WS 1.6 – Stems Dermal Tissue in Stems
advertisement

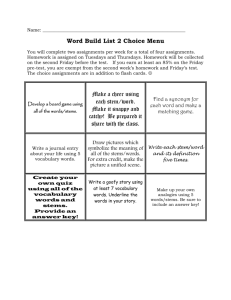
Name:_______________________________ Date:__________ Per:________ WS 1.6 – Stems Dermal Tissue in Stems 1. What is the dermal tissue on trees (woody stems)? 2. What is the dermal tissue in herbaceous stems? 3. What is purpose of the dermal tissue in stems? Vascular Tissue in Stems: 4. What is the difference between xylem and phloem? Observe the stalk of celery: 5. Is celery a root stem or leaf? 6. Does the celery stalk demonstrate capillary action, root pressure or transpiration? Observe the carrot: 7. Is a carrot a root stem or leaf? 8. Does the root stalk demonstrate capillary action, root pressure or transpiration? 9. Is root pressure created by active transport or passive transport of water into the root? Observe the leaf covered with a bag: 10. Where did the leaf get the water that accumulated in the bag? 11. What to water in the root as it evaporated from the leaf? 12. Of the three types of water movement you observed in this lab, which involved the most water moving? 13. What type of water movement (root pressure, capillary action or transpiration) is most responsible for water being sucked from the roots to the leaves? Ground Tissue in Stems: 14. Why are cell walls thickened in the ground tissue of stems? 15. Why does the ground tissue in stems have to be flexible? Identify the different types of plant tissues in the image. Shade in each plant tissue a different color. Color of the dermal tissue Color of the ground tissue Color of the vascular tissue Coloring Flowers Dye the water in 2 test tubes the color you want your flower to turn. (only use 4 or 5 drops of coloring) Take 2 test tubes filled with water and dye the water in each a different color Spit the stem in half and place half the stem in one test tube and the other half in the second 16. Circle the prediction about how these colors will affect your plant. a. They will have no effect, b. The two colors will mix together (red and blue will mix to make a purple flower) c. The two colors will show up separately in the flower (a flower that is half red and half blue) 17. If the flower has no leaves, and no roots, what type of water movement moves the dyed water up the stem to the flower?