Document 14230800
advertisement
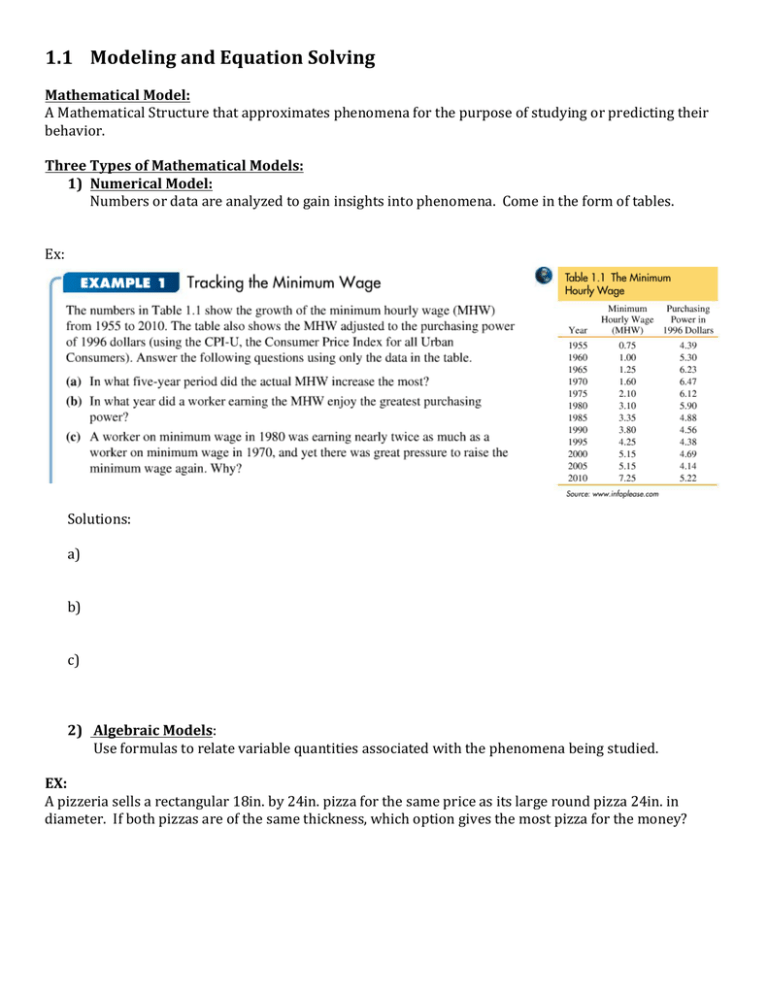
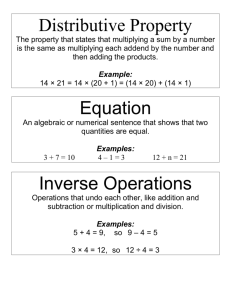
1.1 Modeling and Equation Solving Mathematical Model: A Mathematical Structure that approximates phenomena for the purpose of studying or predicting their behavior. Three Types of Mathematical Models: 1) Numerical Model: Numbers or data are analyzed to gain insights into phenomena. Come in the form of tables. Ex: Solutions: a) b) c) 2) Algebraic Models: Use formulas to relate variable quantities associated with the phenomena being studied. EX: A pizzeria sells a rectangular 18in. by 24in. pizza for the same price as its large round pizza 24in. in diameter. If both pizzas are of the same thickness, which option gives the most pizza for the money? 3) Graphical Models: Visible representations of a numerical or algebraic model that gives insight into the relationships between the two quantities. EX: EX: Zero Factor Property: A product of real numbers is zero if and only if at least one of the factors in the product is zero. ab = 0 either a = 0 or b = 0 EX: Solve the following equations for x using a graphical, numerical, and algebraic approach. a) 6x 3 = 11x 2 + 10x b) x 2 = 10 − 4x