Geos 1000 Exam I, Spring, 2011
advertisement

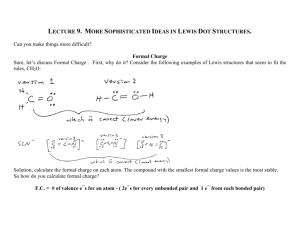
Geos 1000 Exam I, Spring, 2011 Multiple choice. Choose the one best answer. 1. The model that describes the movement of water through the reservoirs of the Earth System is called the _____ cycle. A) rock B) hydrologic C) metamorphic D) tectonic 2. The formation of Earth and other planetary bodies through the processes of condensation and accretion was essentially complete _____ years ago. A) 456 million B) 4.56 million C) 4.56 billion D) 45.6 billion 3. Which of the inner planets has an average surface temperature of -63° Celsius? A) Jupiter B) Venus C) Earth D) Mars 4. Of the other inner planets of the solar system, Earth's size is most similar to _____. A) Mercury B) Venus C) the Moon D) Saturn 5. The principle of Uniformitarianism tells us that _____. A) Earth is not as old as the surrounding planets B) Earth systems don't change over geologic time because material is continually being cycled around; the amounts taken away balance the amounts added C) the present is the key to the past D) All of the above are true 6. The smallest particle that retains all of the chemical properties of an element is called a(n) A) molecule. B) isotope. C) atom. D) ion. E) compound. 7. Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are called A) molecules. B) isotopes. C) elements. D) ions. E) compounds. 8. The atomic number of an atom is A) the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. B) the number of protons in the nucleus. C) the number of neutrons in the nucleus. D) the number of electron energy levels. E) the number of electrons in the outermost energy level. 9. One atom of a hypothetical element X has 27 neutrons while another has 29. This would 1 make the two atoms of the element A) molecules. B) compounds. C) ions. D) isotopes. 10. What type of bond forms from the sharing of electrons between atoms? A) covalent bond B) metallic bond C) ionic bond D) Van der Waals bond 11. What type of bond forms the strongest chemical bonds and compounds that tend to be strong with great hardness? A) covalent bond B) metallic bond C) ionic bond D) Van der Waals bond 12. Based on the definition of a mineral, being a naturally occurring solid, formed by inorganic processes, with a characteristic crystal structure and s specific chemical composition, which materials will be classified as minerals? A) water and ice B) ice and steel C) steel and coal D) ice and quartz 13. Why is coal not considered a mineral? A) it is organic B) it is man made C) it is a solid D) All of the above 14. To which of the following groups do most minerals in the Earth's crust belong? A) oxides B) halides C) carbonates D) silicates E) sulfates 15. The property of a mineral to resist scratching is referred to as A) streak. B) density. C) hardness. D) tenacity. 16. The property of a mineral that relates how heavy it is for its size is referred to as A) streak. B) density. C) hardness. D) tenacity. 17. Which element is the most abundant in Earth's crust? A) silicon B) iron C) calcium D) oxygen 18. What element bonds with a silicon atom to form the “silicate” tetrahedron? A) oxygen B) hydrogen C) oxygen and hydrogen D) carbon 19. Which type of mineral is formed when silicate tetrahedra are arranged in parallel sheets with weak bonds between them. 2 A) quartz C) amphibole (hornblende) B) diamond D) mica 20. When we see sedimentary rock units that are twisted or tilted, we know that some force must have disturbed the strata after they were deposited. The principle upon which we base this inference is the principle of _____. A) stratigraphic superposition B) cross-cutting relationships C) original horizontality. D) stratigraphic correlation 21. The principle of stratigraphic superposition tells us that _____. A) a rock unit is older than any geologic feature that disturbs or cuts it. B) the oldest rock strata in any undisturbed sedimentary sequence are on the bottom, and the youngest are on the top. C) sedimentary rock strata are deposited in flat-lying layers, one on top of another. D) the past is the key to the future 22. If you see a vertical magmatic intrusion embedded in horizontal layers of sedimentary rocks, which principle will help you determine the relative age of the intrusion? A) principle of original horizontality B) principle of stratigraphic superposition C) principle of cross-cutting relationships D) principle of lateral continuity 23 What principle would best allow you to determine the relative ages of different parts of the stratigraphy of this section of the Grand Canyon? A) principle of superposition B) principle of faunal succession C) principle of original horizontality D) principle of cross-cutting relationships 24. The geologic era in which animals with hard shells first developed is the A) Mesozoic. B) Cenozoic C) Paleozoic. D) PreCambrian. 25. Our best estimate for the age of the Earth is _____. A) 4.4 billion years B) 4.56 billion years C) 4.4 million years D) 4.56 million years True-False. (Red is true, black is false) 26. Earth is a fairly close approximation of a closed system. 27. The hydrosphere comprises all of Earth's water and ice, both on the surface and underground. 28. The nebular theory proposes that the solar system coalesced out of a swirling cloud of interstellar dust and gas. 29. The densest planets in the solar system are closest to the sun. 30. The solar nebula was initially cool, but heated up as it contracted. 3 31. Some meteorites formed about the same time as the earth did. 32. Hutton's principle of Uniformitarianism says that the physical processes on Earth have not changed over time. 33. Activity on Earth's surface has erased all traces of ancient meteorite impacts, such as those still visible on the moon. 34. Oxygen can be converted to silicon by chemical processes in the crust. 35. A neutron is a positively charged particle with an atomic mass of 1that resides in the nucleus of an atom. 36. In ionic bonding one atom transfers electrons to another, creating ions with differing electrical charge. 37. Ionic bonds are the strongest chemical bonds, and elements and compounds with ionic bonds (such as diamond) tend to be strong and hard. 38. The color of a mineral is not necessarily useful in identification. 39. Silicon is the most abundant element in Earth's crust. 40. Quarz is a silicate mineral. 41. An ion has a different number of protons and electrons. 42. When an atom loses an electron, it is then known as a cation. 43. Most of geologic time came before the Phanerozoic eon. 44. The oldest rocks on the earth date from the Hadean eon. 45. The atomic number (number of protons) stays the same in beta decay. 46. Marine organisms developed hard shells at the beginning of the Archean eon. 47. Dinosaurs were present on earth during the Mesozoic era. 48. After two half lives, the number of parent and daughter atoms are equal. 49. Carbon-14 is an excellent radioactive isotope with which to date the age of the earth. 50. The Hadean, Archean, and Proterozoic eras can all be grouped into the period of time known as the Precambrian. 4