Hess’s Law Chapter 5.4
advertisement

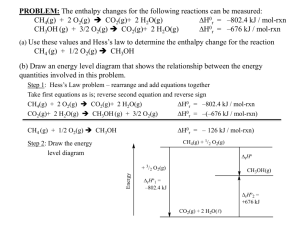
Hess’s Law Chapter 5.4 State Function A state function is a property of a system that is independent of the path taken The net vertical distance is the same whether the car goes up the series of ramps or directly up the elevator Hess’s Law The enthalpy change for the conversion of reactants to products is the same whether the reaction occurs in one step or in several steps. Enthalpy is a State Function Rules for Enthalpy Changes • To use Hess’s Law to calculate enthalpy changes for chemical reactions, you must apply the following rules: 1) If you reverse a chemical reaction, you must also reverse the sign of ∆H CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ∆H = -802 kJ CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) ∆H = + 802 kJ 2) If the coefficients in a balanced equation are multiplied by a factor, the value of ∆H is multiplied by the same factor CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ∆H = -802 kJ 2CH4(g) + 4O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) ∆H = -1604 kJ Enthalpy is a State Function Some reactions cannot be analyzed using calorimetry. Ex: rusting is an exothermic reaction but it happens too slowly to measure in a calorimeter How can we use Hess’s Law to calculate the enthlapy change for the following reaction? C(graphite) + ½ O2(g) CO(g) + ½ O2(g) Practice • Consider the combustion of methane to form CO2 and liquid H2O CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) • This reaction can be thought of as occurring in two steps • In the first step methane is combusted to produce water vapor: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ∆H = -802 kJ • In the second step water vapor condenses from the gas phase to the liquid phase: 2H2O(g) 2H2O(l) ∆H = -88 kJ Practice Find the enthalpy change for the target reaction C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) H = ? Given the following reactions: 3 C(s) + 4 H2(g) C3H8(g) H = -103.85kJ/mol C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) H = -393.51kJ/mol H2(g) + ½ O2(g) H2O(g) H = -241.83kJ/mol Practice Makes Perfect! Find the enthalpy change for the target reaction C(graphite) + 2S(rhombic) CS2 (l) Given the following reactions: C(graphite) + O2 (g) S(rhombic) + O2 (g) CS2(l) + 3O2 (g) CO2 (g) SO2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2SO2 (g) H0 = -393.5 kJ H0 = -296.1 kJ H0 = -1072 kJ HOMEWORK Required Reading: p. 314-318 (remember to supplement your notes!) Questions: p. 317 #1-3 p. 318 #1-8