Distributive Property Equation Inverse Operations
advertisement
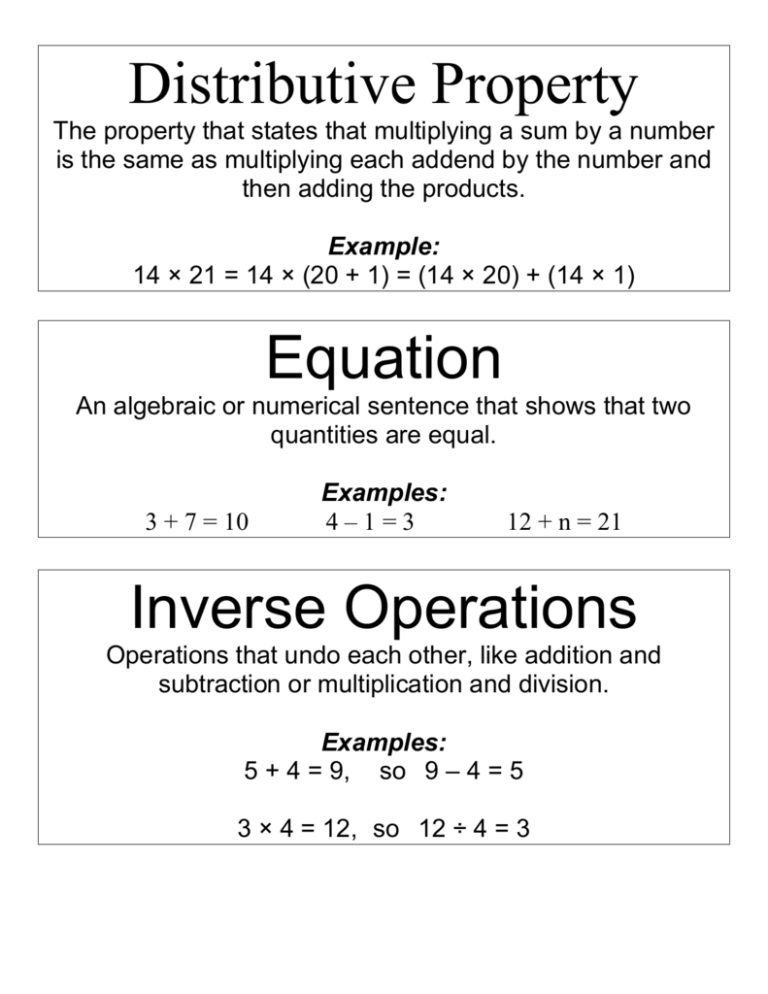
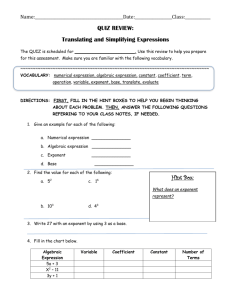
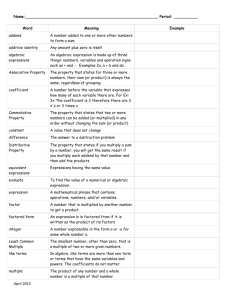
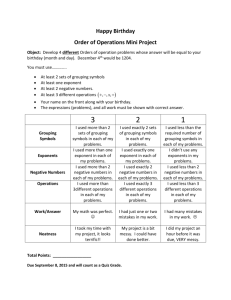
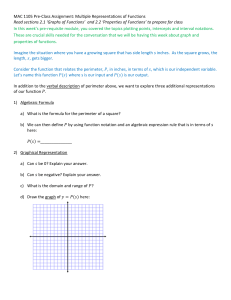
Distributive Property The property that states that multiplying a sum by a number is the same as multiplying each addend by the number and then adding the products. Example: 14 × 21 = 14 × (20 + 1) = (14 × 20) + (14 × 1) Equation An algebraic or numerical sentence that shows that two quantities are equal. 3 + 7 = 10 Examples: 4–1=3 12 + n = 21 Inverse Operations Operations that undo each other, like addition and subtraction or multiplication and division. Examples: 5 + 4 = 9, so 9 – 4 = 5 3 × 4 = 12, so 12 ÷ 4 = 3 Partial Quotient A method of dividing in which multiples of the divisor are subtracted from the dividend and then the quotients are added together. Example: Remainder The amount left over when a number cannot be divided equally. Variable A letter or symbol that stands for one or more numbers. Algebraic Expression An expression that includes at least one variable. Examples: x+5 3a – 4 Base A number used as a repeated factor. 83= 8 x 8 x 8. The base is 8. Evaluate To find the value of a numerical or algebraic expression Exponent A number that shows how many times the base is used as a factor. 3 8 The exponent is 3, indicating that 8 is used as a factor 3 times. Integers The set of whole numbers and their opposites Numerical Expression A mathematical phrase that uses only numbers and operation symbols. 60 + 25 Examples: 42 ÷ 7 51 × 36 Order of Operations Square Number The product of a number and itself. 42 = 16 16 is a square number. Parenthesis The symbols “(” and “)” are called parentheses and are generally used in grouping. The value of the expression 5 × 8 + 4 is 40. But if we use the parentheses with the same expression by grouping, 5 × (8 + 4), the value of the expression will be 60 as the order of operation gets changed in this case.