors to solve the following. Answer with correct sig digits & unit: 72 ft (12 in) 1 ft 72 feet to inches 350. cm to meters 350. cm 25 km to centimeters 25 (1 meter) 100 cm = 860 in = (2 sig) 3.50 m (3 sig) km (1,000 meter)(100 cm) = 2,500,000 cm 1 km 1m (2 sig) 6. A block of aluminum has a mass of 36.40 g and a volume of 13.5 cm3. What is its density? D = m/v D = 36.40 g / 13.5 cm3 = 2.70 g/ cm3 (3 sig) 7. What is the volume of 227 g of olive oil if its density is 0.92 g/mL. D = m/v, so v = m/D v = 227 g/ 0.92 g/ml v = 250 ml (2 sig) 8. Define accuracy close to correct answer & precision repeatable results, numbers close together to a certain # of places. 9. MASS OF SAMPLE Team 1 Team 2 Team 3 Reading 1 41.04 g 31.33 g 42.34 g Reading 2 39.77 g 31.30 g 41.12 g Reading 3 43.15 g 31.36 g 41.21 g Average 41.32 g 31.33 g 41.55 g Accepted measure from issuing lab: 41.33 g Percent error 0.02% 24.2% 0.53% Which team is most accurate? Team 1 Least accurate? Team 2 Which team is most precise? Team 2 Least precise? Team 1 Which team has the best accuracy and precision? Team 3 10. Label the phases, phase changes, and freezing/boiling temperatures on the heating/cooling curve for water. What is happening to kinetic energy during section A? increasing What is happening to kinetic energy during section E/F? staying same Vaporization 100˚C Vapor Condensation Melting 0˚C Liquid Freezing SOLID 11. Pure substances are either elements or compounds. Mixtures may be either Heterogeneous mixtures are: or homogeneous. Three types of homogeneous solutions (clear & uniform), colloids (cloudy & uniform) and alloys (opaque, uniform blend of metals). At first glance a colloid & suspension may look similar. The difference is suspensions will precipitate (separate), colloids will not. 12. Classify the following as element (E), compound (C), solution (S), alloy (A), colloid (CL) or suspension (SP). E CL gold C water A milk S salt/water C E brass carbon dioxide carbon CL whipped cream A gold jewelry SP sand/water 13. Physical properties can be measured without changing the chemical composition of a substance. Chemical properties describe chemical reactions a substance will/will not undergo. Classify the following as physical (P) or chemical (C) properties: P color C tendency to rust P mass C noble gases are inert P C reactivity with oxygen C flammability P density boiling point 14. Physical changes change the appearance, but not the chemical composition of a substance. Chemical changes (chemical reactions) create new substances. Classify the following as physical (P) or chemical (C) changes: P melting iron C burning gasoline P breaking test tube C wood rotting P dissolving NaCl C reacting Mg w HCl P boiling water C iron rusting 15. What are the four signs of a chemical change? change in temperature change in color production of a gas formation of precipitate 16. A student experimentally determined the density of a piece of aluminum to be 2.95 g/cm 3. The accepted value for aluminum density is 2.70 g/cm3. Calculate the student’s percent error. 2.95 g/ cm3 - 2.70 g/cm3 2.70 g/cm3 x 100 % = .25 x 100 % = .093 x 100% 2.70 9.3% (2 sig)








