MATERIAL RESOURCE PLANNING Pendahuluan Definisi
advertisement

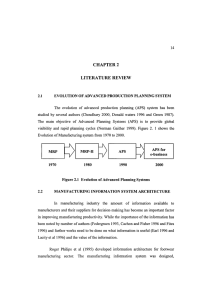
MATERIAL RESOURCE PLANNING Pendahuluan Definisi Tujuan Perencanaan Kebutuhan Kapasitas Apa yang terjadi jika JIP tidak dapat direalisasikan ? Apa yang terjadi jika peralatan dalam manufaktur bermasalah ? Apa yang terjadi jika vendor bermasalah dengan pasokan bahan baku ? PERTANYAAN / MASALAH YANG SERINGKALI TIMBUL DALAM SIKLUS MANUFAKTUR MRP-I THE HEART OF MRP-II SYSTEM DIAGRAM ALIR MRP-II YANG TERMASUK DALAM MRP - II • • • • • • • • • • • Peramalan Pemasukan pesanan pelanggan Perencanana produksi/JIP Stuktur produk / BOM Pengendalian persediaan MRP Perencanaan Kapasitas Shop Floor Control Purchasing Accounting Analisa finansial TUJUAN • The purpose of an MRP system is to reduce the cash needed by a manufacturing organization. This increases the organization's return on investment, directly making the manufacturer a more profitable, atractive invesment. • In a classical manufacturing organization, huge amounts of cash are tied up in inprocess inventory, parts, that must be assembled and then sold. MRP uses planning and management to reduce this cash to the minimum. • The basic idea is simple. A sales or marketing group estimates how many products it will sell at a future time. The MRP software back-dates using the factory's estimated time to assemble each product. Then, the system explodes the product into lists of parts needed, using the bills of materials developed by Engineering. The parts are ordered at times back-dated from the assembly dates. Finally, the cash flow of the above ordering, assembly, ship and payment process is developed. • The system provides reports about which parts are needed to ship an order. If a high-value order is waiting for a few cheap parts, the planner can ask for the parts to be flow in by airfreight, and usually this will improve profits and return on investment. INPUT – A sales estimate for each product. – A bill of materials for each product. – An assembly time for each product. – A complete on-hand inventory of all parts. – Estimated delays from order to receipt for each part, for each vendor that supplies the part. – Estimated proces for each part, by vendor and shipment method. – Inventory deposits and withdrawls. OUTPUT – Needed parts to complete a valuable order. – Invoicing or electronic data interchange to order parts early enough to meet sales forecasts. – Inventory management data.