Mr. Maurer Name:_________________________________ AP Economics
advertisement

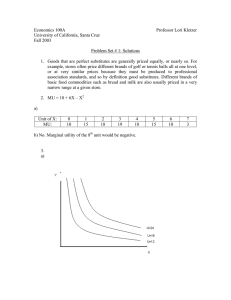
Mr. Maurer AP Economics Name:_________________________________ FRQ #7 - Utility Maximization and Consumer Theory 1. Utility maximization is a fundamental assumption in consumer theory. (a) Explain what is meant by diminishing marginal utility. (1 pt.) The additional satisfaction one gains from consuming additional units of a good decreases as the quantity consumed decreses. (b) Assume that a consumer buys only to goods: X and Y. What is the utility-maximizing decision rule for the consumer in allocating total income to good X and Y? (1 pt.) The last dollar spent on good X and good Y should bring the consumer equal amounts of marginal utility. You could also say that the marginal utility per dollar spent on each good should be equal. (c) Assume that a utility maximizing consumer is spending all of her income on the two goods, X and Y. The price per unit of good X is $2, and the price per unit of good Y is $3. The marginal utility of the last unit of good Y is 15. What is the marginal utility of the last unit of good X consumed? (1 pt.) OK, so the last dollar spent on each good should bring equal marginal utility. The last unit of good brought 15 utils and cost $3. That’s 5 utils per dollar. The last unit of good X must also bring 5 utils per dollar. Since the price of good X is $2, the last unit of good X must have a marginal utility of 10 in order to bring 5 utils per dollar. (15/3 = 10/2) (d) Assume that good X is a normal good and good Y is an inferior good. Assume that the consumer’s income does not change. Assume that the price of good X increases (i) Indicate how the substitution effect of the increase in the price of good X will affect purchases of (1) good X (1 pt.) Purchases of good X will decrease as consumers switch to other products that are now relatively less expensive than good X. (2) good Y (1 pt.) Purchases of good Y may increase if there is any positive cross elasticity of demand between these two goods. Meaning, if they are substitutes at all, then consumers will switch some purchases from Good X to Good Y. (ii) Indicate how the income effect of the increase in the price of good X will affect purchases of (1) good X (1 pt.) People will buy less good X because they will have less real income with which to buy it. (2) good Y (1 pt.) People will buy more good Y because it is an inferior good and they will have less real income to spend due to the increase in the price of Good X.