13.11: Conduct an Investigation pg. 576 Key Concepts:
advertisement

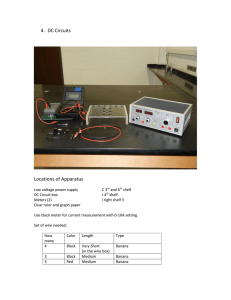
13.11: Conduct an Investigation pg. 576 Key Concepts: 1. Circuits are a part of electrical technology. They can be connected in series and in parallel. 2. Connecting loads in series and parallel affects the current, potential difference, and total resistance. 3. Current, voltage, and resistance measurements can be used to test circuits. The Effect of Increasing the Number of Loads in a Circuit Testable Question: How do the total resistance, current, and voltage compare in series and parallel circuits? Hypothesis/Prediction: Experimental Design: You will connect one load and then two loads in series. Then you will measure the voltage drop across each resistor, the current through each resistor, and the resistance of all the resistors in the circuit. You will repeat the process for a circuit of two loads in parallel. The voltage drop across the power supply will remain constant throughout the investigation. Materials: - Variable DC power supply - voltmeter - ammeter - connecting leads - switch - 2 identical resistors (10.0 Ω) Simulation web site: https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit-construction-kit-dc Procedure: Part A: Resistors in Series 1. Obtain the equipment and place it at your workbench. 2. Copy table 1, 2 and 3 into your notebook. 3. Connect the circuit shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 4. Close the switch. Set the power supply to 2 V or as specified by your teacher. Record this number as the voltage drop across the energy source. 5. Record the voltage drop across and the current through each resistor in your table. 6. Turn off the power supply. Then open the switch 7. Add another resistor in series to the circuit. Repeat steps 4 to 6 for each resistor. 8. Remove the voltmeter and ammeter. Measure the total resistance across both resistors by placing an ohmmeter as shown in Figure 2. 9. Add third resistor in series to the circuit. Repeat steps 4 to 6 for each resistor. Figure 2 Part B: Resistors in Parallel 1. Copy table 4 and 5 into your notebook. 2. Connect the circuit shown in Figure 3. Figure 3 3. Close the switch. Set the power supply to 2 V or as specified by your teacher. Record this number as the voltage drop across the energy source. 4. Measure and record the voltage drop across and the current through resistor 1 5. Move the meters to measure the values for the second resistor. 6. Turn off the power supply. Then open the switch. 7. Remove the voltmeter and ammeter. Measure the total resistance across both resistors by placing an ohmmeter as shown in Figure 4. Record the total resistance. 8. Add third resistor in parallel to the circuit. Repeat steps 3 to 7 for each resistor. Figure 4 Observations: Table 1: One Resistor Voltage (V) Current (A) Resistor 1 Table 2: Two Resistors in Series Voltage (V) Resistor 1 Resistor 2 Total Resistance Current (A) Table 3: Three Resistors in Series Voltage (V) Current (A) Resistor 1 Resistor 2 Resistor 3 Total Resistance Table 4: 2 Resistors in Parallel Voltage (V) Resistor 1 Resistor 2 Total Resistance Table 5: 3 Resistors in Parallel Voltage (V) Resistor 1 Resistor 2 Resistor 3 Total Resistance Resistance (Ω) Resistance (Ω) Current (A) Resistance (Ω) Current (A) Resistance (Ω) Analyze and Evaluate: a) Answer the Testable Question [t/i] b) Did evidence support your hypothesis? Explain [t/i] c) Make a statement about the voltage drop across resistors. Compare resistors in series with resistors in parallel. Also make a statement comparing the voltage drop across the energy source with voltage drop across the resistance. [t/i] d) Make a statement about the currents through resistors. Compare resistors in series with resistors in parallel. [t/i] e) Which circuit, series or parallel, would allow more current to flow if you added one or more resistors? Explain your answer. [t/i] f) Which arrangement of resistors has greater total resistance, series or parallel? Explain your choice. Was your hypothesis correct? [t/i] Apply and Extend: g) Fire departments warn against plugging too many devices into one outlet. Using what you have learned in this investigation, explain why fire departments issue this warning. [app] h) If you have hot wires, then electrical energy is being used to heat the wires. Is this an efficient use of electricity? Explain. [app] i) What would be the advantage of using parallel circuits instead of series circuits in your home? [app] Conclusion: