LOCAL GOVERNMENT
advertisement

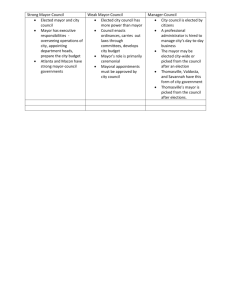
LOCAL GOVERNMENT The General Assembly shall provide by general law for local government within the Commonwealth. Such general law shall be uniform as to all classes of local government… ... Article IX of Pennsylvania Constitution Municipality: a city, township, borough, county, school district, or other unit of local government. A municipality is created by the state upon the consent of the residents in order that they may provide for themselves the services that they need or desire. Some of these services are: fire and police protection, cultural and recreational facilities, water and sewer systems, streets, traffic regulations, building and zoning, and general health and welfare. Pennsylvania is second in the nation in number of local government units, about 5,000 in number. COUNTY GOVERNMENT What is a COUNTY? It is the intermediate form of government between the local municipality and the state. A county government’s headquarters is called the “county seat.” Here in Montgomery County, the county seat is in Norristown. A county is both a geographic area and a political unit; and it is the largest political subdivision of Pennsylvania. There are 67 counties in PA. The 1st three counties established by William Penn were Bucks, Chester and Philadelphia; and Montgomery County split off from Philadelphia County. The Classification of Counties is by POPULATION. 1st Class: 1.5 million + people – Philadelphia 2nd Class: 800,00 to 1,499,999 – Allegheny (Pittsburgh) 2A Class: 500,00 to 799,999 – Bucks, Montgomery, Delaware 3rd Class: 225,000 to 499,999 – Chester and 11 others 4th Class: 150,000 to 224,999 – 6 counties 5th Class: 95,000 to 149,999 – 9 counties 6th Class: 45,000 to 94,999 – 20 counties 7th Class: 20,000 to 44,999 – 8 counties 8th Class: less than 20,000 – 8 counties Smallest Population is Forest County Largest in Size is Lycoming and Smallest in size is Philadelphia HOME RULE – The option under the Pennsylvania State Constitution that gives local governments the power to set up the rules for governing themselves as opposed to following the rules of the state government. Services of the County: 4 categories Records – real estate transactions, marriages, birth, deaths, court cases, weights and measures, property ownership, property value assessment for local property taxes Elections – manage all voting registration and conduct the elections of local, county, state and federal; maintains the voting machines/equipment; publicize elections and election information; count the votes and keep records of election results Courts – although the courts are under the control of the Pennsylvania Supreme Court, the county must manage and fund the day to day administration of the courts and county jail. Judges are paid by the state, but other court employees are paid by the county government- Court of Common Pleas State / Federal Services – deliver services paid for by state and/or federal government such as health, hospitals, welfare, geriatrics, rehab, and veterans services. (Assistance to the elderly, disabled, poor, and drug addicted) Organization of County Government- source www.montcopa.org County Commissioners The legislative and executive arm of the Montgomery County government is the three member Board of Commissioners. Elected at large for four year terms, the three choose one of their members to be chairman. Provisions are made for minority party representation as the electorate votes for two from the four candidates seeking the three positions. If a vacancy occurs, the County judges appoint a replacement. The Commissioners name all department heads, as well as most members of the various boards, authorities, and committees. In addition, the Commissioners appoint all County employees and, sitting as the Salary Board with the Controller, establish salaries of all employees. The management of County property and all phases of financial administration, except final audit, also rests with the Commissioners. They are responsible for the preparation, adoption and execution of the annual budget, as well as for the taxing of all property, both real and personal, for County purposes. They have jurisdiction over County maintained roads and bridges and supervision of the Court House and other County operated facilities. In addition to the County Commissioners, nine County departments are headed by an individual elected directly by the voters. They are elected officials who are independent from Commissioners. All serve a term of four years. The salaries are set by the County Commissioners. These nine officials are commonly referred to as "Row Officers," a term that came about many years ago when the nine departments were first listed in a row on the election ballot. Clerk of Courts The Clerk of Courts is the clerk of the criminal court and retains custody of all original cases. The office maintains a computerized index and docket in which a record is kept of all documents filed in each case. Court costs and restitution are assessed and collected for each case. These court related costs are distributed in accordance with the law to the appropriate municipal, county and state offices and restitution victims. The office is responsible for the collection of bail money and its return to the surety upon completion of court action. The office maintains miscellaneous records and dockets relating to the division of election districts, the appointment of election officials, constables and private detectives. Controller The Controller is an elected row officer and has general supervision over all fiscal affairs of the County and of the accounts of all functions collecting, receiving or disbursing County funds. This includes but is not limited to, the following: General Accounting – Complete records are maintained by the Controller's Office detailing all fiscal operations of the County. Accounts Payable – The Accounts Payable function approves and processes all vendor invoices for payment. Internal Audit – Internal Audit conducts periodic audits of row offices, tax collectors, County departments and other County functions as necessary. Payroll – The Controller manages and processes payroll for all County employees and maintains all payroll records. Retirement – The Controller maintains the accounting records for the Montgomery County Employees’ Retirement System and acts as a liaison between the County and the investment advisors for the Retirement Fund investment portfolio. Coroner The Coroner is charged by law with many responsibilities, the foremost of which is the investigation and certification of a variety of deaths including all deaths of other than natural causes, and any apparently natural deaths in which no physician can reasonably state the cause. The Coroner can utilize any and all medicolegal investigative techniques, including an autopsy, to establish both the medical cause of death, and mode or manner of death (natural, accident, homicide, suicide, or undetermined). Additional mandated responsibilities include the notification of next of kin, granting cremation permits, protection and safekeeping of property belonging to deceased individuals, conducting inquests when indicated, maintaining public records, making reports to other agencies, identification of deceased persons and the interment of indigent dead and unclaimed bodies. There has been continued growth and emphasis on the role of forensic science and medicine. This office has expanded its role in forensic medicine for both living and dead, playing a vital role in the community. These areas include: examination and evaluation of child, elderly and domestic abuse; testimony and interpretation of hospital records and procedures; alcohol and drug interaction in motor vehicle and other fatalities; compiling statistics pertaining to seat belted occupants in motor vehicle fatalities; illicit as well as environmental and industrial toxicology. The Coroner also interfaces with numerous other agencies and departments (Police, District Attorney, Public Defender, Sheriff, Federal Aviation Administration, Sudden Infant Death Syndrome Organization, Children and Youth, State Attorney General, Center for Highway Safety, Drug Abuse Warning Network, Public Health) to support the health and safety of Montgomery County residents. District Attorney The Montgomery County Office of the District Attorney is dedicated to achieving justice and protecting the safety of our community. They fairly investigate, and aggressively prosecute, criminal activity throughout our County. They zealously enforce the law and the rights of crime victims. Their goal is to keep Montgomery County safe and secure by effectively working with the entire law enforcement community. They fight for justice in the courts, seek appropriate punishment for those who commit crimes, provide complete assistance to victims of crime, and offer community-based crime prevention programs to educate the public. They provide investigative assistance to local police departments through the County Detective Bureau. The office provides training to other law enforcement agencies and also coordinates victim/witness assistance program. Prothonotary The Prothonotary is the elected civil clerk of the Court of Common Pleas and is responsible for recording all civil procedures before the court. This official signs and seals all writs and processes numerous other documents of the Court of Common Pleas. The Office of Prothonotary is responsible for the recording and filing of legal papers of a widely diversified character such as: personal injury, medical malpractice, divorce, custody, protection from abuse, judgments, change of name, school audits, driver’s license suspension appeals, District Justice appeals, mechanics liens, Federal income tax liens, and administers oaths and affirmations. This office also processes passport applications, swears in new citizens and participates in naturalization ceremonies for the federal government. Recorder of Deeds The mission of the Montgomery County Recorder of Deeds office is to maintain the integrity of all land records and other documents entrusted to the department as well as the collection and monthly distribution of County / State fees and Real Estate Transfer Taxes for the State, Townships, Boroughs and School Districts; while efficiently serving the public with complete accountability and responsibility. All legal instruments in the County including deeds, real estate transfers and agreements, mortgages and assignments thereof are filed with the Recorder of Deeds. In addition, state highway plans, charters, powers of attorney, subdivision plans and commissions for elected officials and notary publics throughout the County are also filed in this office. Real estate transfer taxes are collected for the state, townships, boroughs and school districts and distributed monthly. Register of Wills The Office probates wills and processes intestate estates (estates without wills). The Office is also agent for the Commonwealth in the collection of inheritance taxes. Accounts by personal representatives of estates are filed with their office. Certificates necessary for the transfer of estate assets are also issued by the Office. As Clerk of the Orphans’ Court, they issue marriage licenses and have charge of the Orphans’ Court dockets. Petitions for adoptions are filed in here as well. The Register of Wills also keeps the records of all persons born in Montgomery County between 1893 and 1915. Birth records of persons born after 1915 are kept on file with the Pennsylvania Department of Health. Sheriff The Sheriff is the chief law enforcement officer of the County under the Pennsylvania Constitution. While most police work is now done by local and state police, the Sheriff's broad powers authorize him and his deputies to enforce the law. The Sheriff is called upon during riots, prison breaches, strikes and other emergencies which are or may be a breach of the peace. In those instances, he is empowered to call upon all able-bodied adults. Among the duties of the Sheriff are service of all writs both criminal and civil issued by the Courts, transportation of prisoners throughout the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and extradictions from other states for the purpose of court proceedings. The Sheriff also issues permits for firearms and conducts sale of real and personal property at the request of litigants, including the city, county and state. Other duties and services available from the sheriff department include bomb disposal unit, (C.E.R.T.) County Emergency Response Team, the operation of five (5) Driving Under the Influence Processing Centers, "TRIAD" program for senior citizens as well as the well known D.A.R.E. program for school children and major sponsor of Camp Cadet for boys and girls 11-14 years of age. Treasurer The Treasurer is the custodian of all County funds. Payments of County taxes and fees, state and federal grants and other monies due the County are received and deposited by this office. The Treasurer is responsible for payment of all funds on proper authorization for obligations incurred by the County. Investment of County funds is also handled by this office. As an agent for the state, the office sells licenses for hunting, fishing, dogs, bingo and small games of Jury Commissioner The Montgomery County Jury Selection Commission is responsible for providing a qualified pool of jurors to ensure the right of all citizens to a trial by an impartial jury. Citizens who fulfill their jury service obligation are continuing a tradition established under the United States Constitution over two hundred years ago. Indeed, the right to a trial by an impartial jury of one's peers is an integral part of the foundation of American democracy. If by the end of your first day of service you are not on a jury or are not in a courtroom for jury selection you will be discharged. If you are chosen for a trial you must serve until that trial is over. ______________________________________________________________________________________ Review Questions: Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper. Be sure your work is thorough and complete. COUNTY 1. Counties in Pennsylvania are classified by what? 2. Give an overview of the work of county government. 3. What activities or services are provided by county governments in Pennsylvania? 4. Why is it important to have records of land transfers, marriages, passports, etc…? 5. County Row Officers are? List all of the county officials (row offices). 6. Choose one county office (department) and explain in detail their responsibilities. 7. Why is it required to have at least one county commissioner be of a different political party? 8. An option that gives local government the power to set up the rules for governing themselves instead of following the rules created by the state legislature is called? 9. What is a municipality? ________________________________________________________________________ CITY OF PHILADELPHIA Philadelphia is classified as a 1st class city under the Pennsylvania Constitution. The City of Philadelphia is both a city and a county. It is divided for political and administrative purposes into 66 WARDS. Each Ward has from 11,000 to over 50,000 people. Philadelphia is like 66 cities consolidated into one. The population of Philadelphia is approximately 1.5 million. It is the fifth largest city in the United States. The city government is headed by the Chief Executive of Philadelphia, the MAYOR. Elected for a term of 4 years – may be re-elected for 1 successive term and can be elected for 2 additional terms after leaving office for 1 term. Qualifications: 25 years of age minimum and a resident of Philadelphia for at least 3 years. Powers: execute and carry out ordinances (LAWS) made by City Council and veto power and Line item veto power in appropriations bills. Mayor’s Cabinet: Managing Director: appointed by Mayor, 2nd most powerful person in city; in charge of fire, health, licenses and inspections, police, water and welfare departments. Director of Finance: appointed by Mayor, chief financial, accounting and budget officer in city. City Representative: director of commerce and represents Mayor at public functions. City Solicitor – head of the city legal department. The City School Board is the only PA. Municipality that has a school board appointed by the Mayor – they are responsible to the Mayor The Legislative Branch – CITY COUNCIL Role: To Pass ordinances (LAWS). Organization: 17 citizens who are elected for a term of 4 years. The city has 10 council districts and 7 council members are elected at large and represent the city as a whole. Voters vote for their district council member and 5 other at large people so this allows for at least 2 at large council members to be from the minority party. Qualifications: must be at least 25 years of age; and American citizen; and live in the city for one year. Philadelphia is controlled by the Democratic Party. Small Cities. have three options of government: 1. Commission Form 2. Council-Manager Form 3. Mayor-Council Form Commission Form Five elected councilmen (commissioners) are elected and constitute the council (commission) which is the governing body of the city. They mayor is one of the members and acts as president. Each of them is in charge of one of the five major departments: Public Affairs, headed by the mayor; Accounts and Finance; Streets and Public Improvements; Park and Public Property; Public Safety. These councilmen, along with the treasurer, controller, and assessor, are elected for four year terms. The council appoints all other officers and employees. Council- Manager In this system, all authority is in the council which is composed for five, seven, or nine members who are elected for four year terms. The council elects one of its members as mayor who presides over the city council, but has no controller. The council appoints a duty clerk, and a city manager. The manager is the chief administrative officer of the city. He appoints department heads and other officers. He may be replaced by the council. Mayor-Council The city council under this form may have five, seven, or nine members elected at large for four year terms. A mayor, treasurer, and a controller are also elected for four year terms. There may be up to nine departments of the city. The mayor is the chief executive of the city and enforces the ordinances of council. He may attend meetings of the council, but has no vote. He may veto ordinances of the city which 2/3 of the council can override. He supervises the work of all city departments and submits a budget for council approval. Under this form the mayor usually appoints various department heads and other officers. TOWNSHIP AND BOROUGH GOVERNMENT Townships can range from as low as 25 people up to over 50,000 people, but the average falls between 1,000 and 5,000 residents. Council members, Commissioners, and Supervisors: These are the most important officials within your borough or township. They are the chief lawmakers and leaders. They control the financial matters by deciding on tax rates, deciding how the budget is organized and approving the spending of municipal funds. They approve the hiring and firing of borough or township staff. They make the ordinances (laws and regulations) for the municipality. Actions can only be taken by these groups when a majority of their members agree and vote together. TOWNSHIPS Townships are classified by POPULATION (Hatfield, Upper Gwynedd) 1st Class Townships: there are 91 in PA. and most could be cities by population but choose not to be. Highly developed and suburbanized township Board of Commissioners 5 Commissioners when elected AT LARGE They are the Legislative and Executive Branch of Township government Proposed Ordinances (LAWS) must be published in local newspaper prior to passage Can have 5 or more Commissioners when elected by WARDS- 1 per ward 4 year terms, elections every 2 years More powers to make laws and provide services than second class townships 2nd Class Township: There are over 1450 of these townships. (Montgomery, Towamencin) Should be more rural and undeveloped Meant to handle only the most basic government services – they don’t expect to have as many complicated issues to manage here Board of Supervisors 3 Supervisors (but the township can choose to have 5 instead) Role is both legislative and executive, meet at least monthly 6 year terms, elections every 2 years Less power to tax and make laws because this area should have less population and face fewer challenges that require municipal government BOROUGHS Small city or town (Lansdale, Hatfield, North Wales) Historically the place where the conveniences of modern living were provided (street lights, libraries, sewers, etc.) “Main Street USA” feel Borough Council Between 7 members if elected AT LARGE or up to 15 members if elected by WARDS 4 year terms, elections every 2 years Mayor: Mayors are only elected for boroughs. (Unless a special arrangement is made in a township with a HRC.) Borough mayors serve 4 year terms. Much of a mayor’s work is symbolic – representing the borough at ceremonial and official functions (parades, greeting visiting officials, openings of new businesses, etc.) The mayor’s main power is supervising the borough police department. Mayor’s have some legislative power: they can vote to break a tie on borough council and can veto certain council votes. (But borough council can override the mayor if the council can get a 2/3 majority vote.) SERVICES PROVIDED BY TOWNSHIPS AND BOROUGHS Building and maintenance of roads and bridges, sidewalks, storm water drainage facilities, wharfs and docks (if applicable), sewers and sewage treatment facilities, public buildings for the operation of the municipality, parks and playgrounds. Lighting of roads & public places Ensure health, safety, and public well-being Provide police and fire protection, hospital services, water services, garbage removal Oversee the operation, condition, and location of cemeteries Zoning and planning commissions Establish and enforce minimum building quality standards Acquiring land for the good of the municipality (Eminent Domain) Collect taxes Provide licenses and permits for activities which the municipality requires them Provide for and maintain shade trees Operate libraries TOWNSHIP AND BOROUGH- ELECTION OPTIONS: Elections by Wards vs. “At Large” Elections There are two different approaches to electing local leaders. Sometimes all elected officials are chosen “at large.” In some communities, some elected officials will be chosen “at large” and others will be chosen by wards. Ward: Elections are conducted for the municipality by subdividing the municipality into sections. These sections are called wards and are simply used as small territories within a municipality from which an elected official must be chosen. Candidates running by ward can only be elected by residents of their ward. Likewise, residents voting by ward can only vote for the candidates on the ballot in their ward. Wards are in no way autonomous – they cannot govern themselves differently from any other part of the municipality. Elections by ward are sometimes done to ensure equal representation for all residents of a municipality. “At Large” Elections: Here, there are no voting subdivisions of the municipality. Everyone within the municipality can vote for any of the candidates running in their municipality. ______________________________________________________________________________________ Review Questions: Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper. Be sure your work is thorough and complete. CITIES, BOROUGHS, TOWNSHIPS 10. Name all the municipalities that make up the North Penn School District. 11. The titles of the directors of a first-class township, a second class township and a borough are. 12. A Borough mayor’s role is what? 13. Identify five (of the many) services boroughs and townships provide that state or national governments do not. 14. Explain two ways Boroughs differ from Townships. 15. What is the difference between a “ward” and an “at large” election? ______________________________________________________________________________________