3.1: Algae- The Evolutionary Link between Protists and the Plant...
advertisement
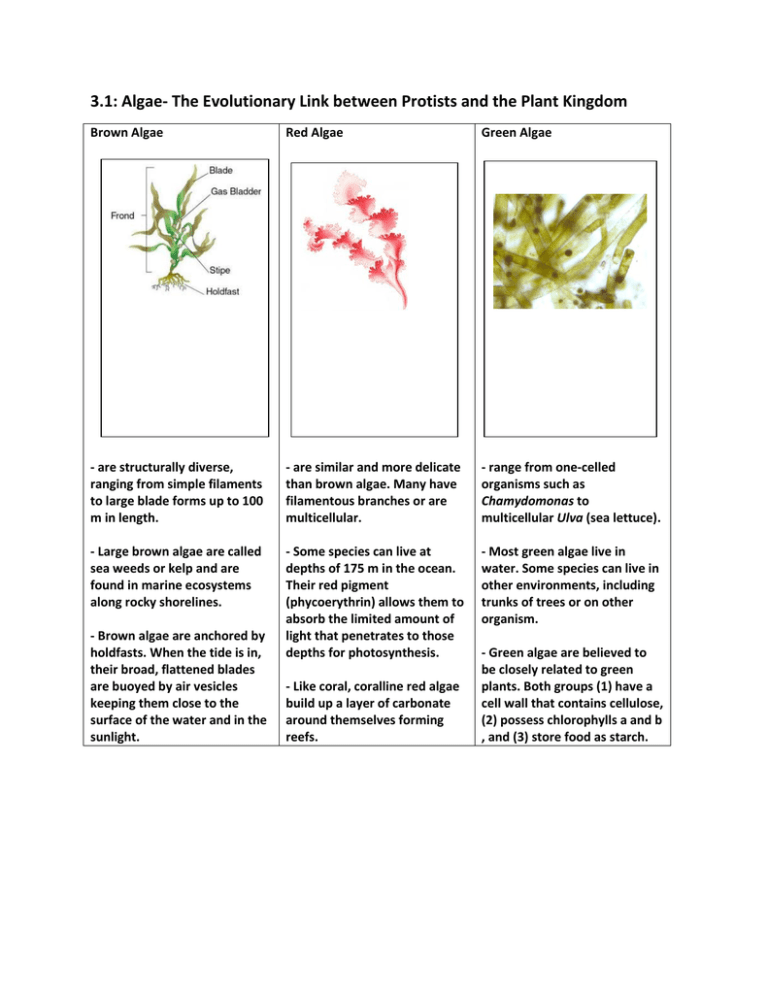
3.1: Algae- The Evolutionary Link between Protists and the Plant Kingdom Brown Algae Red Algae Green Algae - are structurally diverse, ranging from simple filaments to large blade forms up to 100 m in length. - are similar and more delicate than brown algae. Many have filamentous branches or are multicellular. - range from one-celled organisms such as Chamydomonas to multicellular Ulva (sea lettuce). - Large brown algae are called sea weeds or kelp and are found in marine ecosystems along rocky shorelines. - Some species can live at depths of 175 m in the ocean. Their red pigment (phycoerythrin) allows them to absorb the limited amount of light that penetrates to those depths for photosynthesis. - Most green algae live in water. Some species can live in other environments, including trunks of trees or on other organism. - Brown algae are anchored by holdfasts. When the tide is in, their broad, flattened blades are buoyed by air vesicles keeping them close to the surface of the water and in the sunlight. - Like coral, coralline red algae build up a layer of carbonate around themselves forming reefs. - Green algae are believed to be closely related to green plants. Both groups (1) have a cell wall that contains cellulose, (2) possess chlorophylls a and b , and (3) store food as starch.







