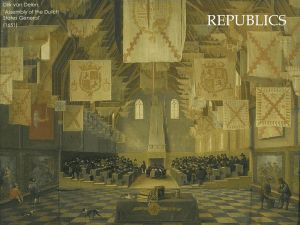
East Asia in the 20 c th
advertisement

East Asia in the th 20 c Wealth & Power Opposite Paths China Japan 1800 1840 1868 1900 Central Theme the connection between economic conditions and government interventions. Post-Dynastic China 1912-1937 How would you characterize China during this time? China, 1912-1937 (post-dynastic system / pre-WWII) “Phantom Republic” 1912-1927 Republic – Nationalist control 1927-1937 China 1912-1927: the “Phantom Republic” Early, factions vie for power : Republican revolutionaries Landlords Foreign powers China 1912-1927: the “Phantom Republic” Republican revolutionaries Led by Sun Yat-sen Western educated “Fundamentals of National Reconstruction” China 1912-1927: the “Phantom Republic” Communism • Why now? Beliefs? Supporters? • Led by Mao Zedong • Aimed at peasant reform China 1927-1937: Republic Nationalists establish control Party militarizes Led by Chiang Kai-Shek 1934 KMT’s brutal crack down on communists leads to Long March KMT = control coastal areas Communists = influential in hinterlands Imperial Japan 1905-1937 1910 Japan’s emerging Asian empire • 1894-1895: SinoJapanese War • 1904-1905: Russo-Japanese War • Result = Korea & Taiwan w/ eyes on Manchuria Japan 1905-1937: Imperial Japan Japan expands during 20th century for lots of reasons And this …is an implicit challenge to West …leads Japan on the road to war Japan 1905-1937: Imperial Japan Reasons to Expand: 1. Need • Island nation, limited resources, limited farmland, overpopulation 2. Anti-Western Sentiment • Racial equality? • Limiting of navy? • End of emigration to U.S.? U.S. Immigration Law of 1924 Barred Chinese & Japanese immigration Reduced Italian immigration Washington Naval Conference [1921-1922] U. S. 5 Britain 5 Japan 3 France 1.67 Italy 1.67 Japan 1905-1937: Imperial Japan 1930 speech of military leader: “We are like a great crowd of people packed into a small narrow room, and there are only three doors through which we might escape, namely emigration, advance into world markets, and expansion of territory. The first door…has been barred to us by the anti-Japanese immigration policies of other countries. The second door…is being pushed shut by tariff barriers…Japan should rush upon the last door [expansion of territory].” Japan 1905-1937: Imperial Japan 1930’s American observation: “In every classroom is a world-map or map of Asia which shows Japan in red as a very small land indeed, compared to the mainland nations of Asia…In a perfectly bland manner some villager, on looking at such a map, will suggest how nice it would be to [acquire] a bit more of China.” Japan 1905-1937: Imperial Japan 1920s & 1930s, mark further industrial advance of Japan • Great Depression = sparks further militarization of Japanese government Germany? Spain? • Example: 1931 – Manchurian Incident Japan 1905-1937: Imperial Japan Histories Intertwined China & Japan 1937-1945 20th Cent. Japan 1937 – Japan launches invasion of coastal China Imperial spirit led to control of islands & much of SE Asia as well • Cultural & economic imperialism Branded as: Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere or an “An Asia for Asians” WWII – Histories Intertwined Strategy • • • Embargo → Pearl Harbor Defensive perimeter → island hopping Fight to the death, suicide missions → more direct strikes WWII – Histories Intertwined A terrified baby after Shanghai is attacked by Japan WWII – Histories Intertwined August 6th & 9th, 1945 Hiroshima = 140,000 deaths by the end of 1945 (200,000 total) • Buildings leveled for a 1.5 miles radius Nagasaki = 70,000 deaths by the end of 1945 (140,000 total) Explosion had temp exceeding 7,000 oC (Sun’s surface temp. = 6,000 oC).