Building Organic Molecules Name_________________ Overview
advertisement

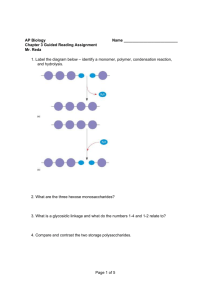
Building Organic Molecules Name_________________ Overview In this activity we will use chemical models to display the structure of basic carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. We will also understand how these molecules bond together. Additionally, we will assess the role of these molecules in the body Procedure 1. You will arrange yourselves in groups of 2-4. Your grade is partially dependant on your group’s ability to understand these molecules. Choose carefully. If you wish, the quizzing can be done individually, but you must work in groups to build the molecules. 2. Each group will receive 1 kit containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms (among other atoms – please keep kits together). 3. From the kit, and using the diagram on the handout provided, each group will have to construct 1 glucose molecule, 1 fatty acid (you are not building glycerol), and 1 amino acid. 4. Students should then familiarize themselves with the information on the back of this sheet for each type of molecule, and be able to answer questions from the teacher. Grading: Each group will be graded on their ability to construct the molecules and answer questions from the teacher. Although I will be asking individuals questions, the whole group’s grade is on the line. That means it is your job to educate your group on the structure and function of each molecule. Grading will work as follows: Molecule built correctly and all questions answered correctly in the 1st round = 6/6 points Molecule built correctly and 2 rounds are needed to answer questions correctly = 5/6 points Molecule built correctly and 3 rounds are needed to answer questions correctly = 4/6 points After 3 rounds, students will be given individual quizzes for 3/6 points or less depending upon number of correct answers. (Students will earn 3 separate grades for models and quizzes on carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, which will add to a total of 18 points) Information each group should know after constructing their glucose molecule: What atoms are found in the molecule. How this molecule compares to other monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Be able to name the process used to build disaccharides and polysaccharides, as well as the process used to break down disaccharides and polysaccharides. Be sure to know whether water is added or removed in each process. The role of glucose and glycogen in the body Information each group should know after constructing their fatty acid molecule: What atoms are found in the molecule. Whether this is a saturated or unsaturated fat – and how you can tell the difference. How many fatty acids are joined to a glycerol to make a lipid Be able to name the process used to build lipids, as well as the process used to break down lipids. Be sure to know whether water is added or removed in each process. The role of lipids in the body. Information each group should know after constructing their amino acid molecule: What atoms are found in the molecule. What groups make up an amino acid, and be able to identify them. How each amino acid is different from one another. What polymer is built by joining amino acids. The bond that holds two amino acids together. Be able to name the process used to build proteins, as well as the process used to break down proteins. Be sure to know whether water is added or removed in each process. The role of proteins in the body.