Ecology (BIO 47) Review for Exam 2 Population Dynamics
advertisement

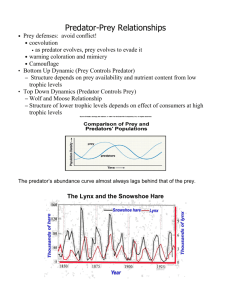
Ecology (BIO 47) Review for Exam 2 Population Dynamics Abiotic vs. Biotic factors Exponential growth Unlimited resources J-shaped curve Steeper J means faster growth Logistic growth Resources are rarely limited for long Carrying Capacity = K S-shaped curve Factors affecting population growth Density dependent (disease, parasites, food, etc) Density Independent (storms, fire, other natural disasters) Dispersal and Metapopulations Growth rate = birth rate + immigration – death rate – emigration Salamander example – small pops of salamanders may require immigrants to maintain a viable population Source – Sink Populations Dispersal Metapopulations Environmental stochasticity (randomness) Demographic stochasticity Life Histories Life history definition Trade-offs in life history strategies Examples Successful life history strategy means the population is stable or growing r>0 Age structure graphs – stable vs. growing Life table – what kind of info is found there? Use info to build Survivorship curves Survivorship curves – identify & give examples for types I, II, & III SimSturgeon example of tradeoffs Reproductive effort Classifying life histories **r-selected species – characteristics & examples **K-selected species – characteristics & examples Ruderals/stress tolerant/competitive life histories in plants Opportunistic/equilibrium/periodic Competition Limited resources result in competition Cost for both -/Land iguana simutext example Examples of resources Direct vs. indirect competition Niche Fundamental vs. realized niche **Niche overlap & competition in barnacles Example of fundamental vs realized niche Environmental tolerance Mosquito example Principle of competitive exclusion Resource competition – Exploitative competition Indirect Results in self-thinning in plants Interference competition Direct Allelopathy (toxins secreted by plants – affect growth of other species) Territoriality in animals Preemption Intraspecific Competition vs. Interspecific competition **Lotka-Volterra Competition equations Four possible outcomes: Species 2 eliminated. Species 1 eliminated. Either species 1 or species 2 eliminated, depending on starting conditions. Both species coexist. Flour beetle example Common garden experiments Definition & examples Spatial and temporal variability Character displacement (example) Coexistence Mosquito example Exploitative Interactions – Predation herbivory & parasitism Beneficial for one, cost for the other species +/Who benefits? Other types of species interactions: Competition -/Amensalism -/0 Commensalism +/0 Mutualism +/+ Parasitism Parasite (+) Host (-) Usually not fatal Complex life cycles – often multiple hosts for different life stages Endoparasites vs. ectoparasites Parasitoids & hyperparasites Examples Effects of parasites on hosts – examples Herbivores Grazers vs. browsers Frugivores, granivores Plant defenses Mechanical Chemical Nutritional Tolerance Predation Stalk Pursuit Ambush Random encounter Prey defenses Physical Chemical Behavioral Aposematism Crypsis Mimicry Predator-Prey Dynamics Lynx/Hare example Often other factors affect predator & prey populations Deterministic vs. stochastic models Assumptions of Lotka Volterra predator prey equations Density dependence reduces cycling Refuges for prey Functional response Orange mite example Evolutionary arms race Coevolution Predator prey coevolution example – newt/garter snake Trade-offs involved in coevolution Red Queen hypothesis