12.4: Forms of Current Electricity pg. 514 Key Concepts:
advertisement
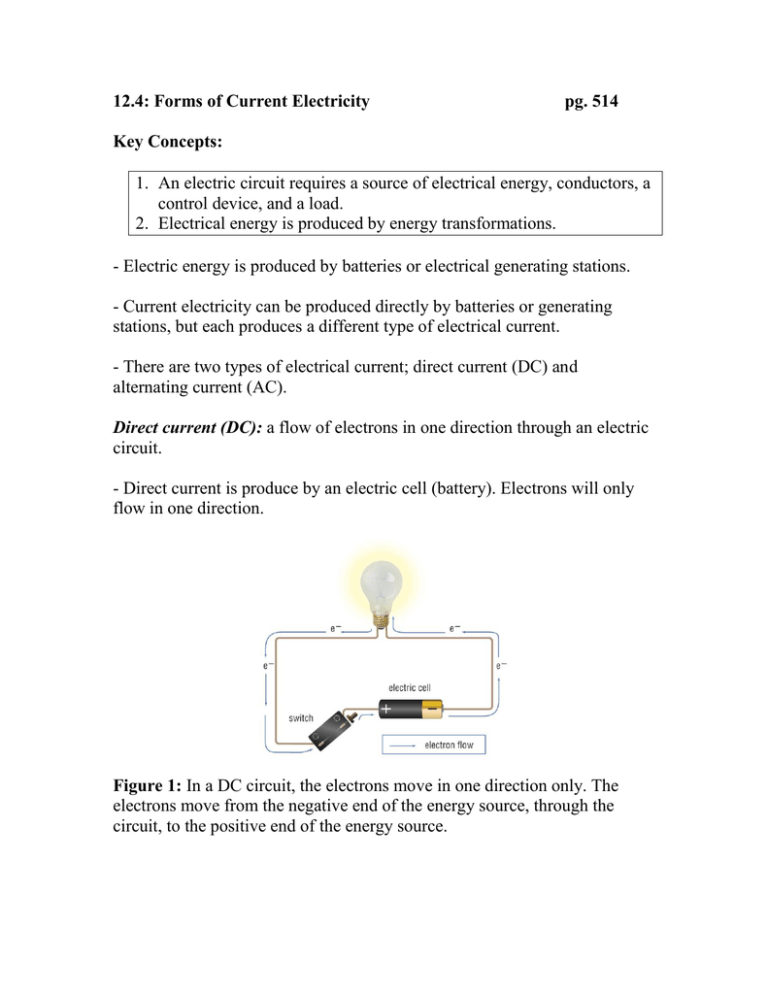
12.4: Forms of Current Electricity pg. 514 Key Concepts: 1. An electric circuit requires a source of electrical energy, conductors, a control device, and a load. 2. Electrical energy is produced by energy transformations. - Electric energy is produced by batteries or electrical generating stations. - Current electricity can be produced directly by batteries or generating stations, but each produces a different type of electrical current. - There are two types of electrical current; direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). Direct current (DC): a flow of electrons in one direction through an electric circuit. - Direct current is produce by an electric cell (battery). Electrons will only flow in one direction. Figure 1: In a DC circuit, the electrons move in one direction only. The electrons move from the negative end of the energy source, through the circuit, to the positive end of the energy source. Alternating current (AC): a flow of electrons that alternates in direction in an electric circuit. - Alternating current, the electrons travel back and forth, or alternating their direction. - Electric generation stations produce alternating current flow. Figure 2: In an AC circuit, the direction of electron flow changes as often as 60 times per second. Generating Electricity - Electrical energy is produced when one type of energy is converted into electrical energy. - Generating stations use mechanical energy to produce electrical energy. - Generating stations consists of a turbine, a generator, and transmission lines. - An external energy source (water) flows over a turbine. The turbine is turned very rapidly and is connected to the generator. - The generator consists of coiled copper wire surrounded by magnet. Electrons begin to flow in the copper wire. - The electrons travel to transmission lines and latter to the outlets found in your home. - The generator ensures a constant flow of electrons along the transmission lines. - Electrical energy is controlled and can travel long distances. - Electrical energy can easily be transformed into other forms of energy. Figure 3: An electrical generator obtains energy from a non-electrical source of energy and converts it into electrical energy. The external energy source spins a turbine consisting of a set of fan-like blades. The turbine spins a coil of wire inside a magnet, producing electrical energy. Evidence of Learning …. Students can - define direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). - distinguish between direct and alternating current. - explain how generators create alternating current. Check Your Learning: Questions 1 – 4, page 517 Summary: - Current electricity can be produced directly (direct current) or it can be generated in a generating plant (alternating current). - In direct current (DC), electrons flow in one direction only. Electric cells produce direct current. - In alternating current (AC), electrons flow back and forth. Alternating current is produced in generating plants. - Electrical generating plants convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. - An electrical device that uses DC electricity requires a DC energy source, such as a battery. A device that uses AC electricity must be plugged into a wall outlet.





