Endocrine System Chapter 10
advertisement

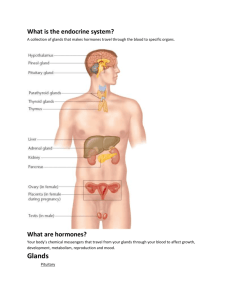
Endocrine System Chapter 10 Endocrine Glands • Endocrine glands are ductless glands and tissues that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. • Hormone – Hormon- gr. to excite. – Chemical messengers. – Released in small amounts. – Affect target cells. General Functions of Hormones • • • • • • Growth and development Reproduction Metabolism Biological clock Contraction of cardiac and smooth muscle Glandular secretion Feedback mechanisms regulate the secretion of hormones • Negative feedback- the outcome of a process feeds back on the system, shutting down the process. • Antagonistic feedback- one hormone has an opposite effect of another hormone on the system. • Positive feedback- the outcome of a process feeds back on the system, further stimulating the process. Negative Feedback Antagonistic Feedback Positive Feedback “I’m good enough, I’m smart enough, and doggone it, people like me!” Positive Feedback- Oxytocin (OCT) • Sucking by the infant stimulates nerve receptors in the nipple. • The resulting impulses travel along nerves to the hypothalamus. • The hypothalamus signals the posterior pituitary to release OCT. • OCT travels via the bloodstream to the mammary glands. • Milk is ejected from the mammary glands. Hypothalamus • Anatomy – Part of the diencephalon, inferior to the thalamus. • Functions – Regulates the internal environment through the autonomic nervous system. – Controls glandular secretions of the pituitary gland. Pituitary Gland- anatomy • Anatomy – Pea-shaped structure. – ½ inch in diameter. – Lies in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone. – 2 anatomically and functionally different portions. Posterior Anterior Posterior Pituitary Anterior Pituitary Pineal Gland • Anatomy – Pine cone shape. – In the epithalamus. – Covered by a capsule made of pia mater. • Function – Secretes melatonin that targets the brain; involved in regulating daily sleep-wake cycle. Thyroid Gland • Anatomy – Inferior to the larynx. – 2 lobes, shield-shaped and deep red in color. – Isthmus connects the lobes. – 30g in weight (=1 oz.). • Functions – Increases metabolic rate. – Regulate growth and development. Isthmus The Thyroid Gland Secretes Thyroid Hormone (TH) • Hypothyroidism- undersecretion of the thyroid hormone. – Fetus or infant- cretinism. • Dwarfism and mental retardation. – Adult- myxedema. • • • • Weight gain. Lethargy. Loss of hair. Lowered body temperature. • Hyperthyroidism- oversecretion of thyroid hormone. – Adult- Graves’ disease • • • • • Increased metabolic rate. Enlargement of the thyroid gland. Rapid heart rate. High blood pressure. Exophthalmos. – Treatment for Graves’ disease • Surgery. • Ingestion of radioactive iodine. Parathyroid Glands • • • • Anatomy- 4 small masses at the back of the thyroid gland. Hormones- parathyroid hormones. Target- bones, kidneys, intestines. Hormone Functions – Increase blood calcium level. – Antagonistic action between calcitonin and parathyroid hormone maintains blood calcium levels. Thymus Gland • Anatomy – Upper mediastinum. – Large in infants (70 g), atrophied in adult (3 g). – 2 lobed organ. • Hormones- thymosins. • Target- T lymphocytes (white blood cells). • Hormone Functions – Promote production and maturation of T lymphocytes. Adrenal Glands • Anatomy – Almond-shaped, located at the tops of the kidneys. – Consists of adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex. • Hormones and Functions – Adrenal Medulla • Epinephrine- adrenaline. Fight or flight. • Norepinephrine- noradrenaline. “ “ – Adrenal Cortex • Sex Hormones. Development. • Mineralocorticoids. Salt & water balance. • Glucocorticoids. Regulate glucose levels. • Targets- all tissues. Pancreas • Anatomy – 5-6 inches long, 1 inch thick. – Attached to the duodenum, posterior to the stomach. – Two tissue types. • Exocrine tissue- produce and secrete digestive juices. • Endocrine tissue- produce and secrete insulin and glucagon directly into the blood. • Target- liver, muscles, adipose tissue. • Hormones and Functions – Insulin- lowers blood sugar. – Glucagon- increases blood sugar. Testes • Anatomy – Scrotum of male. – 2 oval glands. – 2 inches long, 1 inch in width. • Hormone- testosterone. • Target- gonads, skin, muscles, bones. • Hormone Function – Stimulate male sex characteristics. Ovaries • Anatomy – Abdomen of female – 5 cm X 2.5 cm (2 X 1 inch). • Hormones – Estrogens. – Progesterone. • Targets – Gonads, skin, muscles, bones. • Hormone Function – Stimulate female sex characteristics.