Pertemuan 09 Database Matakuliah : D0524 / Algoritma dan Pemrograman Komputer
advertisement

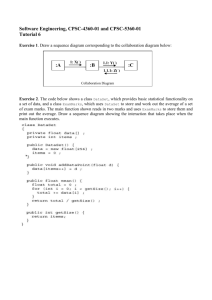
Matakuliah Tahun Versi : D0524 / Algoritma dan Pemrograman Komputer : 2005 : Pertemuan 09 Database 1 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • Menerapkan penggunaan database dalam aplikasi 2 Outline Material • • • • • • Introduction to Database Stored and Index Ordering Using ADO with Visual Basic Dataset Datagrid Common Programming Errors and Problem 3 Introduction to Databases • Database: any collection of related data used by an organization • Organization: any self-contained social unit such as a company, university, hospital, or family • The data in a database consist of two types: – Entities – Relationships • Relational database: a database in which data is stored in tables 4 Introduction to Database • Record: a row in a table • Field name: the heading of a column in a table • Entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs) express the relationships between entities • Cardinality of a relationship refers to the number of one entity that is related to another entity 5 Introduction to Database Related to Exactly One Related to One or More Related to Zero or One Related to Zero or More ERD Symbols 6 Introduction to Database Manajer Departemen Karyawan Kendaraan Operasional Example of ER Diagram 7 Stored and Index Ordering • Stored order – A table’s original order – Determined by the order in which records have been added to the table • Index: a separate table of record positions, called pointers, which lists the positions of the table’s records in the desired order • Key field: the field on which a table’s records are ordered 8 Using ADO with Visual Basic • ADO is an extremely powerful data access component that allow you to access database data in many formats • Using databases in Visual Basic – Create a link or connection between the database, known as the data source, and the Visual Basic application – Retrieve fields from tables in the database and display them on a Form – Store values on the Form in the database 9 Using ADO with Visual Basic • To use a database, an application must: – Set up a connection to a data source – Create a data adapter to handle the transfer of data to and from the data source and the application – Create a dataset to hold the data in memory while the application works with it – Add controls to the form and set their properties to bind the controls to the fields in the dataset 10 Using ADO with Visual Basic Data Source Connection Data Adapter Dataset Setting up Data Access in Visual Basic Windows Form 11 Setting Up a Data Connection • Any database that is ODBC (Open DataBase Connectivity) compliant can be accessed from within Visual Basic • Visual Basic provides a set of Data controls in the Toolbox that are used to set up database access • To establish a connection to an Access database: – Select the OleDbConnection object – Drag an OleDbConnection control from the Toolbox to the Form 12 Setting up a Data Adapter • The data adapter passes data back and forth between a data source and a program • Use the OleDbDataAdapter control for a Microsoft Access database • Data Adapter Configuration Wizard simplifies the task of using a database table 13 Setting up a Data Adapter First Screen of the Data Adapter Configuration Wizard 14 Creating a Dataset • Dataset: a copy of the data that is retrieved from the database and then inserted into memory • To create a dataset: – Select the OleDbAdapter control – Right-click on the control and select Generate dataset – Generate dataset dialog box opens 15 Binding Data to Controls • Data binding: the process of connecting a control to one or more data elements • A data-aware control is capable of automatically displaying data from a field(s) in a dataset • Simple binding connects one control to one data element • Complex binding is used when more than one data element is bound to a control 16 Filling the Dataset • The data adapter’s Fill method – Used to fill the dataset at run-time – DataAdaptername.Fill(DataSetName) 17 Navigating through the Dataset • BindingContext object manages all of the data bindings for the controls on the form • CurrencyManager object provides a simple way to navigate among the rows in a dataset 18 Updating a Dataset • Changes to data in the dataset do not affect the database unless an explicit operation is executed • Via the data adapter, you can make the changes in the dataset and then write the changes back to the data source • Initialization code 19 Updating a Dataset • Adding a record – Create an empty row that has the same fields as in the table to be modified – Enter data into the fields of the new row – Add the new row to the table in the dataset – Save the updated table back to the data source 20 Updating a Datase • Delete a record – RemoveAt method – Ensure that the user really wants to proceed with the deletion – Update method • Editing a record – Update method – Many safeguards are needed 21 Creating Datasets Using SQL • Structured query: a statement written according to the rules of a language called Structured Query Language (SQL), that uniquely identifies a set of records from one or more tables • Basic syntax of an SQL SELECT command (or a structured query) – SELECT field(s) FROM table(s) [WHERE condition(s)] [ORDER BY field(s)] 22 Creating Datasets Using SQL • SELECT clause specifies the field values that will be returned by the query – SELECT * specifies that all fields are to be obtained • FROM clause specifies the table or tables where records will be searched • WHERE clause is used to place any restrictions on the data to be selected • ORDER BY clause is used if the selected information is to be presented in a 23 specified order DataGrid Control • Used to display and modify one or more database tables • To create a DataGrid on a form – Click on the DataGrid control in the toolbox and then draw it on the Form, or – Double-click on the tool and resize it on the Form • To associate a DataGrid control with a table in an existing dataset – Set the DataSource property to the name of the table 24 DataGrid Control DataGrid Control Initially placed on a Form 25 Common Programming Errors and Problems • Not saving the last edit performed on a dataset • Forgetting that changes to the dataset are not automatically reflected in the data source • Forgetting to put quotes around the string in a WHERE clause of an SQL statement that is equal to a field • Forgetting that the Position property starts at zero and that the first record in a dataset is at position zero, not one 26