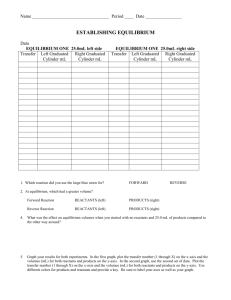
14.1 Review Name__________________________ Period_________Date_____________
advertisement

14.1 Review Name__________________________ The Concept of Equilibrium Period_________Date_____________ Part I: Matching _____ 1. the formation of products from reactants A. reversible reaction _____ 2. a chemical reaction in which the products can generate The original reactants B. chemical equilibrium _____ 3. the speed at which a reaction occurs C. reverse reaction _____ 4. the regeneration of reactants from products D. reaction rate _____ 5. the state in which the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant with time E. forward reaction Part II: Short Answer 6. Explain how reaction rate and equilibrium are related. Give an example illustrating this relationship. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 7. In performing most calculations with chemical reactions, it is assumed that the reactants are entirely consumed. Is this assumption always appropriate? Explain. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Can all reversible reactions be observed in the laboratory? _______Why or why not? ______________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Write the forward reaction and the reverse reactions for the following: _____________________________________ 2SO2 + O2 ↔ 2SO3 ___________________________________________ 10. List four factors that control the rate of a reaction: 1. _________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________ 4. _________________________________________ 11. The higher the concentration of reactants, the ( slower / faster ) the rate of the reaction. The lower the concentration of reactants, the ( slower / faster ) the rate of the reaction. 12. When placed in a sealed container, N2 and H2 react according to the following equation: N2 + 3H2 ↔ 2NH3 Over time, the rate of the forward reaction ( increases / decreases ) and the rate of the reverse reaction ( increases / decreases .) During the course of the reaction the concentration of the reactant ( increases / decreases ), while the concentration of the product ( increases / decreases .) 13. Why will any chemical reaction reach equilibrium in a closed container? _______________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Does a reaction stop once it has reached equilibrium? ________ Explain: ______________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________